9 Firewalling #
This chapter presents information about restricting access to the system using firewalling and encryption and gives information about connecting to the system remotely.
9.1 Configuring SuSEfirewall2 #
By default, the installation workflow of SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP applications enables SuSEfirewall2. The firewall needs to be manually configured to allow network access for the following:
SAP application
Database (see the documentation of your database vendor; for SAP HANA, see Section 9.2, “Configuring HANA-Firewall”)
Additionally, open the ports 1128 (TCP) and
1129 (UDP).
SAP applications require many open ports and port ranges in the firewall. The exact numbers depend on the selected instance. For more information, see the documentation provided to you by SAP.
9.2 Configuring HANA-Firewall #
To simplify setting up a firewall for SAP HANA, install the package HANA-Firewall. HANA-Firewall adds rule sets to your existing SuSEfirewall2 configuration.
HANA-Firewall consists of the following parts:
YaST Module . Allows configuring, applying, and reverting firewall rules for SAP HANA from a graphical user interface.
Command Line Utility
hana-firewall. Allows applying and reverting the configured firewall rules for SAP HANA.If you prefer, you can configure the rule sets using the configuration file at
/etc/sysconfig/hana-firewallinstead of using YaST.Service
hana-firewall. Ensures that configured firewall rules for SAP HANA are kept.
For multi-tenant SAP HANA (MDC) databases, determining the port numbers that need to be opened is not yet possible automatically. If you are working with a multi-tenant SAP HANA database system: Before you use YaST, run a script on the command line to create a new service definition:
#cd /etc/hana-firewall.d#./create_new_service
You need to switch to the directory
/etc/hana-firewall.d,
otherwise the rule file for the new service will be created in a place
where it cannot be used.
The script will ask several questions: Importantly, it will ask for TCP and UDP port ranges that need to be opened.
Before continuing, make sure that the packages HANA-Firewall and yast2-hana-firewall are installed.
Make sure the SAP HANA databases for which you want to configure the firewall are correctly installed.
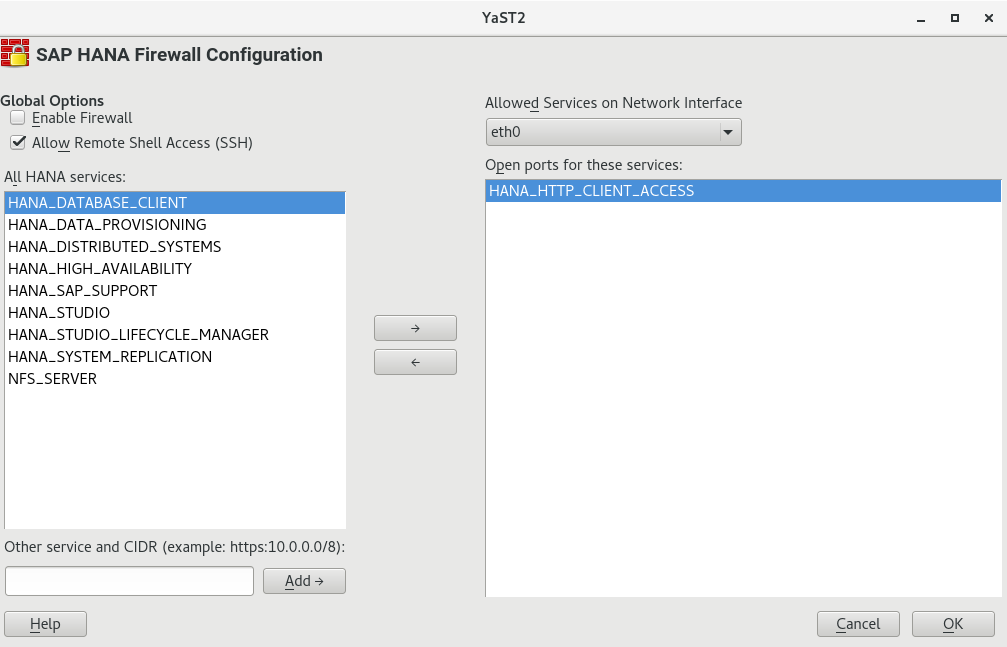
To open the appropriate YaST module, select › , › .
When you open this YaST module, it will create a configuration proposal based on the number of installed SAP HANA instances.
Choose whether you want to accept the proposal using or .
Important: Narrow Down Settings from ProposalThe proposed settings allow all detected SAP HANA instances on all detected network interfaces. Narrow down the proposal to secure the system further.
Under , activate . Additionally, decide whether to .
Choose a network interface under .
Allow network services by selecting them in the list box on the left and clicking . Remove services by selecting them in the list box on the right and clicking .
To add services other than the preconfigured ones, add them using the following notation:
SERVICE_NAME:CIDR_NOTATION
For more information about the CIDR notation, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Classless_Inter-Domain_Routing. To find out which services are available on your system, use
getent services.Repeat from Step 5 for all network interfaces.
When you are done, click .
The firewall rules from HANA-Firewall will now be compiled and applied. Then, the service
hana-firewallwill be restarted.Finally, check whether HANA-Firewall was enabled correctly:
#hana-firewall statusHANA firewall is active. Everything is OK.Tip: Checking Which Firewall Rules Are EnabledGaining an overview of which firewall rules are enabled in the current configuration of the script is possible using the command line:
#hana-firewall dry-run
For more information, see the man page of hana-firewall.
9.3 SAProuter Integration #
The SAProuter software from SAP allows proxying network traffic
between different SAP
systems or between an SAP system and outside networks. SUSE Linux Enterprise Server for SAP applications now
provides integration for SAProuter into
systemd. This means, SAProuter
will be started and stopped properly with the operating system and can be
controlled using systemctl.
Before you can use this functionality, make sure the following has been installed, in this order:
An SAP application that includes SAProuter
The SAProuter systemd integration, packaged as saprouter-systemd
If you got the order of applications to install wrong initially, reinstall saprouter-systemd.
To control SAProuter with systemctl, use:
Enabling the SAProuter Service:
systemctl enable saprouterStarting the SAProuter Service:
systemctl start saprouterShowing the Status of SAProuter Service:
systemctl status saprouterStopping the SAProuter Service:
systemctl stop saprouterDisabling the SAProuter Service:
systemctl disable saprouter