Tracing quickstart
This section shows how to enable tracing support for Policy Server.
|
Before continuing, make sure you completed the previous OpenTelemetry section of this documentation. It’s required for this section to work correctly. |
Tracing lets you collect fine grained details about policy evaluations. It can be a useful tool for debugging issues in your Kubewarden deployment and policies.
You use Jaeger — used to receive, store and visualize trace events.
Install Jaeger
You use the Jaeger Operator to manage all the different Jaeger components. You can install the Jaeger Operator using Helm charts.
|
At the time of writing (2022-06-21), only specific versions of Jaeger are compatible with Cert Manager, see the compatability chart. |
To install the Helm Chart:
helm repo add jaegertracing https://jaegertracing.github.io/helm-charts
helm upgrade -i --wait \
--namespace jaeger \
--create-namespace \
--version 2.49.0 \
jaeger-operator jaegertracing/jaeger-operator \
--set rbac.clusterRole=true|
This is not suitable for production deployment. You should consult read Jaeger’s official documentation. |
To create a Jaeger resource:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: jaegertracing.io/v1
kind: Jaeger
metadata:
name: my-open-telemetry
namespace: jaeger
spec:
ingress:
enabled: true
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
EOFAfter creation of Jaeger Operator resources, you have a
Service under my-open-telemetry-collector.jaeger.svc.cluster.local.
The Jaeger Query UI is reachable at the following address:
echo http://`minikube ip`Install Kubewarden
Now you can proceed to the deployment of Kubewarden in the usual way.
|
cert-manager is a requirement of OpenTelemetry, but you have already installed it in a previous section of this documentation. |
As a first step, you add the Helm repository that contains Kubewarden:
helm repo add kubewarden https://charts.kubewarden.ioThen you install the Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) defined by Kubewarden:
helm install --wait \
--namespace kubewarden \
--create-namespace \
kubewarden-crds kubewarden/kubewarden-crdsNow you can deploy the rest of the Kubewarden stack. The official
kubewarden-defaults helm chart creates a PolicyServer named default. You
want this PolicyServer instance to have tracing enabled.
To do that, you need to specify some extra values for the
kubewarden-controller chart. You should create a values.yaml file with the
following contents:
telemetry:
mode: sidecar
tracing: True
sidecar:
tracing:
jaeger:
endpoint: "my-open-telemetry-collector.jaeger.svc.cluster.local:4317"
tls:
insecure: true|
For simplicity, there is no encryption of the communication between the OpenTelemetry collector and the Jaeger endpoint. Again, this is unsuitable for a production deployment. Consult Jaeger’s official documentation. |
Then you can proceed with the installation of the helm charts:
helm install --wait --namespace kubewarden --create-namespace \
--values values.yaml \
kubewarden-controller kubewarden/kubewarden-controller
helm install --wait --namespace kubewarden --create-namespace \
kubewarden-defaults kubewarden/kubewarden-defaultsThis creates the default instance of PolicyServer:
kubectl get policyservers.policies.kubewarden.io
NAME AGE
default 3m7sLooking closer at the Pod running the PolicyServer instance, you can see it has
two containers in it. The policy-server and the OpenTelemetry
Collector sidecar otc-container.
Enforcing a policy
You start by deploying the safe-labels policy.
You want the policy enforced only in Namespaces that have a
label environment with a value of production.
To a Namespace that has such a label:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: team-alpha-prod
labels:
environment: production
EOFNext, let’s define a ClusterAdmissionPolicy:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: policies.kubewarden.io/v1
kind: ClusterAdmissionPolicy
metadata:
name: safe-labels
spec:
module: registry://ghcr.io/kubewarden/policies/safe-labels:v0.1.6
settings:
mandatory_labels:
- owner
rules:
- apiGroups:
- apps
apiVersions:
- v1
resources:
- deployments
operations:
- CREATE
- UPDATE
namespaceSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: environment
operator: In
values: ["production"]
mutating: false
EOFYou need to wait for the policy to become active:
kubectl wait --for=condition=PolicyActive clusteradmissionpolicy/safe-labelsOnce the policy is active, you can try it:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
namespace: team-alpha-prod
labels:
owner: octocat
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOFThe policy permits the creation of this Deployment object as it doesn’t violate the policy.
The policy blocks this Deployment object:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment-without-labels
namespace: team-alpha-prod
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOFThe policy isn’t enforced in another Namespace.
