Virtualization Best Practices
1 Virtualization scenarios #
Virtualization offers a lot of capabilities to your environment. It can be used in multiple scenarios. To get more details about it, refer to the Virtualization Guide and in particular, to the following sections:
This best practice guide will provide advice for making the right choice in your environment. It will recommend or discourage the usage of options depending on your workload. Fixing configuration issues and performing tuning tasks will increase the performance of VM Guest's near to bare metal.
2 Before you apply modifications #
2.1 Back up first #
Changing the configuration of the VM Guest or the VM Host Server can lead to data loss or an unstable state. It is really important that you do backups of files, data, images, etc. before making any changes. Without backups you cannot restore the original state after a data loss or a misconfiguration. Do not perform tests or experiments on production systems.
2.2 Test your workloads #
The efficiency of a virtualization environment depends on many factors. This guide helps to make good choices when configuring virtualization in a production environment. Nothing is carved in stone. Hardware, workloads, resource capacity, etc. should all be considered when planning, testing, and deploying your virtualization infrastructure. Testing your virtualized workloads is vital to a successful virtualization implementation.
3 Recommendations #
3.1 Prefer the libvirt framework #
SUSE strongly recommends using the libvirt framework to configure,
manage, and operate VM Host Servers and VM Guest. It offers a single
interface (GUI and shell) for all supported virtualization technologies
and therefore is easier to use than the hypervisor-specific tools.
We do not recommend using libvirt and hypervisor-specific tools at the
same time, because changes done with the hypervisor-specific tools may
not be recognized by the libvirt tool set. See
Chapter 8, libvirt daemons for more information on libvirt.
3.2 qemu-system-i386 compared to qemu-system-x86_64 #
Similar to real 64-bit PC hardware,
qemu-system-x86_64 supports VM Guests running a
32-bit or a 64-bit operating system. Because
qemu-system-x86_64 usually also provides better
performance for 32-bit guests, SUSE generally recommends using
qemu-system-x86_64 for both 32-bit and 64-bit
VM Guests on KVM. Scenarios where qemu-system-i386
is known to perform better are not supported by SUSE.
Xen also uses binaries from the qemu package but prefers
qemu-system-i386, which can be used for both 32-bit
and 64-bit Xen VM Guests. To maintain compatibility with the upstream
Xen Community, SUSE encourages using
qemu-system-i386 for Xen VM Guests.
4 VM Host Server configuration and resource allocation #
Allocation of resources for VM Guests is a crucial point when administrating virtual machines. When assigning resources to VM Guests, be aware that overcommitting resources may affect the performance of the VM Host Server and the VM Guests. If all VM Guests request all their resources simultaneously, the host needs to be able to provide all of them. If not, the host's performance will be negatively affected and this will in turn also have negative effects on the VM Guest's performance.
4.1 Memory #
Linux manages memory in units called pages. On most systems the default page size is 4 KB. Linux and the CPU need to know which pages belong to which process. That information is stored in a page table. If a lot of processes are running, it takes more time to find where the memory is mapped, because of the time required to search the page table. To speed up the search, the TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffer) was invented. But on a system with a lot of memory, the TLB is not enough. To avoid any fallback to normal page table (resulting in a cache miss, which is time consuming), huge pages can be used. Using huge pages will reduce TLB overhead and TLB misses (pagewalk). A host with 32 GB (32*1014*1024 = 33,554,432 KB) of memory and a 4 KB page size has a TLB with 33,554,432/4 = 8,388,608 entries. Using a 2 MB (2048 KB) page size, the TLB only has 33554432/2048 = 16384 entries, considerably reducing the TLB misses.
