Installation Details
SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery can be installed in two modes: single-cluster and multi-cluster.
-
Single-cluster install: Recommended for getting started. This mode runs both the Fleet manager and agent on the same cluster.
-
Multi-cluster install: Used to manage multiple downstream clusters from a central manager.
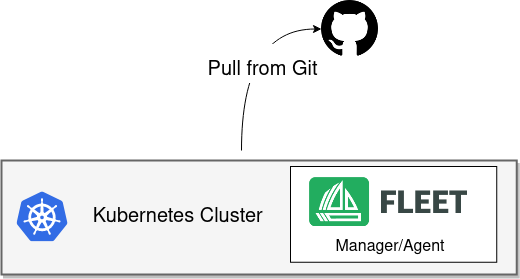
In the single-cluster setup, the same cluster runs both the Fleet manager and the Fleet agent. The cluster connects directly to the Git server to deploy resources locally. This is a simple, production-supported setup ideal for development, testing, and small-scale use.
Prerequisites
Helm 3
SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery is distributed as a Helm chart. Helm 3 is a client-only CLI with no server-side component. To install Helm 3, follow the official instructions at Helm installation guide.
Kubernetes
SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery runs as a controller on an existing Kubernetes cluster. For a single-cluster setup, install SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery on the same cluster that you intend to manage with GitOps. SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery supports any community-supported Kubernetes version, typically {versions.next.kubernetes} or later.
Default Installation
Install the following Helm charts to set up SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery.
|
SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery in Rancher Rancher includes separate Helm charts for SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery and uses a different repository. |
Install the Fleet CustomResourceDefinitions
helm -n cattle-fleet-system install --create-namespace --wait fleet-crd \
fleet/fleet-crdInstall the Fleet controllers
helm -n cattle-fleet-system install --create-namespace --wait fleet \
fleet/fleetVerify the installation
Run the following commands to verify that the SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery controller pods are running:
kubectl -n cattle-fleet-system logs -l app=fleet-controller
kubectl -n cattle-fleet-system get pods -l app=fleet-controllerExample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
fleet-controller-64f49d756b-n57wq 1/1 Running 0 3m21sYou can now register Git repositories in the fleet-local namespace to start deploying resources.
Tweaking Your Fleet Installation
Controller and Agent Replicas
Starting with SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery v0.13, the Helm chart exposes replica count settings for each controller type and the agent:
-
controller.replicas: Controlsfleet-controllerpods managing bundles, clusters, and groups. -
gitjob.replicas: Controls GitOpsGitReporeconciliation. -
helmops.replicas: Controls the experimental HelmOps controller. -
agent.replicas: Controls the Fleet agent.
Each defaults to one replica.
Multi-Controller Installation: Sharding
Deployment
From version 0.10 onward, SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery supports static sharding. Each shard is defined by a unique shard ID. You can optionally assign a node selector so all controller pods for that shard run on specific nodes.
Install SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery with the following Helm options:
-
--set shards[$index].id=$shard_id -
--set shards[$index].nodeSelector.$key=$value
Example:
helm -n cattle-fleet-system install --create-namespace --wait fleet fleet/fleet \
--set shards[0].id=foo \
--set shards[0].nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/hostname"=k3d-upstream-server-0 \
--set shards[1].id=bar \
--set shards[1].nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/hostname"=k3d-upstream-server-1 \
--set shards[2].id=baz \
--set shards[2].nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/hostname"=k3d-upstream-server-2Verify SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery controllers and GitJob pods:
kubectl -n cattle-fleet-system get pods -l app=fleet-controller \
-o=custom-columns='Name:.metadata.name,Shard-ID:.metadata.labels.fleet\.cattle\.io/shard-id,Node:spec.nodeName'Name Shard-ID Node
fleet-controller-b4c469c85-rj2q8 k3d-upstream-server-2
fleet-controller-shard-bar-5f5999958f-nt4bm bar k3d-upstream-server-1
fleet-controller-shard-baz-75c8587898-2wkk9 baz k3d-upstream-server-2
fleet-controller-shard-foo-55478fb9d8-42q2f foo k3d-upstream-server-0Similarly for GitJob pods:
kubectl -n cattle-fleet-system get pods -l app=gitjob \
-o=custom-columns='Name:.metadata.name,Shard-ID:.metadata.labels.fleet\.cattle\.io/shard-id,Node:spec.nodeName'How It Works
Each Fleet controller processes resources labeled with its shard ID. The unsharded controller handles all resources without a shard ID.
