23 Air-gapped deployments with Edge Image Builder #
23.1 Intro #
This guide will show how to deploy several of the SUSE Edge components completely air-gapped on SLE Micro 6.0 utilizing Edge Image Builder(EIB) (Chapter 9, Edge Image Builder). With this, you’ll be able to boot into a customized, ready to boot (CRB) image created by EIB and have the specified components deployed on either a RKE2 or K3s cluster without an Internet connection or any manual steps. This configuration is highly desirable for customers that want to pre-bake all artifacts required for deployment into their OS image, so they are immediately available on boot.
We will cover an air-gapped installation of:
EIB will parse and pre-download all images referenced in the provided Helm charts and Kubernetes manifests. However, some of those may be attempting to pull container images and create Kubernetes resources based on those at runtime. In these cases we have to manually specify the necessary images in the definition file if we want to set up a completely air-gapped environment.
23.2 Prerequisites #
If you’re following this guide, it’s assumed that you are already familiar with EIB (Chapter 9, Edge Image Builder). If not, please follow the quick start guide (Chapter 3, Standalone clusters with Edge Image Builder) to better understand the concepts shown in practice below.
23.3 Libvirt Network Configuration #
To demo the air-gapped deployment, this guide will be done using a simulated air-gapped libvirt network and the following configuration will be tailored to that. For your own deployments, you may have to modify the host1.local.yaml configuration that will be introduced in the next step.
If you would like to use the same libvirt network configuration, follow along. If not, skip to Section 23.4, “Base Directory Configuration”.
Let’s create an isolated network configuration with an IP address range 192.168.100.2/24 for DHCP:
cat << EOF > isolatednetwork.xml
<network>
<name>isolatednetwork</name>
<bridge name='virbr1' stp='on' delay='0'/>
<ip address='192.168.100.1' netmask='255.255.255.0'>
<dhcp>
<range start='192.168.100.2' end='192.168.100.254'/>
</dhcp>
</ip>
</network>
EOFNow, the only thing left is to create the network and start it:
virsh net-define isolatednetwork.xml
virsh net-start isolatednetwork23.4 Base Directory Configuration #
The base directory configuration is the same across all different components, so we will set it up here.
We will first create the necessary subdirectories:
export CONFIG_DIR=$HOME/config
mkdir -p $CONFIG_DIR/base-images
mkdir -p $CONFIG_DIR/network
mkdir -p $CONFIG_DIR/kubernetes/helm/valuesMake sure to add whichever base image you plan to use into the base-images directory. This guide will focus on the Self Install ISO found here.
Let’s copy the downloaded image:
cp SL-Micro.x86_64-6.0-Base-SelfInstall-GM2.install.iso $CONFIG_DIR/base-images/slemicro.isoEIB is never going to modify the base image input.
Let’s create a file containing the desired network configuration:
cat << EOF > $CONFIG_DIR/network/host1.local.yaml
routes:
config:
- destination: 0.0.0.0/0
metric: 100
next-hop-address: 192.168.100.1
next-hop-interface: eth0
table-id: 254
- destination: 192.168.100.0/24
metric: 100
next-hop-address:
next-hop-interface: eth0
table-id: 254
dns-resolver:
config:
server:
- 192.168.100.1
- 8.8.8.8
interfaces:
- name: eth0
type: ethernet
state: up
mac-address: 34:8A:B1:4B:16:E7
ipv4:
address:
- ip: 192.168.100.50
prefix-length: 24
dhcp: false
enabled: true
ipv6:
enabled: false
EOFThis configuration ensures the following are present on the provisioned systems (using the specified MAC address):
an Ethernet interface with a static IP address
routing
DNS
hostname (
host1.local)
The resulting file structure should now look like:
├── kubernetes/
│ └── helm/
│ └── values/
├── base-images/
│ └── slemicro.iso
└── network/
└── host1.local.yaml23.5 Base Definition File #
Edge Image Builder is using definition files to modify the SLE Micro images. These files contain the majority of configurable options. Many of these options will be repeated across the different component sections, so we will list and explain those here.
Full list of customization options in the definition file can be found in the upstream documentation
We will take a look at the following fields which will be present in all definition files:
apiVersion: 1.0
image:
imageType: iso
arch: x86_64
baseImage: slemicro.iso
outputImageName: eib-image.iso
operatingSystem:
users:
- username: root
encryptedPassword: $6$jHugJNNd3HElGsUZ$eodjVe4te5ps44SVcWshdfWizrP.xAyd71CVEXazBJ/.v799/WRCBXxfYmunlBO2yp1hm/zb4r8EmnrrNCF.P/
kubernetes:
version: v1.30.14+rke2r4
embeddedArtifactRegistry:
images:
- ...The image section is required, and it specifies the input image, its architecture and type, as well as what the output image will be called.