4.1.1 Configuring the VM Host Server and the VM Guest to use huge pages #
The AMD64/Intel 64 CPU architecture supports larger pages than 4 KB: huge
pages. To determine the size of huge pages available on your system
(could be 2 MB or 1 GB), check the flags
line in the output of /proc/cpuinfo for
occurrences of pse and/or
pdpe1gb.
|
CPU flag |
Huge pages size available |
|---|---|
|
Empty string |
No huge pages available |
|
pse |
2 MB |
|
pdpe1gb |
1 GB |
Using huge pages improves the performance of VM Guests and reduces host memory consumption.
By default, the system uses THP. To make huge pages available on your
system, activate it at boot time with hugepages=1,
and—optionally—add the huge pages size with, for example,
hugepagesz=2MB.
1 GB pages can only be allocated at boot time and cannot be freed afterward.
To allocate and use the huge page table (HugeTlbPage), you need to
mount hugetlbfs with correct permissions.
Even if huge pages provide the best performance, they do come with some drawbacks. You lose features such as Memory ballooning (see Section 6.1.3, “virtio balloon”), KSM (see Section 4.1.4, “KSM and page sharing”), and huge pages cannot be swapped.
Mount
hugetlbfsto/dev/hugepages:>sudomount -t hugetlbfs hugetlbfs /dev/hugepagesTo reserve memory for huge pages, use the
sysctlcommand. If your system has a huge page size of 2 MB (2048 KB), and you want to reserve 1 GB (1,048,576 KB) for your VM Guest, you need 1,048,576/2048=512 pages in the pool:>sudosysctl vm.nr_hugepages=512The value is written to
/proc/sys/vm/nr_hugepagesand represents the current number of persistent huge pages in the kernel's huge page pool. Persistent huge pages will be returned to the huge page pool when freed by a task.Add the
memoryBackingelement in the VM Guest configuration file (by runningvirsh edit CONFIGURATION).<memoryBacking> <hugepages/> </memoryBacking>
Start your VM Guest and check on the host whether it uses hugepages:
>cat /proc/meminfo | grep HugePages_ HugePages_Total:1 512 HugePages_Free:2 92 HugePages_Rsvd:3 0 HugePages_Surp:4 0Size of the pool of huge pages
Number of huge pages in the pool that are not yet allocated
Number of huge pages for which a commitment to allocate from the pool has been made, but no allocation has yet been made
Number of huge pages in the pool above the value in
/proc/sys/vm/nr_hugepages. The maximum number of surplus huge pages is controlled by/proc/sys/vm/nr_overcommit_hugepages
4.1.2 Transparent huge pages #
Transparent huge pages (THP) provide a way to dynamically allocate
huge pages with the khugepaged kernel thread,
rather than manually managing their allocation and use. Workloads
with contiguous memory access patterns can benefit greatly from THP.
A 1000 fold decrease in page faults can be observed when running
synthetic workloads with contiguous memory access patterns.
Conversely, workloads with sparse memory access patterns (like
databases) may perform poorly with THP. In such cases it may be
preferable to disable THP by adding the kernel parameter
transparent_hugepage=never, rebuild your grub2
configuration, and reboot. Verify if THP is disabled with:
> cat /sys/kernel/mm/transparent_hugepage/enabled
always madvise [never]
If disabled, the value never is shown in square
brackets like in the example above.
THP is not available under Xen.
4.1.3 Xen-specific memory notes #
4.1.3.1 Managing domain-0 memory #
In previous versions of SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, the default memory allocation scheme of a Xen host was to allocate all host physical memory to Dom0 and enable auto-ballooning. Memory was automatically ballooned from Dom0 when additional domains were started. This behavior has always been error prone and disabling it was strongly encouraged. Starting in SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15 SP1, auto-ballooning has been disabled by default and Dom0 is given 10% of host physical memory + 1 GB. For example, on a host with 32 GB of physical memory, 4.2 GB of memory is allocated to Dom0.
The use of dom0_mem Xen command-line option in
/etc/default/grub is still supported and
encouraged (see Section 7.5, “Change kernel parameters at boot time” for
more information). You can restore the old behavior by setting
dom0_mem to the host physical memory size and
enabling the autoballoon setting in
/etc/xen/xl.conf.
