Using Webhooks Instead of Polling
By default, SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery utilizes polling (default: every 15 seconds) to pull from a Git repo. This is a convenient default that works reasonably well for a small number of repos (up to a few tens).
For installations with multiple tens up to hundreds of Git repos, and in general to reduce latency (the time between a push to Git and fleet reacting to it), configuring webhooks is recommended instead of polling.
SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery currently supports Azure DevOps, GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Bitbucket Server, and Gogs.
1. Configure the webhook service. SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery uses a gitjob service to handle webhook requests. Create an ingress that points to the gitjob service.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: webhook-ingress
namespace: cattle-fleet-system
spec:
rules:
- host: your.domain.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: gitjob
port:
number: 80If you want to have the webhook available using the same host name as your Rancher or another service, you can use the following YAML with the URL http://your.domain.com/gitjob. The below YAML is specific for the Nginx Ingress Controller:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/use-regex: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2
name: webhook-ingress
namespace: cattle-fleet-system
spec:
rules:
- host: your.domain.com
http:
paths:
- path: /gitjob(/|$)(.*)
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
backend:
service:
name: gitjob
port:
number: 80|
You can configure TLS on ingress. |
2. Go to your webhook provider and configure the webhook callback url. Here is a Github example.
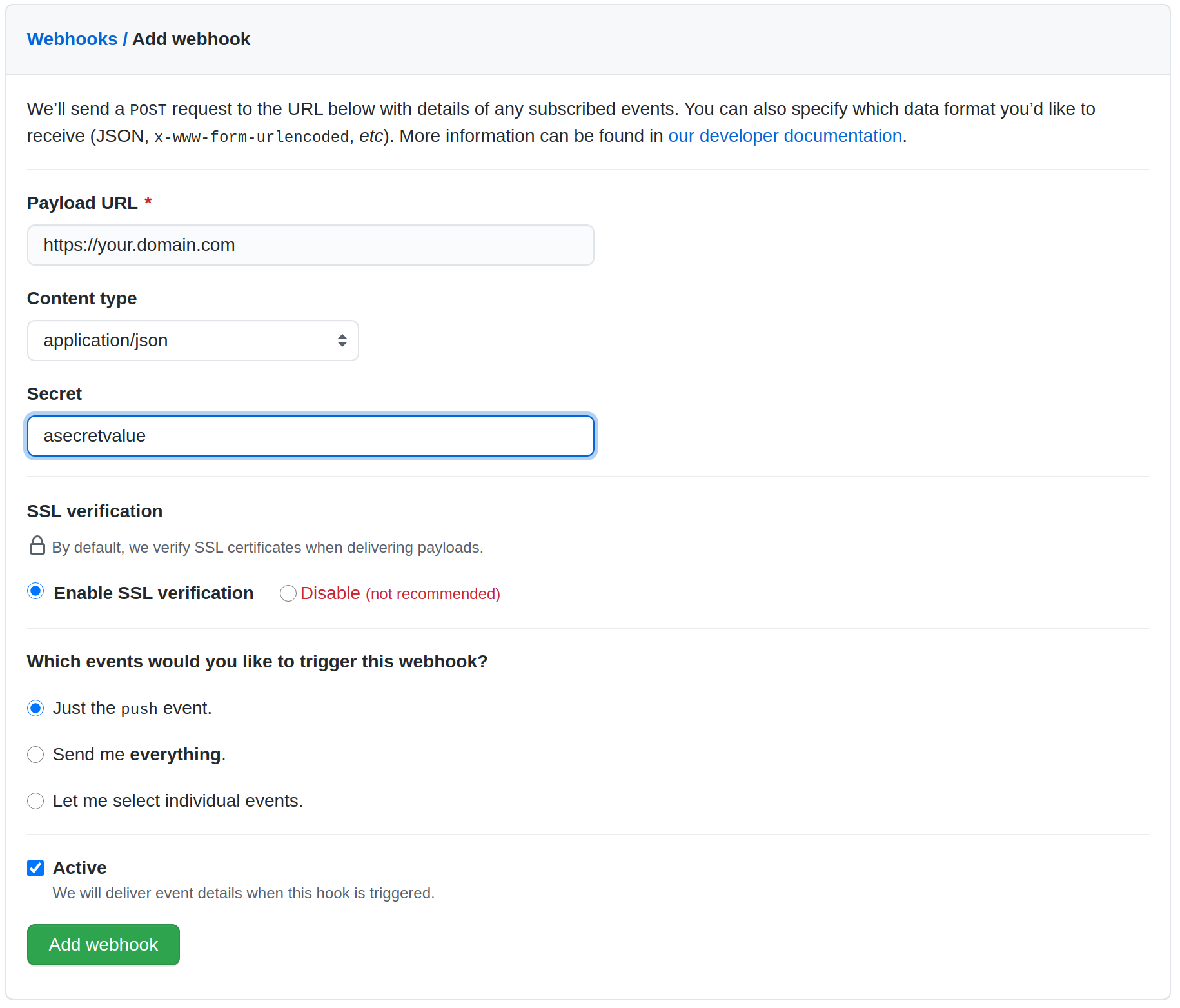
Configuring a secret is optional. This is used to validate the webhook payload as the payload should not be trusted by default. If your webhook server is publicly accessible to the Internet, then it is recommended to configure the secret. If you do configure the secret, follow step 3.
|
only application/json is supported due to the limitation of webhook library. |
|
If you configured the webhook the polling interval will be automatically adjusted to 1 hour. |
3. (Optional) Configure webhook secret. The secret is for validating webhook payload. Make sure to put it in a k8s secret called gitjob-webhook in cattle-fleet-system.
| Provider | K8s Secret Key |
|---|---|
GitHub |
|
GitLab |
|
BitBucket |
|
BitBucketServer |
|
Gogs |
|
Azure DevOps |
|
Azure DevOps |
|
For example, to create a secret containing a GitHub secret to validate the webhook payload, run:
kubectl create secret generic gitjob-webhook -n cattle-fleet-system --from-literal=github=webhooksecretvalueFor Azure DevOps:
-
Enable basic authentication in Azure
-
Create a secret containing the credentials for the basic authentication
kubectl create secret generic gitjob-webhook -n cattle-fleet-system --from-literal=azure-username=user --from-literal=azure-password=pass123