The operatingSystem section is optional, and contains configuration to enable login on the provisioned systems with the root/eib username/password.
The kubernetes section is optional, and it defines the Kubernetes type and version. We are going to use Kubernetes 1.30.5 and RKE2 by default.
Use kubernetes.version: v1.30.5+k3s1 if K3s is desired instead. Unless explicitly configured via the kubernetes.nodes field, all clusters we bootstrap in this guide will be single-node ones.
The embeddedArtifactRegistry section will include all images which are only referenced and pulled at runtime for the specific component.
23.6 Rancher Installation #
The Rancher (Chapter 4, Rancher) deployment that will be demonstrated will be highly slimmed down for demonstration purposes. For your actual deployments, additional artifacts may be necessary depending on your configuration.
The Rancher v2.9.12 release assets contain a rancher-images.txt which can be seen here file which lists all the images required for an air-gapped installation.
There are over 600 container images in total which means that the resulting CRB image would be roughly 30GB. For our Rancher installation, we will strip down that list to the smallest working configuration. From there, you can add back any images you may need for your deployments.
We will create the definition file and include the stripped down image list:
apiVersion: 1.0
image:
imageType: iso
arch: x86_64
baseImage: slemicro.iso
outputImageName: eib-image.iso
operatingSystem:
users:
- username: root
encryptedPassword: $6$jHugJNNd3HElGsUZ$eodjVe4te5ps44SVcWshdfWizrP.xAyd71CVEXazBJ/.v799/WRCBXxfYmunlBO2yp1hm/zb4r8EmnrrNCF.P/
kubernetes:
version: v1.30.14+rke2r4
network:
apiVIP: 192.168.100.151
manifests:
urls:
- https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.15.3/cert-manager.crds.yaml
helm:
charts:
- name: rancher
version: 2.9.12
repositoryName: rancher-prime
valuesFile: rancher-values.yaml
targetNamespace: cattle-system
createNamespace: true
installationNamespace: kube-system
- name: cert-manager
installationNamespace: kube-system
createNamespace: true
repositoryName: jetstack
targetNamespace: cert-manager
version: 1.15.3
repositories:
- name: jetstack
url: https://charts.jetstack.io
- name: rancher-prime
url: https://charts.rancher.com/server-charts/prime
embeddedArtifactRegistry:
images:
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/backup-restore-operator:v5.0.4
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/calico-cni:v3.28.1-rancher1
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/cis-operator:v1.2.6
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/flannel-cni:v1.4.1-rancher1
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/fleet-agent:v0.10.16
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/fleet:v0.10.16
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-addon-resizer:1.8.23-build20250612
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-calico:v3.30.2-build20250711
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-cluster-autoscaler:v1.10.2-build20250611
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-cni-plugins:v1.7.1-build20250611
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-coredns:v1.12.2-build20250611
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-dns-node-cache:1.26.0-build20250611
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-etcd:v3.5.21-k3s1-build20250612
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-flannel:v0.27.1-build20250710
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-k8s-metrics-server:v0.8.0-build20250704
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-kubernetes:v1.30.14-rke2r4-build20250911
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-multus-cni:v4.2.1-build20250627
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-node-feature-discovery:v0.15.6-build20240822
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/hardened-whereabouts:v0.9.1-build20250704
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/k3s-upgrade:v1.30.14-k3s2
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/klipper-helm:v0.9.8-build20250709
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/klipper-lb:v0.4.13
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/kube-api-auth:v0.2.2
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/kubectl:v1.30.5
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/kuberlr-kubectl:v3.0.1
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/local-path-provisioner:v0.0.31
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/machine:v0.15.0-rancher125
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-cluster-api-controller:v1.7.3
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/nginx-ingress-controller:v1.12.4-hardened2
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/prometheus-federator:v0.4.4
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/pushprox-client:v0.1.4-rancher2-client
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/pushprox-proxy:v0.1.4-rancher2-proxy
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/rancher-agent:v2.9.12
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/rancher-csp-adapter:v4.0.0
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/rancher-webhook:v0.5.12
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/rancher:v2.9.12
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/rke-tools:v0.1.114
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/rke2-cloud-provider:v1.30.13-rc1.0.20250516172343-e77f78ee9466-build20250613
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/rke2-runtime:v1.30.14-rke2r4
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/rke2-upgrade:v1.30.14-rke2r4
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/security-scan:v0.4.4
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/shell:v0.3.0
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/supportability-review-app-frontend:latest
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/supportability-review-internal:latest
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/supportability-review-operator:latest
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/supportability-review:latest
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/system-agent-installer-k3s:v1.30.14-k3s2
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/system-agent-installer-rke2:v1.30.14-rke2r4
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/system-agent:v0.3.10-suc
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller:v0.13.4
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/ui-plugin-catalog:4.0.5
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/shell:v0.1.24
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v1.4.1
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v1.4.3
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v1.4.4
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v1.5.0
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v1.5.2
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v1.5.3
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v1.6.0
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v20230312-helm-chart-4.5.2-28-g66a760794
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v20231011-8b53cabe0
- name: registry.rancher.com/rancher/mirrored-ingress-nginx-kube-webhook-certgen:v20231226-1a7112e06As compared to the full list of 600+ container images, this slimmed down version only contains ~60 which makes the new CRB image only about 7GB.