4.1.4 KSM and page sharing #
Kernel Samepage Merging is a kernel feature that reduces memory
consumption on the VM Host Server by sharing blocks of memory that
VM Guests have in common. The KSM daemon
ksmd periodically scans
user memory, looking for pages with identical contents, which can be
replaced by a single write-protected page. To enable the KSM service,
first make sure that the package qemu-ksm is
installed, then run the command:
>sudosystemctl enable --now ksm.service
Alternatively, it can also be started by running the command:
# echo 1 > /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/runOne advantage of using KSM from a VM Guest's perspective is that all guest memory is backed by host anonymous memory. You can share pagecache, tmpfs or any kind of memory allocated in the guest.
KSM is controlled by sysfs. You can check
KSM's values in /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/:
pages_shared: the number of shared pages that are being used (read-only).pages_sharing: the number of sites sharing the pages (read-only).pages_unshared: the number of pages that are unique and repeatedly checked for merging (read-only).pages_volatile: the number of pages that are changing too fast to be considered for merging (read-only).full_scans: the number of times all mergeable areas have been scanned (read-only).sleep_millisecs: the number of millisecondsksmdshould sleep before the next scan. A low value will overuse the CPU, consuming CPU time that could be used for other tasks. We recommend a value greater than1000.pages_to_scan: the number of present pages to scan before ksmd goes to sleep. A high value will overuse the CPU. We recommend starting with a value of1000and then adjusting as necessary based on the KSM results observed while testing your deployment.merge_across_nodes: by default, the system merges pages across NUMA nodes. Set this option to0to disable this behavior.
KSM is a good technique to over-commit host memory when running multiple instances of the same application or VM Guest. When applications and VM Guest are heterogeneous and do not share any common data, it is preferable to disable KSM. To do that, run:
>sudosystemctl disable --now ksm.service
Alternatively, it can also be disabled by running the command:
# echo 0 > /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/run
In a mixed heterogeneous and homogeneous environment, KSM can be
enabled on the host but disabled on a per VM Guest basis. Use
virsh edit to disable page sharing of a
VM Guest by adding the following to the guest's XML configuration:
<memoryBacking> <nosharepages/> </memoryBacking>
KSM can free up some memory on the host system, but the administrator should reserve enough swap to avoid out-of-memory conditions if that shareable memory decreases. If the amount of shareable memory decreases, the use of physical memory is increased.
By default, KSM will merge common pages across NUMA nodes. If the
merged, common page is now located on a distant NUMA node (relative
to the node running the VM Guest vCPUs), this may degrade
VM Guest performance. If increased memory access latencies are
noticed in the VM Guest, disable cross-node merging with the
merge_across_nodes sysfs control:
# echo 0 > /sys/kernel/mm/ksm/merge_across_nodes4.1.5 VM Guest: memory hotplug #
To optimize the usage of your host memory, it may be useful to
hotplug more memory for a running VM Guest when required. To support
memory hotplugging, you must first configure the
<maxMemory> tag in the VM Guest's
configuration file:
<maxMemory1 slots='16'2 unit='KiB'>209715203</maxMemory> <memory4 unit='KiB'>1048576</memory> <currentMemory5 unit='KiB'>1048576</currentMemory>
Runtime maximum memory allocation of the guest. | |
Number of slots available for adding memory to the guest | |
Valid units are:
| |
Maximum allocation of memory for the guest at boot time | |
Actual allocation of memory for the guest |
To hotplug memory devices into the slots, create a file
mem-dev.xml like the following:
<memory model='dimm'> <target> <size unit='KiB'>524287</size> <node>0</node> </target> </memory>
And attach it with the following command:
> virsh attach-device vm-name mem-dev.xmlFor memory device hotplug, the guest must have at least 1 NUMA cell defined (see Section 4.6.3.1, “VM Guest virtual NUMA topology”).
