Unified Virtual Machine Administration using libvirt
- WHAT?
This article introduces
libvirt—a set of tools that unify the management of virtual machines.- WHY?
By understanding
libvirt, you make the first step to easily manage virtual machines regardless of the virtualization technology used.- EFFORT
It takes 15 minutes to understand
libvirt.- GOAL
Basic understanding of
libvirtand related tools.
1 What is libvirt? #
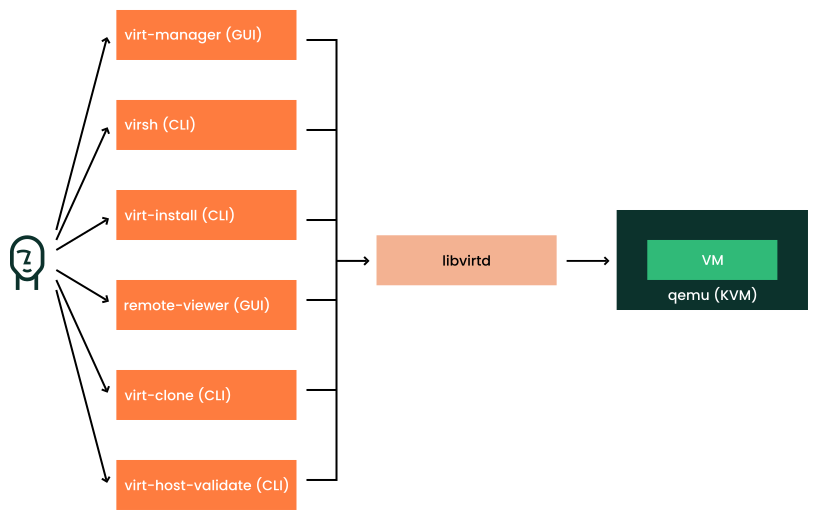
libvirt is a collection of software that provides a common API (Application Programming Interface) for managing popular virtualization solutions, for example, KVM, QEMU, Xen, Virtuozzo, VMware ESX, and so on. libvirt consists of an API library, a system service libvirtd, and a command-line utility virsh.
The modular architecture of libvirt allows developers to extend the functionality. Using libvirt, live migration of virtual machines between physical hosts is possible without downtime, and this facilitates in load balancing and maintenance.
libvirt allows remote management of virtual machines and host resources for multiple VM hosts and is a single tool for different hypervisors. libvirt has a graphical user interface and a command line to write XML configurations.
1.1 How does libvirt work? #
The libvirtd service runs on the VM host. The libvirt client libraries and utilities connect to libvirtd and collect configuration information and resources of the host servers.
The configuration of each virtual machine is stored in an XML file, and you can manage this configuration in different ways.
You can configure virtual machines managed by libvirt using a command line or using Virtual Machine Manager. Interoperability between libvirt and libvirt-based applications is tested and is an essential part of SUSE's support stance.
libvirt tools are designed to work with the libvirt API and support virtualization technologies and hypervisors. You can use the libvirt-based tools for managing VM Guests. Commonly used tools for libvirt are virsh, virt-manager, virt-install, virt-clone, virt-image, and so on. libvirt supports using graphical user interface and commands to write XML configurations.
For example, you can use virsh to configure virtual machines (VM) on the command line as an alternative to using the graphical Virtual Machine Manager. You can also manage virtual disks using this tool.
The management of virtual machines on the command line provides more control over the host machines than using the graphical interface applications as it allows scripting and automation.
1.2 Benefits of using libvirt #
The major advantages of using libvirt through command-line are listed below:
Allows basic monitoring of host and virtual machines.
Allows automating and scripting complex virtualization tasks and workflows.
Enables remote management of virtualization host. This helps in managing virtualization resources on remote servers over SSH or other secure protocols.
Allows managing headless servers. In server environments, where systems may not have a graphical interface or GUI tools installed, the command-line tool is the only option for managing virtualization.
Allows using scripts and commands to create custom reports.
Supports working with multiple hypervisors.
2 Virtual Machine Manager #
Virtual Machine Manager is a GUI (graphical user interface) application for viewing and configuring virtual machines managed by libvirt
The Virtual Machine Manager displays the summary of running domains, their live performance and resource utilization statistics. Use wizards to create new domains, configure and adjust resource allocation and virtual machine.