We also need to create a Helm values file for Rancher:
cat << EOF > $CONFIG_DIR/kubernetes/helm/values/rancher-values.yaml
hostname: 192.168.100.50.sslip.io
replicas: 1
bootstrapPassword: "adminadminadmin"
systemDefaultRegistry: registry.rancher.com
useBundledSystemChart: true
EOFSetting the systemDefaultRegistry to registry.rancher.com allows Rancher to automatically look for images in the embedded artifact registry started within the CRB image at boot. Omitting this field may result in failure to find the container images on the node.
Let’s build the image:
podman run --rm -it --privileged -v $CONFIG_DIR:/eib \
registry.suse.com/edge/3.1/edge-image-builder:1.1.2 \
build --definition-file eib-iso-definition.yamlThe output should be similar to the following:
Downloading file: dl-manifest-1.yaml 100% |█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| (583/583 kB, 12 MB/s)
Pulling selected Helm charts... 100% |██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| (4/4, 1 it/s)
Generating image customization components...
Identifier ................... [SUCCESS]
Custom Files ................. [SKIPPED]
Time ......................... [SKIPPED]
Network ...................... [SUCCESS]
Groups ....................... [SKIPPED]
Users ........................ [SUCCESS]
Proxy ........................ [SKIPPED]
Rpm .......................... [SKIPPED]
Os Files ..................... [SKIPPED]
Systemd ...................... [SKIPPED]
Fips ......................... [SKIPPED]
Elemental .................... [SKIPPED]
Suma ......................... [SKIPPED]
Populating Embedded Artifact Registry... 100% |████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| (57/57, 2020 it/s)
Embedded Artifact Registry ... [SUCCESS]
Keymap ....................... [SUCCESS]
Configuring Kubernetes component...
The Kubernetes CNI is not explicitly set, defaulting to 'cilium'.
Downloading file: rke2_installer.sh
Downloading file: rke2-images-core.linux-amd64.tar.zst 100% (780/780 MB, 115 MB/s)
Downloading file: rke2-images-cilium.linux-amd64.tar.zst 100% (367/367 MB, 108 MB/s)
Downloading file: rke2.linux-amd64.tar.gz 100% (34/34 MB, 117 MB/s)
Downloading file: sha256sum-amd64.txt 100% (3.9/3.9 kB, 34 MB/s)
Downloading file: dl-manifest-1.yaml 100% (437/437 kB, 106 MB/s)
Kubernetes ................... [SUCCESS]
Certificates ................. [SKIPPED]
Cleanup ...................... [SKIPPED]
Building ISO image...