4.2 Swap #
Swap is usually used by the system to store underused physical memory (low usage, or not accessed for a long time). To prevent the system running out of memory, setting up a minimum swap is highly recommended.
4.2.1 swappiness #
The swappiness setting controls your system's swap
behavior. It defines how memory pages are swapped to disk. A high
value of swappiness results in a system that
swaps more often. Available values range from 0 to
200. A value of 200 tells the
system to find inactive pages and put them in swap. A value of
0 disables swapping.
To do some testing on a live system, change the value of
/proc/sys/vm/swappiness on the fly and check the
memory usage afterward:
# echo 35 > /proc/sys/vm/swappiness> free -h
total used free shared buffers cached
Mem: 24616680 4991492 19625188 167056 144340 2152408
-/+ buffers/cache: 2694744 21921936
Swap: 6171644 0 6171644
To permanently set a swappiness value, add a line in
/etc/systcl.conf, for example:
vm.swappiness = 35
You can also control the swap by using the
swap_hard_limit element in the XML configuration
of your VM Guest. Before setting this parameter and using it in a
production environment, do some testing because the host can
terminate the domain if the value is too low.
<memtune>1 <hard_limit unit='G'>1</hard_limit>2 <soft_limit unit='M'>128</soft_limit>3 <swap_hard_limit unit='G'>2</swap_hard_limit>4 </memtune>
This element provides memory tunable parameters for the domain. If this is omitted, it defaults to the defaults provided b the operating system. | |
Maximum memory the guest can use. To avoid any problems on the VM Guest it is strongly recommended not to use this parameter. | |
The memory limit to enforce during memory contention. | |
The maximum memory plus swap the VM Guest can use. |
4.3 I/O #
4.3.1 I/O scheduler #
The I/O scheduler for SUSE Linux Enterprise 15 SP2 and up is Budget Fair Queueing (BFQ). The main aim of the BFQ scheduler is to provide a fair allocation of the disk I/O bandwidth for all processes that request an I/O operation. You can have different I/O schedulers for different devices.
To get better performance in host and VM Guest, use
none in the VM Guest (disable the I/O scheduler)
and the mq-deadline scheduler for a virtualization
host.
To check your current I/O scheduler for your disk (replace sdX by the disk you want to check), run:
>cat /sys/block/sdX/queue/scheduler mq-deadline kyber [bfq] noneThe value in square brackets is the one currently selected (
bfqin the example above).You can change the scheduler at runtime by running the following command as
root:#echo mq-deadline > /sys/block/sdX/queue/scheduler
If you need to specify different I/O schedulers for each disk, create
the file /usr/lib/tmpfiles.d/IO_ioscheduler.conf
with content similar to the following example. It defines the
mq-deadline scheduler for
/dev/sda and the none
scheduler for /dev/sdb. Keep in mind that the
device name can be different depending on the device type. This
feature is available on SLE 12 and up.
w /sys/block/sda/queue/scheduler - - - - mq-deadline w /sys/block/sdb/queue/scheduler - - - - none
4.3.2 Asynchronous I/O #
Many of the virtual disk back-ends use Linux Asynchronous I/O (aio) in their implementation. By default, the maximum number of aio contexts is set to 65536, which can be exceeded when running hundreds of VM Guests using virtual disks serviced by Linux Asynchronous I/O. When running large numbers of VM Guests on a VM Host Server, consider increasing /proc/sys/fs/aio-max-nr.