This command creates a new Namespace called team-alpha-staging:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: team-alpha-staging
labels:
environment: staging
EOFThe policy permits the creation of a Deployment resource,
without any labels, in the team-alpha-staging Namespace:
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment-without-labels
namespace: team-alpha-staging
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 0
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
EOF
As expected, this resource is successfully created.
Exploring the Jaeger UI
You can see the trace events are sent by the PolicyServer instance to Jaeger,
as there is a new service kubewarden-policy-server listed in the UI:
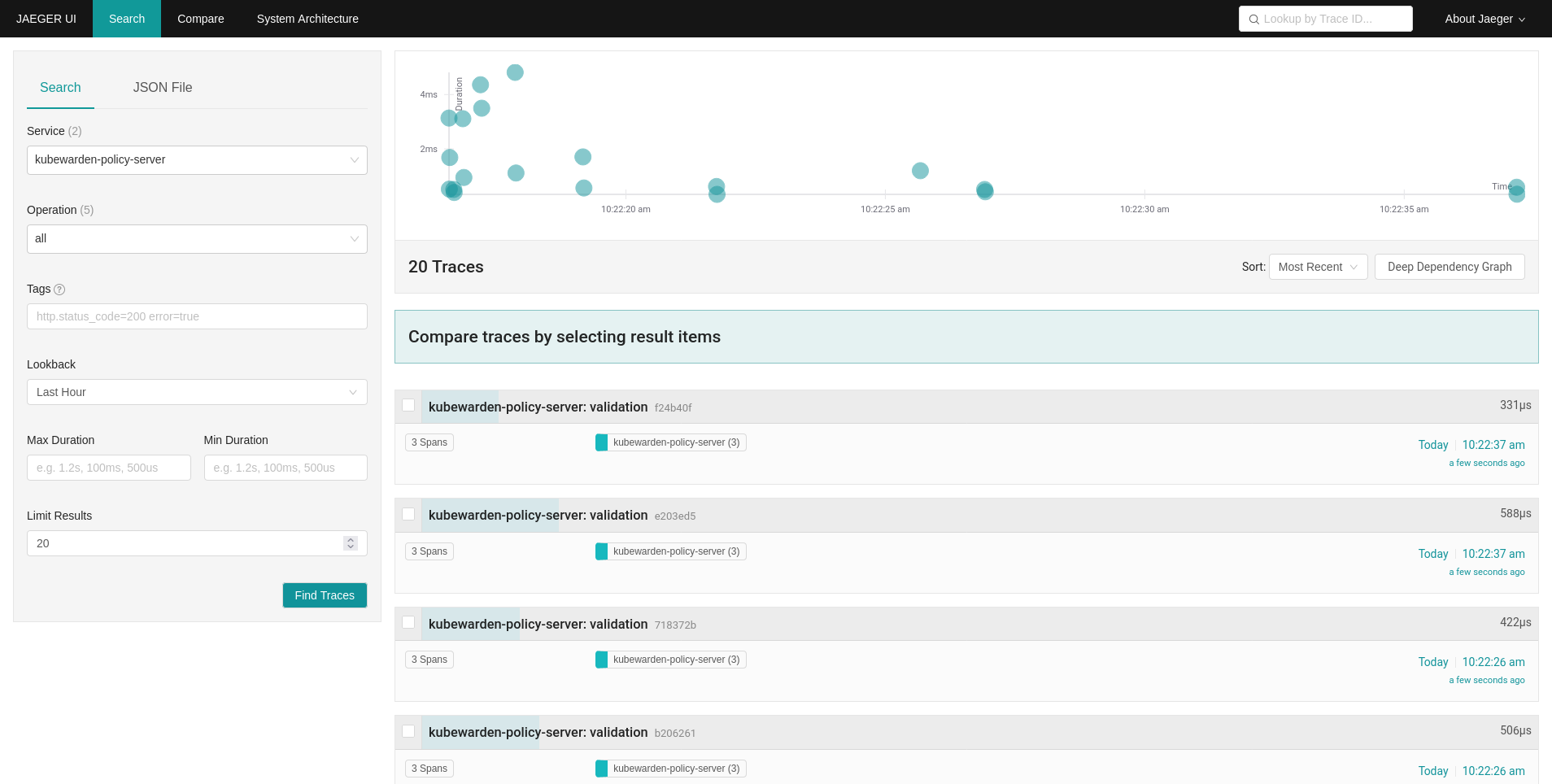
The Jaeger collector is properly receiving the traces generated by our PolicyServer.
To access the Jaeger UI, you can create an ingress or use
kubectl -n jaeger port-forward service/my-open-telemetry-query 16686
then go to localhost:16686.