Kernel Params ................ [SKIPPED]
Build complete, the image can be found at: eib-image.isoOnce a node using the built image is provisioned, we can verify the Rancher installation:
/var/lib/rancher/rke2/bin/kubectl get all -n cattle-system --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/rke2/rke2.yamlThe output should be similar to the following, showing that everything has been successfully deployed:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/helm-operation-5v24z 0/2 Completed 0 2m18s
pod/helm-operation-jqjkg 0/2 Completed 0 101s
pod/helm-operation-p88bw 0/2 Completed 0 112s
pod/helm-operation-sdnql 2/2 Running 0 73s
pod/helm-operation-xkpkj 0/2 Completed 0 119s
pod/rancher-844dc7f5f6-pz7bz 1/1 Running 0 3m14s
pod/rancher-webhook-5c87686d68-hsllv 1/1 Running 0 97s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/rancher ClusterIP 10.43.96.117 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP 3m14s
service/rancher-webhook ClusterIP 10.43.112.253 <none> 443/TCP 97s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/rancher 1/1 1 1 3m14s
deployment.apps/rancher-webhook 1/1 1 1 97s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/rancher-844dc7f5f6 1 1 1 3m14s
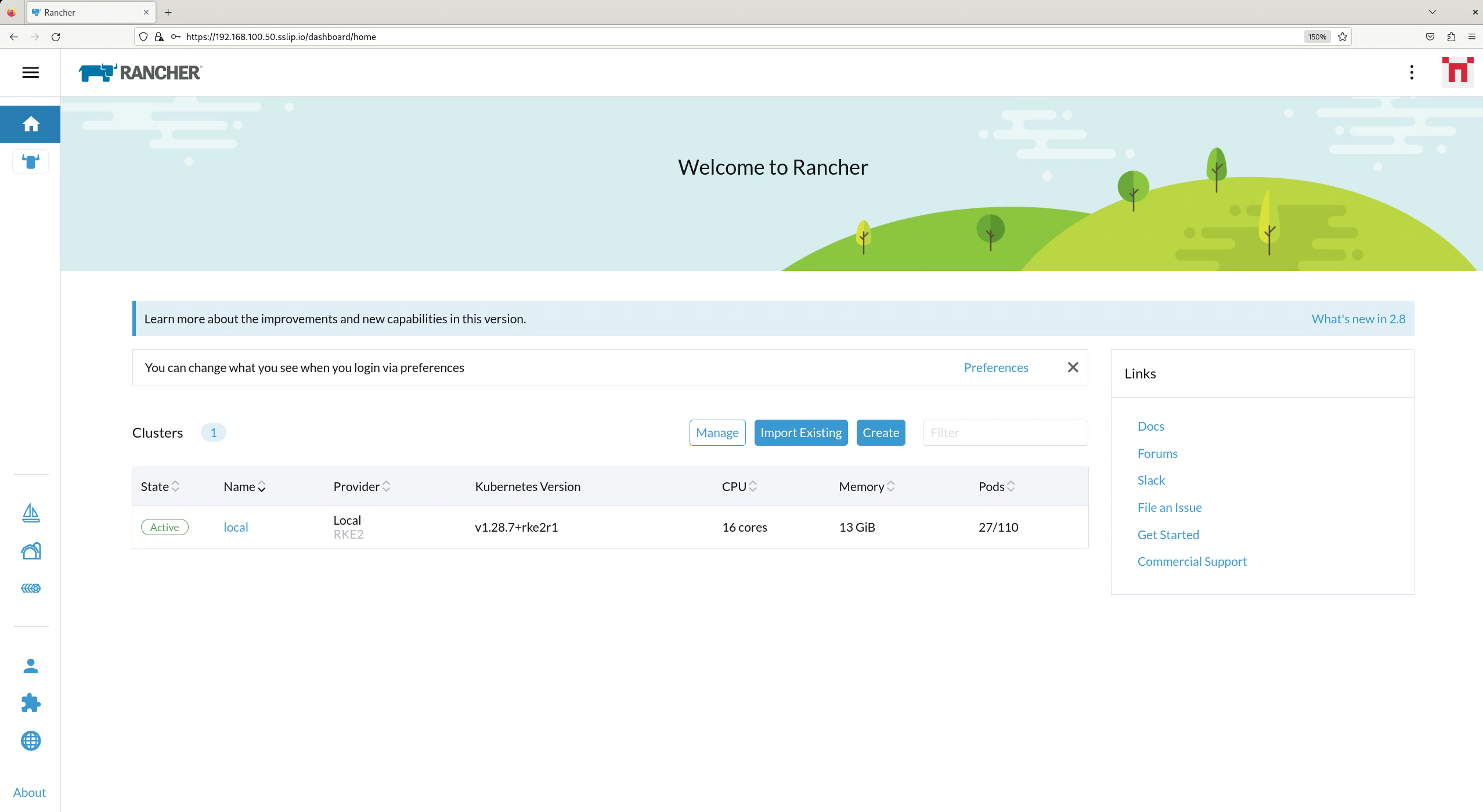
replicaset.apps/rancher-webhook-5c87686d68 1 1 1 97sAnd when we go to https://192.168.100.50.sslip.io and log in with the adminadminadmin password that we set earlier, we are greeted with the Rancher dashboard:
23.7 NeuVector Installation #
Unlike the Rancher installation, the NeuVector installation does not require any special handling in EIB. EIB will automatically air-gap every image required by NeuVector.