To check your current aio-max-nr setting run:
>cat /proc/sys/fs/aio-max-nr 65536You can change aio-max-nr at runtime with the following command:
#echo 131072 > /proc/sys/fs/aio-max-nr
To permanently set aio-max-nr, add an entry to a
custom sysctl file. For example, include the following to
/etc/sysctl.d/aio-max-nr.conf:
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576
4.3.3 I/O Virtualization #
SUSE products support various I/O virtualization technologies. The following table lists advantages and disadvantages of each technology. For more information about I/O in virtualization refer to the Section 1.4, “I/O virtualization”.
|
Technology |
Advantage |
Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
|
Device Assignment (pass-through) |
Device accessed directly by the guest |
No sharing among multiple guests |
|
High performance |
Live migration is complex | |
|
PCI device limit is 8 per guest | ||
|
Limited number of slots on a server | ||
|
Full virtualization (IDE, SATA, SCSI, e1000) |
VM Guest compatibility |
Bad performance |
|
Easy for live migration |
Emulated operation | |
|
Para-virtualization (virtio-blk, virtio-net, virtio-scsi) |
Good performance |
Modified guest (PV drivers) |
|
Easy for live migration | ||
|
Efficient host communication with VM Guest |
4.4 Storage and file system #
Storage space for VM Guests can either be a block device (for example, a partition on a physical disk), or an image file on the file system:
|
Technology |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
|
Block devices |
|
|
|
Image files |
|
|
For detailed information about image formats and maintaining images refer to Section 5, “VM Guest images”.
If your image is stored on an NFS share, you should check some server and client parameters to improve access to the VM Guest image.
4.4.1 NFS read/write (client) #
Options rsize and wsize specify the
size of the chunks of data that the client and server pass back and
forth to each other. You should ensure NFS read/write sizes are
sufficiently large, especially for large I/O. Change the
rsize and wsize parameter in your
/etc/fstab by increasing the value to 16 KB.
This will ensure that all operations can be frozen if there is any
instance of hanging.
nfs_server:/exported/vm_images1 /mnt/images2 nfs3 rw4,hard5,sync6, rsize=81927,wsize=81928 0 0
NFS server's host name and export path. | |
Where to mount the NFS exported share. | |
This is an | |
This mount point will be accessible in read/write. | |
Determines the recovery behavior of the NFS client after an NFS
request times out. | |
Any system call that writes data to files on that mount point causes that data to be flushed to the server before the system call returns control to user space. | |
Maximum number of bytes in each network READ request that the NFS client can receive when reading data from a file on an NFS server. | |
Maximum number of bytes per network WRITE request that the NFS client can send when writing data to a file on an NFS server. |
4.4.2 NFS threads (server) #
Your NFS server should have enough NFS threads to handle
multi-threaded workloads. Use the nfsstat tool to
get RPC statistics on your server:
>sudonfsstat -rc Client rpc stats: calls retrans authrefrsh 6401066 198 0 0
If the retrans is equal to 0, everything is fine.
Otherwise, the client needs to retransmit, so increase the
USE_KERNEL_NFSD_NUMBER variable in
/etc/sysconfig/nfs, and adjust accordingly until
retrans is equal to 0.
4.5 CPUs #
Host CPU “components” will be “translated” to virtual CPUs in a VM Guest when being assigned. These components can either be:
CPU processor: this describes the main CPU unit, which usually has multiple cores and may support Hyper-Threading.
CPU core: a main CPU unit can provide more than one core, and the proximity of cores speeds up the computation process and reduces energy costs.
CPU Hyper-Threading: this implementation is used to improve parallelization of computations, but this is not as efficient as a dedicated core.
4.5.1 Assigning CPUs #
CPU overcommit occurs when the cumulative number of virtual CPUs of all VM Guests becomes higher than the number of host CPUs. Best performance is likely to be achieved when there is no overcommit and each virtual CPU matches one hardware processor or core on the VM Host Server. In fact, VM Guests running on an overcommitted host will experience increased latency and a negative effect on per-VM Guest throughput is also likely to be observed. Therefore, you should try to avoid overcommitting CPUs.