Listed below are a few configuration options available on Virtual Machine Manager:
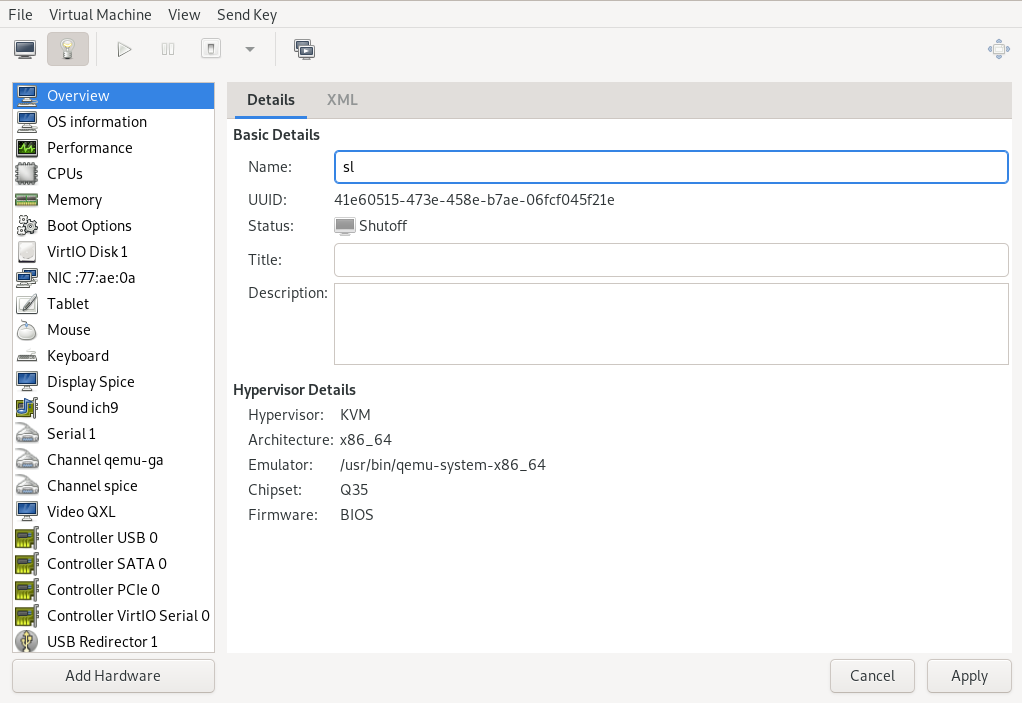
- View and configure VM Guest details
The view of the Virtual Machine Manager displays detailed information about the VM Guest's complete configuration and hardware equipment. Using this view, you can also change the guest configuration or add and modify virtual hardware to an existing virtual machine.
- View Performance Statistics of CPU usage, memory usage, disk and network I/O of the VM guest.
The view shows regularly updated charts of CPU and memory usage, and disk and network I/O of the VM guest.
You can also set up the virtualized processor and memory. In the CPUs section, you can configure the number of virtual CPUs allocated to the VM Guest. Logical host CPUs shows the number of online and usable CPUs on the VM Host Server. In the you can configure the CPU model and topology.
- Configure Boot options, Storage, Controllers, Networking, Input devices
You can configure options affecting the VM Guest boot process and you can configure both hard disks and removable media, such as USB or CD-ROM drives in . and allows you to add and configure new controllers and network device respectively. The configuration of input devices such as mouse, keyboard or tablet is possible through the option.
- Assign a host PCI device to a VM Guest
You can directly assign PCI devices on the VM Host Server to guests (PCI pass-through). When the PCI device is assigned to one VM Guest, it cannot be used on the host or by another VM Guest unless it is re-assigned.
- Take snapshot of the VM host
You can take snapshots of the VM host and you can access the option from VM Details toolbar.
- View and configure details of VM Host
You can create and manage connection, storage pools, and virtual networks.
3 Command-line tools #
libvirt includes several command-line utilities to manage virtual machines. A few of the command-line utilities are listed below:
virsh(Package: libvirt-client)A command-line tool to manage VM Guests with similar functionality as the Virtual Machine Manager. Allows you to change a VM Guest's status (start, stop, pause, etc.), to set up new guests and devices, or to edit existing configurations. virsh is also useful to script VM Guest management operations.
virt-install(Package: virt-install)A command-line tool for creating new VM Guests using the libvirt library. It supports graphical installations via VNC or SPICE protocols. Given suitable command-line arguments, virt-install can run completely unattended. This allows for easy automation of guest installs. virt-install is the default installation tool used by the Virtual Machine Manager.
remote-viewer(Package: virt-viewer)A simple viewer of a remote desktop. It supports SPICE and VNC protocols.
virt-clone(Package: virt-install)A tool for cloning existing virtual machine images using the libvirt hypervisor management library.
virt-host-validate(Package: libvirt-client)A tool that validates whether the host is configured in a suitable way to run libvirt hypervisor drivers.
4 For more information #
For more information on
libvirt, refer to https://libvirt.org/.For
libvirtdocumentation, refer to https://libvirt.org/docs.html.For information on Managing Virtual Machines with
libvirt, refer to https://documentation.suse.com/sles/html/SLES-all/part-virt-libvirt.html.
5 Legal Notice #
Copyright© 2006–2026 SUSE LLC and contributors. All rights reserved.
Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or (at your option) version 1.3; with the Invariant Section being this copyright notice and license. A copy of the license version 1.2 is included in the section entitled “GNU Free Documentation License”.
For SUSE trademarks, see https://www.suse.com/company/legal/. All other third-party trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Trademark symbols (®, ™ etc.) denote trademarks of SUSE and its affiliates. Asterisks (*) denote third-party trademarks.
All information found in this book has been compiled with utmost attention to detail. However, this does not guarantee complete accuracy. Neither SUSE LLC, its affiliates, the authors, nor the translators shall be held liable for possible errors or the consequences thereof.