We will create the definition file:
apiVersion: 1.0
image:
imageType: iso
arch: x86_64
baseImage: slemicro.iso
outputImageName: eib-image.iso
operatingSystem:
users:
- username: root
encryptedPassword: $6$jHugJNNd3HElGsUZ$eodjVe4te5ps44SVcWshdfWizrP.xAyd71CVEXazBJ/.v799/WRCBXxfYmunlBO2yp1hm/zb4r8EmnrrNCF.P/
kubernetes:
version: v1.30.14+rke2r4
helm:
charts:
- name: neuvector-crd
version: 104.0.8+up2.8.8
repositoryName: rancher-charts
targetNamespace: neuvector
createNamespace: true
installationNamespace: kube-system
valuesFile: neuvector-values.yaml
- name: neuvector
version: 104.0.8+up2.8.8
repositoryName: rancher-charts
targetNamespace: neuvector
createNamespace: true
installationNamespace: kube-system
valuesFile: neuvector-values.yaml
repositories:
- name: rancher-charts
url: https://charts.rancher.io/We will also create a Helm values file for NeuVector:
cat << EOF > $CONFIG_DIR/kubernetes/helm/values/neuvector-values.yaml
controller:
replicas: 1
manager:
enabled: false
cve:
scanner:
enabled: false
replicas: 1
k3s:
enabled: true
crdwebhook:
enabled: false
EOFLet’s build the image:
podman run --rm -it --privileged -v $CONFIG_DIR:/eib \
registry.suse.com/edge/3.1/edge-image-builder:1.1.2 \
build --definition-file eib-iso-definition.yamlThe output should be similar to the following:
Generating image customization components...
Identifier ................... [SUCCESS]
Custom Files ................. [SKIPPED]
Time ......................... [SKIPPED]
Network ...................... [SUCCESS]
Groups ....................... [SKIPPED]
Users ........................ [SUCCESS]
Proxy ........................ [SKIPPED]
Rpm .......................... [SKIPPED]
Systemd ...................... [SKIPPED]
Elemental .................... [SKIPPED]
Suma ......................... [SKIPPED]
Populating Embedded Artifact Registry... 100% (6/6, 20 it/min)
Embedded Artifact Registry ... [SUCCESS]
Keymap ....................... [SUCCESS]
Configuring Kubernetes component...
The Kubernetes CNI is not explicitly set, defaulting to 'cilium'.
Downloading file: rke2_installer.sh
Kubernetes ................... [SUCCESS]
Certificates ................. [SKIPPED]
Building ISO image...
Kernel Params ................ [SKIPPED]
Image build complete!Once a node using the built image is provisioned, we can verify the NeuVector installation:
/var/lib/rancher/rke2/bin/kubectl get all -n neuvector --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/rke2/rke2.yamlThe output should be similar to the following, showing that everything has been successfully deployed:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/neuvector-controller-pod-7db4c6c9f4-qq7cf 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
pod/neuvector-enforcer-pod-qfdp2 1/1 Running 0 2m46s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/neuvector-svc-admission-webhook ClusterIP 10.43.254.230 <none> 443/TCP 2m46s
service/neuvector-svc-controller ClusterIP None <none> 18300/TCP,18301/TCP,18301/UDP 2m46s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
daemonset.apps/neuvector-enforcer-pod 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 2m46s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/neuvector-controller-pod 1/1 1 1 2m46s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/neuvector-controller-pod-7db4c6c9f4 1 1 1 2m46s
NAME SCHEDULE TIMEZONE SUSPEND ACTIVE LAST SCHEDULE AGE
cronjob.batch/neuvector-updater-pod 0 0 * * * <none> False 0 <none> 2m46s23.8 Longhorn Installation #
The official documentation for Longhorn contains a
longhorn-images.txt file which lists all the images required for an air-gapped installation.
We will be including their mirrored counterparts from the Rancher container registry in our definition file.
