Custom OpenTelemetry Collector
This guide explains how to configure Kubewarden to send telemetry data to an OpenTelemetry collector already deployed on the cluster.
You should deploy only one instance of the OpenTelemetry Collector in the cluster.
Install dependencies
First, begin by installing the dependencies of OpenTelemetry Collector.
You need the communication between the Kubewarden components and the collector to be encrypted. You can use cert-manager to manage all the certificates required for secure communication.
OpenTelemetry Collector traces get sent to a Jaeger instance.
The Kubewarden stack sends metrics to the OpenTelemetry Collector. This one exposes the metrics as a Prometheus endpoint. The metrics are then collected by a Prometheus instance and stored in its database. The same Prometheus instance also exposes a UI to view and use the metrics.
Resources you create are get defined in the kubewarden
Namespace, or expect its existence. Due to that, you should begin by creating the Namespace:
kubectl create namespace kubewardenInstall cert-manager and OpenTelemetry
You install cert-manager and OpenTelemetry operator in this way:
helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io
helm install --wait \
--namespace cert-manager \
--create-namespace \
--set crds.enabled=true \
--version 1.15.1 \
cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager
helm repo add open-telemetry https://open-telemetry.github.io/opentelemetry-helm-charts
helm install --wait \
--namespace open-telemetry \
--create-namespace \
--version 0.65.0 \
--set "manager.collectorImage.repository=otel/opentelemetry-collector-contrib" \
my-opentelemetry-operator open-telemetry/opentelemetry-operatorYou setup communication between Kubewarden components and the OpenTelemetry Collector using mTLS.
To do that, you need to create the whole PKI infrastructure:
# pki.yaml file
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: my-client-certificate
namespace: kubewarden
spec:
dnsNames:
- kubewarden.kubewarden.svc
- kubewarden.kubewarden.svc.cluster.local
issuerRef:
kind: Issuer
name: my-selfsigned-issuer
secretName: my-client-cert
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: my-certificate
namespace: kubewarden
spec:
dnsNames:
- my-collector-collector.kubewarden.svc
- my-collector-collector.kubewarden.svc.cluster.local
issuerRef:
kind: Issuer
name: my-selfsigned-issuer
secretName: my-server-cert
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: my-selfsigned-issuer
namespace: kubewarden
spec:
selfSigned: {}yamlApply the manifest:
kubectl apply -f pki.yamlInstall Jaeger and Prometheus
After that, you install Jaeger to store and visualize trace events.
helm repo add jaegertracing https://jaegertracing.github.io/helm-charts
helm upgrade -i --wait \
--namespace jaeger \
--create-namespace \
--version 2.49.0 \
jaeger-operator jaegertracing/jaeger-operator \
--set rbac.clusterRole=true
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: jaegertracing.io/v1
kind: Jaeger
metadata:
name: my-open-telemetry
namespace: jaeger
spec:
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
EOFNow you install Prometheus to store and visualize metrics.
cat <<EOF > kube-prometheus-stack-values.yaml
prometheus:
additionalServiceMonitors:
- name: kubewarden
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: kubewarden.my-collector
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- kubewarden
endpoints:
- port: prometheus
interval: 10s
EOF
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts
helm install --wait --create-namespace \
--namespace prometheus \
--version 51.5.3 \
--values kube-prometheus-stack-values.yaml \
prometheus prometheus-community/kube-prometheus-stack|
The Prometheus service monitor obtains the Kubewarden metrics by scraping the
OpenTelemetry collector running in the |
Install OpenTelemetry Collector
Now you can deploy a custom OpenTelemetry Collector inside of the kubewarden Namespace.
# otel-collector.yaml file
apiVersion: opentelemetry.io/v1beta1
kind: OpenTelemetryCollector
metadata:
name: my-collector
namespace: kubewarden
spec:
mode: deployment # This configuration is omittable.
volumes:
- name: server-certificate
secret:
secretName: my-server-cert
- name: client-certificate
secret:
secretName: my-client-cert
volumeMounts:
- name: server-certificate
mountPath: /tmp/etc/ssl/certs/my-server-cert
readOnly: true
- name: client-certificate
mountPath: /tmp/etc/ssl/certs/my-client-cert
readOnly: true
config:
receivers:
otlp:
protocols:
grpc:
tls:
cert_file: /tmp/etc/ssl/certs/my-server-cert/tls.crt
key_file: /tmp/etc/ssl/certs/my-server-cert/tls.key
client_ca_file: /tmp/etc/ssl/certs/my-client-cert/ca.crt
processors: {}
exporters:
debug:
verbosity: normal
prometheus:
endpoint: ":8080"
otlp/jaeger:
endpoint: "my-open-telemetry-collector.jaeger.svc.cluster.local:4317"
tls:
insecure: true
service:
pipelines:
metrics:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: []
exporters: [debug, prometheus]
traces:
receivers: [otlp]
processors: []
exporters: [debug, otlp/jaeger]yamlApply the manifest:
kubectl apply -f otel-collector.yamlThat configuration uses a trivial processing pipeline to receive trace events and to forward them to Jaeger. It also receives metrics and exposes them for collection by Prometheus.
You secure communication between the Kubewarden stack and the OpenTelemetry Collector using mTLS. However the communication between the OpenTelemetry Collector and Jaeger isn’t secured, to reduce the complexity of the example.
Install Kubewarden stack
When the OpenTelemetry Collector is running, you can deploy Kubewarden in the usual way.
You need to configure the Kubewarden components so they send events and metrics to the OpenTelemetry Collector.