Deciding whether to allow CPU overcommit or not requires good a-priori knowledge of workload as a whole. For example, if you know that all the VM Guests virtual CPUs will not be loaded more than 50% then you can assume that overcommitting the host by a factor of 2 (which means having 128 virtual CPUs in total, on a host with 64 CPUs) will work well. On the other hand, if you know that all the virtual CPUs of the VM Guests will try to run at 100% for most of the time then even having one virtual CPU more than the host has CPUs is already a misconfiguration.
Overcommitting to a point where the cumulative number of virtual CPUs is higher than 8 times the number of physical cores of the VM Host Server will most likely lead to a malfunctioning and unstable system and should hence be avoided.
Unless you know exactly how many virtual CPUs are required for a VM Guest, start with one. Target a CPU workload of approximately 70% inside your VM (see Section 2.3, “Processes” for information on monitoring tools). If you allocate more processors than needed in the VM Guest, this will negatively affect the performance of host and guest. Cycle efficiency will be degraded, as the unused vCPU will still cause timer interrupts. In case you primarily run single threaded applications on a VM Guest, a single virtual CPU is the best choice.
A single VM Guest with more virtual CPUs than the VM Host Server has CPUs is always a misconfiguration.
4.5.2 VM Guest CPU configuration #
This section describes how to choose and configure a CPU type for a VM Guest. You will also learn how to pin virtual CPUs to physical CPUs on the host system. For more information about virtual CPU configuration and tuning parameters refer to the libvirt documentation at https://libvirt.org/formatdomain.html#elementsCPU.
4.5.2.1 Virtual CPU models and features #
The CPU model and topology can be specified individually for each
VM Guest. Configuration options range from selecting specific CPU
models to excluding certain CPU features. Predefined CPU models are
listed in files in the directory
/usr/share/libvirt/cpu_map/. A CPU model and
topology that is similar to the host generally provides the best
performance. The host system CPU model and topology can be
displayed by running virsh capabilities.
Note that changing the default virtual CPU configuration will require a VM Guest shutdown when migrating it to a host with different hardware. More information on VM Guest migration is available at Section 11.7, “Migrating VM Guests”.
To specify a particular CPU model for a VM Guest, add a respective entry to the VM Guest configuration file. The following example configures a Broadwell CPU with the invariant TSC feature:
<cpu mode='custom' match='exact'> <model>Broadwell</model> <feature name='invtsc'/> </cpu>
For a virtual CPU that most closely resembles the host physical
CPU, <cpu mode='host-passthrough'> can be
used. Note that a host-passthrough CPU model may
not exactly resemble the host physical CPU, since by default KVM
will mask any non-migratable features. For example invtsc is not
included in the virtual CPU feature set. Changing the default KVM
behavior is not directly supported through libvirt, although it
does allow arbitrary pass-through of KVM command line arguments.
Continuing with the invtsc example, you can
achieve pass-through of the host CPU (including
invtsc) with the following command line
pass-through in the VM Guest configuration file:
<domain type='kvm' xmlns:qemu='http://libvirt.org/schemas/domain/qemu/1.0'>
<qemu:commandline>
<qemu:arg value='-cpu'/>
<qemu:arg value='host,migratable=off,+invtsc'/>
</qemu:commandline>
...
</domain>host-passthrough mode
Since host-passthrough exposes the physical
CPU details to the virtual CPU, migration to dissimilar hardware
is not possible. See
Section 4.5.2.3, “Virtual CPU migration considerations” for
more information.
4.5.2.2 Virtual CPU pinning #
Virtual CPU pinning is used to constrain virtual CPU threads to a
set of physical CPUs. The vcpupin element
specifies the physical host CPUs that a virtual CPU can use. If
this element is not set and the attribute cpuset
of the vcpu element is not specified, the
virtual CPU is free to use any of the physical CPUs.