Let’s create it:
apiVersion: 1.0
image:
imageType: iso
arch: x86_64
baseImage: slemicro.iso
outputImageName: eib-image.iso
operatingSystem:
users:
- username: root
encryptedPassword: $6$jHugJNNd3HElGsUZ$eodjVe4te5ps44SVcWshdfWizrP.xAyd71CVEXazBJ/.v799/WRCBXxfYmunlBO2yp1hm/zb4r8EmnrrNCF.P/
packages:
sccRegistrationCode: <reg-code>
packageList:
- open-iscsi
kubernetes:
version: v1.30.14+rke2r4
helm:
charts:
- name: longhorn
repositoryName: longhorn
targetNamespace: longhorn-system
createNamespace: true
version: 104.2.2+up1.7.3
- name: longhorn-crd
repositoryName: longhorn
targetNamespace: longhorn-system
createNamespace: true
installationNamespace: kube-system
version: 104.2.2+up1.7.3
repositories:
- name: longhorn
url: https://charts.rancher.io
embeddedArtifactRegistry:
images:
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-csi-attacher:v4.8.0
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-csi-provisioner:v4.0.1-20250204
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-csi-resizer:v1.13.1
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-csi-snapshotter:v7.0.2-20250204
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-csi-node-driver-registrar:v2.13.0
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-livenessprobe:v2.15.0
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-openshift-origin-oauth-proxy:4.15
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-backing-image-manager:v1.7.3
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-longhorn-engine:v1.7.3
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-longhorn-instance-manager:v1.7.3
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-longhorn-manager:v1.7.3
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-longhorn-share-manager:v1.7.3
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-longhorn-ui:v1.7.3
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-longhorn-cli:v1.7.3
- name: registry.suse.com/rancher/mirrored-longhornio-support-bundle-kit:v0.0.51You will notice that the definition file lists the open-iscsi package. This is necessary since Longhorn
relies on a iscsiadm daemon running on the different nodes to provide persistent volumes to Kubernetes.
Let’s build the image:
podman run --rm -it --privileged -v $CONFIG_DIR:/eib \
registry.suse.com/edge/3.1/edge-image-builder:1.1.2 \
build --definition-file eib-iso-definition.yamlThe output should be similar to the following:
Setting up Podman API listener...
Pulling selected Helm charts... 100% |██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| (2/2, 3 it/s)
Generating image customization components...
Identifier ................... [SUCCESS]
Custom Files ................. [SKIPPED]
Time ......................... [SKIPPED]
Network ...................... [SUCCESS]
Groups ....................... [SKIPPED]
Users ........................ [SUCCESS]
Proxy ........................ [SKIPPED]
Resolving package dependencies...
Rpm .......................... [SUCCESS]
Os Files ..................... [SKIPPED]
Systemd ...................... [SKIPPED]
Fips ......................... [SKIPPED]
Elemental .................... [SKIPPED]
Suma ......................... [SKIPPED]
Populating Embedded Artifact Registry... 100% |███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| (15/15, 20956 it/s)
Embedded Artifact Registry ... [SUCCESS]
Keymap ....................... [SUCCESS]
Configuring Kubernetes component...
The Kubernetes CNI is not explicitly set, defaulting to 'cilium'.
Downloading file: rke2_installer.sh
Downloading file: rke2-images-core.linux-amd64.tar.zst 100% (782/782 MB, 108 MB/s)
Downloading file: rke2-images-cilium.linux-amd64.tar.zst 100% (367/367 MB, 104 MB/s)
Downloading file: rke2.linux-amd64.tar.gz 100% (34/34 MB, 108 MB/s)
Downloading file: sha256sum-amd64.txt 100% (3.9/3.9 kB, 7.5 MB/s)
Kubernetes ................... [SUCCESS]
Certificates ................. [SKIPPED]
Cleanup ...................... [SKIPPED]
Building ISO image...
