Virtualization on SUSE Linux with Benefits and Setup
- WHAT?
Virtualization is a technology that allows a single physical server (host) to run multiple virtual machines (guests), each with its own operating system.
- WHY?
Use virtualization to reduce hardware costs, save power and space, and improve infrastructure flexibility and productivity.
- EFFORT
It takes less than 15 minutes to understand the core concepts of virtualization.
- GOAL
By the end of this article, you will understand the benefits of virtualization and the basic setup of a virtual machine host and guest environment.
1 Introduction to virtualization #
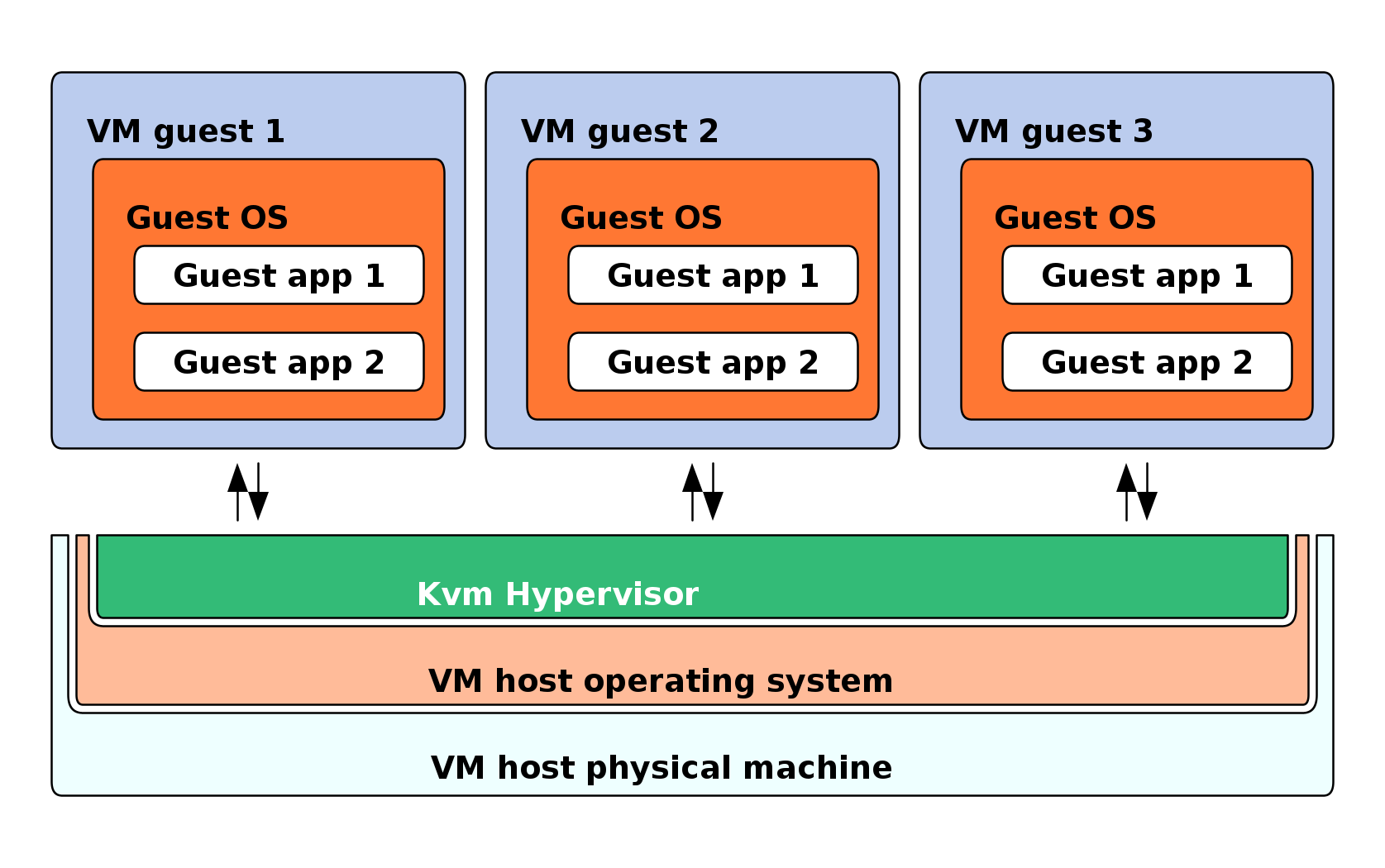
Virtualization is a technology that provides a way for a machine (VM Host Server) to run another operating system (VM Guest) on top of the host operating system.