To deploy a GitRepo to a specific shard, add the label fleet.cattle.io/shard-ref to the resource.
Example:
apiVersion: fleet.cattle.io/v1alpha1
kind: GitRepo
metadata:
name: sharding-test
labels:
fleet.cattle.io/shard-ref: foo
spec:
repo: https://github.com/rancher/fleet-examples
paths:
- single-cluster/helmA GitRepo with a known shard ID (for example, foo) is processed by that controller.
Unknown shard IDs (for example, boo) are ignored.
To add or remove shards, redeploy SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery with an updated shard list.
Configuration for Multi-Cluster
|
Downstream clusters in Rancher are automatically registered in SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery. The setup below applies only to standalone SUSE® Rancher Prime Continuous Delivery and is not QA-tested by Rancher. |
|
The installation steps are identical to a single-cluster setup. After installing the Fleet manager, register remote clusters manually. For manager-initiated registration, additional API server details are required. Without them, only agent-initiated registration is possible. |
API Server URL and CA Certificate
The Fleet manager requires access to the Kubernetes API server. Agents use the API server URL and CA certificate to communicate securely.
Obtain these values from your kubeconfig file ($HOME/.kube/config):
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: LS0tLS1CRUdJTi...
server: https://example.com:6443Extract CA Certificate
The certificate-authority-data field is Base64 encoded.
Decode it and save to a file:
base64 -d encoded-file > ca.pemUse this command to extract all CAs:
kubectl config view -o json --raw | jq -r '.clusters[].cluster["certificate-authority-data"]' | base64 -d > ca.pemFor multi-cluster kubeconfigs:
kubectl config view -o json --raw | jq -r '.clusters[] | select(.name=="CLUSTERNAME").cluster["certificate-authority-data"]' | base64 -d > ca.pemExtract API Server
API_SERVER_URL=$(kubectl config view -o json --raw | jq -r '.clusters[] | select(.name=="CLUSTER").cluster["server"]')
API_SERVER_CA="ca.pem"Validate
Verify the API server URL:
curl -fLk "$API_SERVER_URL/version"Expected output: JSON version info or a 401 Unauthorized error.
Then validate the CA certificate:
curl -fL --cacert "$API_SERVER_CA" "$API_SERVER_URL/version"You should see valid JSON or a 401 Unauthorized message.
If you get an SSL error, the CA file is incorrect.
Example CA file (ca.pem):
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIBVjCB/qADAgECAgEAMAoGCCqGSM49BAMCMCMxITAfBgNVBAMMGGszcy1zZXJ2
ZXItY2FAMTU5ODM5MDQ0NzAeFw0yMDA4MjUyMTIwNDdaFw0zMDA4MjMyMTIwNDda
...
-----END CERTIFICATE-----Install for Multi-Cluster
Assume the API server URL is https://example.com:6443 and CA is in ca.pem.
If your API server uses a well-known CA, omit the CA parameter.
API_SERVER_URL="https://example.com:6443"
API_SERVER_CA="ca.pem"Then install the Fleet charts:
helm repo add fleet https://rancher.github.io/fleet-helm-charts/Install CustomResourceDefinitions:
helm -n cattle-fleet-system install --create-namespace --wait \
fleet-crd fleet/fleet-crdInstall Fleet controllers:
helm -n cattle-fleet-system install --create-namespace --wait \
--set apiServerURL="$API_SERVER_URL" \
--set-file apiServerCA="$API_SERVER_CA" \
fleet fleet/fleetVerify
kubectl -n cattle-fleet-system logs -l app=fleet-controller
kubectl -n cattle-fleet-system get pods -l app=fleet-controllerNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
fleet-controller-64f49d756b-n57wq 1/1 Running 0 3m21sAt this point, the Fleet manager should be ready. You can now register clusters and add Git repositories.