CPU intensive workloads can benefit from virtual CPU pinning by increasing the physical CPU cache hit ratio. To pin a virtual CPU to a specific physical CPU, run the following commands:
>virsh vcpupin DOMAIN_ID --vcpu vCPU_NUMBER VCPU: CPU Affinity ---------------------------------- 0: 0-7#virsh vcpupin SLE15 --vcpu 0 0 --config
The last command generates the following entry in the XML configuration:
<cputune> <vcpupin vcpu='0' cpuset='0'/> </cputune>
To confine a VM Guest's CPUs and its memory to a NUMA node, you can use virtual CPU pinning and memory allocation policies on a NUMA system. See Section 4.6, “NUMA tuning” for more information related to NUMA tuning.
Even though vcpupin can improve performance,
it can complicate live migration. See
Section 4.5.2.3, “Virtual CPU migration considerations” for
more information on virtual CPU migration considerations.
4.5.2.3 Virtual CPU migration considerations #
Selecting a virtual CPU model containing all the latest features
may improve performance of a VM Guest workload, but often at the
expense of migratability. Unless all hosts in the cluster contain
the latest CPU features, migration can fail when a destination host
lacks the new features. If migratability of a virtual CPU is
preferred over the latest CPU features, a normalized CPU model and
feature set should be used. The virsh
cpu-baseline command can help define a normalized virtual
CPU that can be migrated across all hosts. The following command,
when run on each host in the migration cluster, illustrates the
collection of all hosts' capabilities in
all-hosts-caps.xml.
>sudovirsh capabilities >> all-hosts-cpu-caps.xml
With the capabilities of each host collected in all-hosts-caps.xml,
use virsh cpu-baseline to create a virtual CPU
definition that will be compatible across all hosts.
>sudovirsh cpu-baseline all-hosts-caps.xml
The resulting virtual CPU definition can be used as the
cpu element in the VM Guest configuration file.
At a logical level, virtual CPU pinning is a form of hardware pass-through. CPU pinning couples physical resources to virtual resources, which can also be problematic for migration. For example, the migration will fail if the requested physical resources are not available on the destination host, or if the source and destination hosts have different NUMA topologies. For more recommendations about Live Migration, see Section 11.7.1, “Migration requirements”.
4.6 NUMA tuning #
NUMA is an acronym for Non Uniform Memory Access. A NUMA system has multiple physical CPUs, each with local memory attached. Each CPU can also access other CPUs' memory, known as “remote memory access”, but it is much slower than accessing local memory. NUMA systems can negatively affect VM Guest performance if not tuned properly. Although ultimately tuning is workload dependent, this section describes controls that should be considered when deploying VM Guests on NUMA hosts. Always consider your host topology when configuring and deploying VMs.
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server contains a NUMA auto-balancer that strives to reduce
remote memory access by placing memory on the same NUMA node as the CPU
processing it. Standard tools such as cgset and
virtualization tools such as libvirt provide mechanisms to constrain
VM Guest resources to physical resources.
numactl is used to check for host NUMA capabilities:
>sudonumactl --hardware available: 4 nodes (0-3) node 0 cpus: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 node 0 size: 31975 MB node 0 free: 31120 MB node 1 cpus: 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 node 1 size: 32316 MB node 1 free: 31673 MB node 2 cpus: 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 node 2 size: 32316 MB node 2 free: 31726 MB node 3 cpus: 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 node 3 size: 32314 MB node 3 free: 31387 MB node distances: node 0 1 2 3 0: 10 21 21 21 1: 21 10 21 21 2: 21 21 10 21 3: 21 21 21 10
The numactl output shows this is a NUMA system with
4 nodes or cells, each containing 36 CPUs and approximately 32G memory.
virsh capabilities can also be used to examine the
systems NUMA capabilities and CPU topology.
4.6.1 NUMA balancing #
On NUMA machines, there is a performance penalty if remote memory is
accessed by a CPU. Automatic NUMA balancing scans a task's address
space and unmaps pages. By doing so, it detects whether pages are
properly placed or whether to migrate the data to a memory node local
to where the task is running. In defined intervals (configured with
numa_balancing_scan_delay_ms), the task scans the
next scan size number of pages (configured with
numa_balancing_scan_size_mb) in its address space.