# values.yaml
telemetry:
mode: custom
metrics: True
tracing: True
custom:
endpoint: "https://my-collector-collector.kubewarden.svc:4317"
insecure: false
otelCollectorCertificateSecret: "my-server-cert"
otelCollectorClientCertificateSecret: "my-client-cert"yamlThe Secret referenced by the otelCollectorCertificateSecret key must have an
entry named ca.crt.
That holds the certificate of the CA that issued the
certificate used by the OpenTelemetry Collector.
The Secret referenced by the otelCollectorClientCertificateSecret key must have
the following entries: tls.crt and tls.key keys. These are the client certificate and
its key used by the Kubewarden stack to authenticate against the OpenTelemetry Collector.
Leave these values empty if you do not use encryption or mTLS.
Install the Kubewarden stack:
helm install --wait \
--namespace kubewarden --create-namespace \
kubewarden-crds kubewarden/kubewarden-crds
helm install --wait \
--namespace kubewarden \
--create-namespace \
--values values.yaml \
kubewarden-controller kubewarden/kubewarden-controller
helm install --wait \
--namespace kubewarden \
--create-namespace \
kubewarden-defaults kubewarden/kubewarden-defaults \
--set recommendedPolicies.enabled=True \
--set recommendedPolicies.defaultPolicyMode=monitorNow everything is in place.
Exploring the Jaeger UI
You can see the trace events generated by Kubewarden by using the Jaeger web UI.
They’re grouped under the kubewarden-policy-server service:
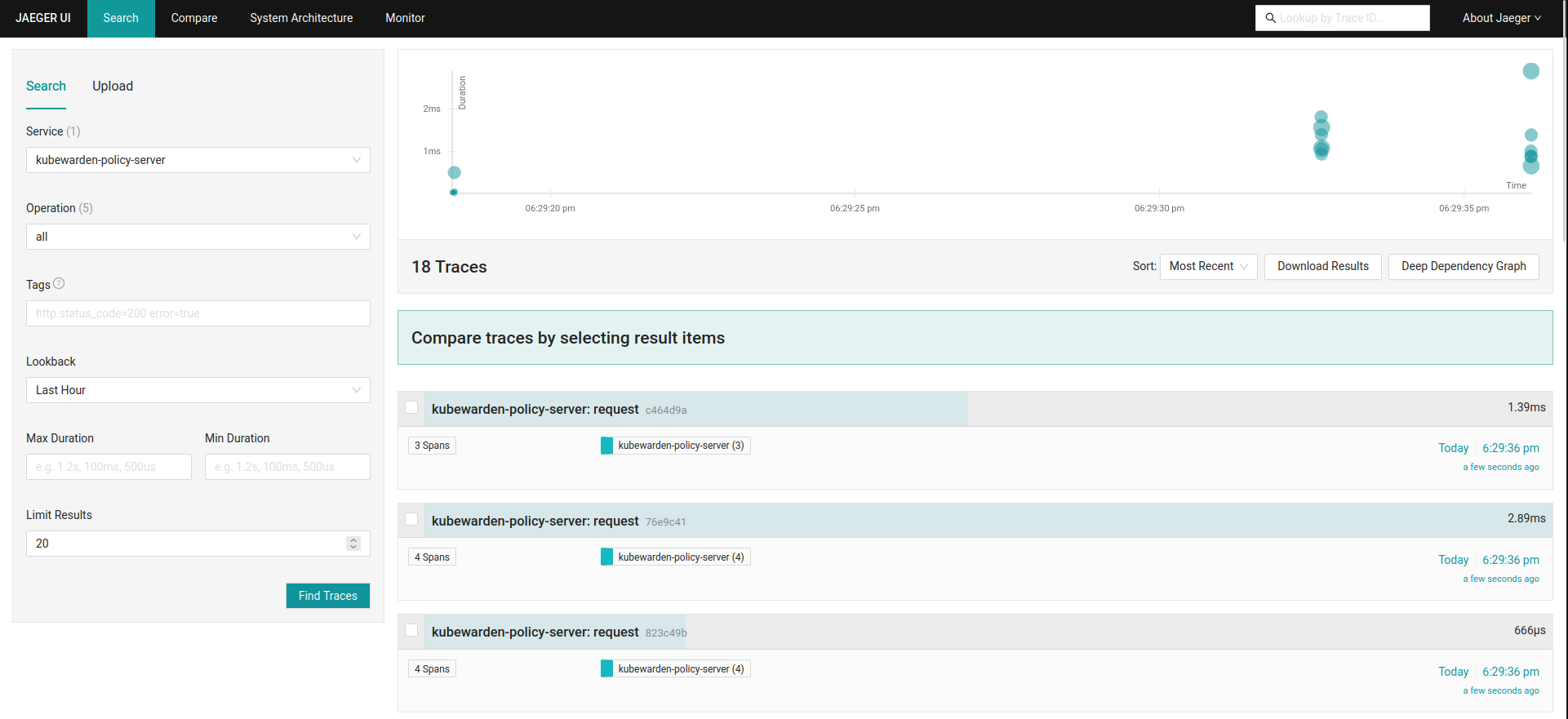
To access the Jaeger UI, you can create an Ingress or you can do a port forwarding to your local machine:
kubectl -n jaeger port-forward service/my-open-telemetry-query 16686The web UI is reachable at localhost:16686.
Exploring the Prometheus UI
The Prometheus UI can be accessed doing a port forwarding to your local machine:
kubectl port-forward -n prometheus --address 0.0.0.0 svc/prometheus-operated 9090The web UI is now reachable at localhost:9090.