1.1 How does virtualization work? #
The primary component of VM Host Server that enables virtualization is a hypervisor. A hypervisor is a layer of software that runs directly on VM Host Server's hardware. It controls platform resources, sharing them among multiple VM Guests and their operating systems by presenting virtualized hardware interfaces to each VM Guest.
1.2 Benefits of virtualization #
Virtualization brings a lot of advantages while providing the same service as a hardware server.
Virtualization reduces the cost of your infrastructure. Servers are mainly used to provide a service to a customer. A virtualized operating system can provide the same service but with the following advantages:
Less hardware: you can run several operating systems on one host, therefore all hardware maintenance is reduced.
Less power/cooling: less hardware means you do not need to invest more in electric power, backup power, and cooling if you need more service.
Save space: your data center space is saved because you do not need more hardware servers (fewer servers than services running).
Less management: using a VM Guest simplifies the administration of your infrastructure.
Agility and productivity: virtualization provides migration capabilities, live migration and snapshots. These features reduce downtime and bring an easy way to move your service from one place to another without any service interruption.
2 Installation of virtualization components #
To run a virtualization server (VM Host Server) that can host multiple guest systems (VM Guests), you need to install required virtualization components on the server. These components vary depending on which virtualization technology you want to use.
You can install the virtualization tools required to run a VM Host Server either when installing the system (see the manual installation), or from an alerady installed system by installing a virtualization pattern. The later option is described bellow:
>sudozypper install -t pattern PATTERN_NAME
Replace the PATTERN_NAME with one of the following values:
kvm_serverInstalls a basic VM Host Server with the KVM and QEMU environments.
kvm_toolsInstalls
libvirttools for managing and monitoring VM Guests in the KVM environment.
3 Virtualization modes #
Virtualization is a technology that provides a way for a machine (VM Host Server) to run another operating system (VM Guest) on top of the host operating system. There are two basic modes of hosting VM Guests on virtual machines—full virtualization mode and paravirtual mode.
- Full virtualization (FV)
FV lets virtual machines run unmodified operating systems. It uses either Binary Translation or hardware-assisted virtualization technology, such as AMD* Virtualization or Intel* Virtualization Technology, to improve performance on processors that support it. In FV mode, VM Guest is also called the Hardware Virtual Machine (HVM).
TipCertain guest operating systems hosted in full virtualization mode can be configured to use drivers from the SUSE Virtual Machine Drivers Pack (VMDP) instead of drivers included in the operating system. Running virtual machine drivers improves performance on guest operating systems, such as Windows Server.
- Paravirtualization (PV)
PV normally requires that guest operating systems are modified for the virtualization environment. VM Guests running in paravirtual mode have better performance than those running under full virtualization. Operating systems currently modified to run in paravirtual mode are called paravirtualized operating systems and include SLES for SAP.
- PV on HVM (PVHVM)
PVHVM enhances HVM (see Full virtualization (FV)) with paravirtualized drivers, and handling of paravirtualized interrupts and timers.
4 For more information #
For further steps in virtualization, refer to the following sources:
5 Legal Notice #
Copyright© 2006–2026 SUSE LLC and contributors. All rights reserved.
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or (at your option) version 1.3; with the Invariant Section being this copyright notice and license. A copy of the license version 1.2 is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”.
For SUSE trademarks, see https://www.suse.com/company/legal/. All other third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Trademark symbols (®, ™ etc.) denote trademarks of SUSE and its affiliates. Asterisks (*) denote third-party trademarks.
All information found in this book has been compiled with utmost attention to detail. However, this does not guarantee complete accuracy. Neither SUSE LLC, its affiliates, the authors, nor the translators shall be held liable for possible errors or the consequences thereof.