Kernel Params ................ [SKIPPED]
Build complete, the image can be found at: eib-image.isoOnce a node using the built image is provisioned, we can verify the Longhorn installation:
/var/lib/rancher/rke2/bin/kubectl get all -n longhorn-system --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/rke2/rke2.yamlThe output should be similar to the following, showing that everything has been successfully deployed:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/csi-attacher-5dbc6d6479-jz2kf 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-attacher-5dbc6d6479-k2t47 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-attacher-5dbc6d6479-ms76j 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-provisioner-55749f6bd8-cv7k2 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-provisioner-55749f6bd8-qxmdd 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-provisioner-55749f6bd8-rjqpl 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-resizer-68fc4f8555-7sxr4 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-resizer-68fc4f8555-blxlt 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-resizer-68fc4f8555-ww6tc 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-snapshotter-6876488cb5-fw7vg 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-snapshotter-6876488cb5-xmz7l 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/csi-snapshotter-6876488cb5-zt6ht 1/1 Running 0 116s
pod/engine-image-ei-f586bff0-m6vzb 1/1 Running 0 2m34s
pod/instance-manager-d8b2d035a5c84130de8779e3b4c29113 1/1 Running 0 2m4s
pod/longhorn-csi-plugin-8dgxw 3/3 Running 0 116s
pod/longhorn-driver-deployer-65b7c7c8cc-pz8lr 1/1 Running 0 3m13s
pod/longhorn-manager-pllq7 2/2 Running 0 3m13s
pod/longhorn-ui-5c76575888-2rkpj 1/1 Running 3 (2m52s ago) 3m13s
pod/longhorn-ui-5c76575888-6z69x 1/1 Running 3 (2m55s ago) 3m13s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/longhorn-admission-webhook ClusterIP 10.43.213.17 <none> 9502/TCP 3m14s
service/longhorn-backend ClusterIP 10.43.11.79 <none> 9500/TCP 3m14s
service/longhorn-conversion-webhook ClusterIP 10.43.152.173 <none> 9501/TCP 3m14s
service/longhorn-frontend ClusterIP 10.43.150.97 <none> 80/TCP 3m14s
service/longhorn-recovery-backend ClusterIP 10.43.99.138 <none> 9503/TCP 3m14s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
daemonset.apps/engine-image-ei-f586bff0 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 2m34s
daemonset.apps/longhorn-csi-plugin 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 116s
daemonset.apps/longhorn-manager 1 1 1 1 1 <none> 3m13s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/csi-attacher 3/3 3 3 116s
deployment.apps/csi-provisioner 3/3 3 3 116s
deployment.apps/csi-resizer 3/3 3 3 116s
deployment.apps/csi-snapshotter 3/3 3 3 116s
deployment.apps/longhorn-driver-deployer 1/1 1 1 3m13s
deployment.apps/longhorn-ui 2/2 2 2 3m13s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/csi-attacher-5dbc6d6479 3 3 3 116s
replicaset.apps/csi-provisioner-55749f6bd8 3 3 3 116s
replicaset.apps/csi-resizer-68fc4f8555 3 3 3 116s
replicaset.apps/csi-snapshotter-6876488cb5 3 3 3 116s
replicaset.apps/longhorn-driver-deployer-65b7c7c8cc 1 1 1 3m13s
replicaset.apps/longhorn-ui-5c76575888 2 2 2 3m13s23.9 KubeVirt and CDI Installation #
The Helm charts for both KubeVirt and CDI are only installing their respective operators. It is up to the operators to deploy the rest of the systems which means we will have to include all necessary container images in our definition file. Let’s create it:
apiVersion: 1.0
image:
imageType: iso
arch: x86_64
baseImage: slemicro.iso
outputImageName: eib-image.iso
operatingSystem:
users:
- username: root
encryptedPassword: $6$jHugJNNd3HElGsUZ$eodjVe4te5ps44SVcWshdfWizrP.xAyd71CVEXazBJ/.v799/WRCBXxfYmunlBO2yp1hm/zb4r8EmnrrNCF.P/
kubernetes:
version: v1.30.14+rke2r4
helm:
charts:
- name: kubevirt-chart
repositoryName: suse-edge
version: 0.4.0
targetNamespace: kubevirt-system
createNamespace: true
installationNamespace: kube-system
- name: cdi-chart
repositoryName: suse-edge
version: 0.4.0
targetNamespace: cdi-system
createNamespace: true
installationNamespace: kube-system
repositories:
- name: suse-edge
url: oci://registry.suse.com/edge/3.1
embeddedArtifactRegistry:
images:
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/cdi-uploadproxy:1.60.1-150600.3.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/cdi-uploadserver:1.60.1-150600.3.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/cdi-apiserver:1.60.1-150600.3.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/cdi-controller:1.60.1-150600.3.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/cdi-importer:1.60.1-150600.3.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/cdi-cloner:1.60.1-150600.3.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/virt-api:1.3.1-150600.5.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/virt-controller:1.3.1-150600.5.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/virt-launcher:1.3.1-150600.5.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/virt-handler:1.3.1-150600.5.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/virt-exportproxy:1.3.1-150600.5.9.1
- name: registry.suse.com/suse/sles/15.6/virt-exportserver:1.3.1-150600.5.9.1Let’s build the image:
podman run --rm -it --privileged -v $CONFIG_DIR:/eib \
registry.suse.com/edge/3.1/edge-image-builder:1.1.2 \
build --definition-file eib-iso-definition.yamlThe output should be similar to the following:
Pulling selected Helm charts... 100% |███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| (2/2, 48 it/min)
Generating image customization components...
Identifier ................... [SUCCESS]
Custom Files ................. [SKIPPED]
Time ......................... [SKIPPED]
Network ...................... [SUCCESS]
Groups ....................... [SKIPPED]
Users ........................ [SUCCESS]
Proxy ........................ [SKIPPED]
Rpm .......................... [SKIPPED]
Os Files ..................... [SKIPPED]
Systemd ...................... [SKIPPED]
Fips ......................... [SKIPPED]
Elemental .................... [SKIPPED]
Suma ......................... [SKIPPED]
Populating Embedded Artifact Registry... 100% |██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| (15/15, 4 it/min)
Embedded Artifact Registry ... [SUCCESS]
Keymap ....................... [SUCCESS]
Configuring Kubernetes component...
The Kubernetes CNI is not explicitly set, defaulting to 'cilium'.
Downloading file: rke2_installer.sh
Kubernetes ................... [SUCCESS]
Certificates ................. [SKIPPED]
Cleanup ...................... [SKIPPED]
Building ISO image...
Kernel Params ................ [SKIPPED]
Build complete, the image can be found at: eib-image.isoOnce a node using the built image is provisioned, we can verify the installation of both KubeVirt and CDI.
Verify KubeVirt:
/var/lib/rancher/rke2/bin/kubectl get all -n kubevirt-system --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/rke2/rke2.yamlThe output should be similar to the following, showing that everything has been successfully deployed:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/virt-api-59cb997648-mmt67 1/1 Running 0 2m34s
pod/virt-controller-69786b785-7cc96 1/1 Running 0 2m8s
pod/virt-controller-69786b785-wq2dz 1/1 Running 0 2m8s
pod/virt-handler-2l4dm 1/1 Running 0 2m8s
pod/virt-operator-7c444cff46-nps4l 1/1 Running 0 3m1s
pod/virt-operator-7c444cff46-r25xq 1/1 Running 0 3m1s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kubevirt-operator-webhook ClusterIP 10.43.167.109 <none> 443/TCP 2m36s
service/kubevirt-prometheus-metrics ClusterIP None <none> 443/TCP 2m36s
service/virt-api ClusterIP 10.43.18.202 <none> 443/TCP 2m36s
service/virt-exportproxy ClusterIP 10.43.142.188 <none> 443/TCP 2m36s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
daemonset.apps/virt-handler 1 1 1 1 1 kubernetes.io/os=linux 2m8s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/virt-api 1/1 1 1 2m34s
deployment.apps/virt-controller 2/2 2 2 2m8s
deployment.apps/virt-operator 2/2 2 2 3m1s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/virt-api-59cb997648 1 1 1 2m34s
replicaset.apps/virt-controller-69786b785 2 2 2 2m8s
replicaset.apps/virt-operator-7c444cff46 2 2 2 3m1s
NAME AGE PHASE
kubevirt.kubevirt.io/kubevirt 3m1s DeployedVerify CDI:
/var/lib/rancher/rke2/bin/kubectl get all -n cdi-system --kubeconfig /etc/rancher/rke2/rke2.yamlThe output should be similar to the following, showing that everything has been successfully deployed:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/cdi-apiserver-5598c9bf47-pqfxw 1/1 Running 0 3m44s
pod/cdi-deployment-7cbc5db7f8-g46z7 1/1 Running 0 3m44s
pod/cdi-operator-777c865745-2qcnj 1/1 Running 0 3m48s
pod/cdi-uploadproxy-646f4cd7f7-fzkv7 1/1 Running 0 3m44s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/cdi-api ClusterIP 10.43.2.224 <none> 443/TCP 3m44s
service/cdi-prometheus-metrics ClusterIP 10.43.237.13 <none> 8080/TCP 3m44s
service/cdi-uploadproxy ClusterIP 10.43.114.91 <none> 443/TCP 3m44s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/cdi-apiserver 1/1 1 1 3m44s
deployment.apps/cdi-deployment 1/1 1 1 3m44s
deployment.apps/cdi-operator 1/1 1 1 3m48s
deployment.apps/cdi-uploadproxy 1/1 1 1 3m44s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/cdi-apiserver-5598c9bf47 1 1 1 3m44s
replicaset.apps/cdi-deployment-7cbc5db7f8 1 1 1 3m44s
replicaset.apps/cdi-operator-777c865745 1 1 1 3m48s
replicaset.apps/cdi-uploadproxy-646f4cd7f7 1 1 1 3m44s23.10 Troubleshooting #
If you run into any issues while building the images or are looking to further test and debug the process, please refer to the upstream documentation.