When the end of the address space is reached, the scanner restarts
from the beginning.
Higher scan rates cause higher system overhead as page faults must be
trapped and data needs to be migrated. However, the higher the scan
rate, the more quickly a task's memory migrates to a local node when
the workload pattern changes. This minimizes the performance impact
caused by remote memory accesses. These sysctl
directives control the thresholds for scan delays and the number of
pages scanned:
>sudosysctl -a | grep numa_balancing kernel.numa_balancing = 11 kernel.numa_balancing_scan_delay_ms = 10002 kernel.numa_balancing_scan_period_max_ms = 600003 kernel.numa_balancing_scan_period_min_ms = 10004 kernel.numa_balancing_scan_size_mb = 2565
Enables/disables automatic page fault-based NUMA balancing | |
Starting scan delay used for a task when it initially forks | |
Maximum time in milliseconds to scan a task's virtual memory | |
Minimum time in milliseconds to scan a task's virtual memory | |
Size in megabytes' worth of pages to be scanned for a given scan |
For more information, see Chapter 11, Automatic Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA) balancing.
The main goal of automatic NUMA balancing is either to reschedule tasks on the same node's memory (so the CPU follows the memory), or to copy the memory's pages to the same node (so the memory follows the CPU).
There are no rules to define the best place to run a task, because
tasks could share memory with other tasks. For the best
performance, we recommend to group tasks sharing memory on the same
node. Check NUMA statistics with # cat /proc/vmstat | grep
numa_.
4.6.2 Memory allocation control with the CPUset controller #
The cgroups cpuset controller can be used confine memory used by a process to a NUMA node. There are three cpuset memory policy modes available:
interleave: this is a memory placement policy which is also known as round-robin. This policy can provide substantial improvements for jobs that need to place thread local data on the corresponding node. When the interleave destination is not available, it will be moved to another node.bind: this will place memory only on one node, which means in case of insufficient memory, the allocation will fail.preferred: this policy will apply a preference to allocate memory to a node. If there is not enough space for memory on this node, it will fall back to another node.
You can change the memory policy mode with the
cgset tool from the
libcgroup-tools package:
>sudocgset -r cpuset.mems=NODE sysdefault/libvirt/qemu/KVM_NAME/emulator
To migrate pages to a node, use the migratepages
tool:
> migratepages PID FROM-NODE TO-NODE
To check everything is fine. use: cat
/proc/PID/status | grep Cpus.
For more information see Kernel NUMA memory policy and cpusets memory policy. Check also the Libvirt NUMA Tuning documentation.
4.6.3 VM Guest: NUMA related configuration #
libvirt allows to set up virtual NUMA and memory access policies.
Configuring these settings is not supported by
virt-install or virt-manager
and needs to be done manually by editing the VM Guest configuration
file with virsh edit.
4.6.3.1 VM Guest virtual NUMA topology #
Creating a VM Guest virtual NUMA (vNUMA) policy that resembles the
host NUMA topology can often increase performance of traditional
large, scale-up workloads. VM Guest vNUMA topology can be
specified using the numa element in the XML
configuration:
<cpu>
...
<numa>
<cell1 id="0"2 cpus='0-1'3 memory='512000' unit='KiB'/>
<cell id="1" cpus='2-3' memory='256000'4
unit='KiB'5 memAccess='shared'6/>
</numa>
...
</cpu>
Each | |
All cells should have an | |
The CPU or range of CPUs that are part of the node | |
The node memory | |
Units in which node memory is specified | |
Optional attribute which can control whether the memory is to
be mapped as |
To find where the VM Guest has allocated its pages. use:
cat
/proc/PID/numa_maps and
cat
/sys/fs/cgroup/memory/sysdefault/libvirt/qemu/KVM_NAME/memory.numa_stat.
The libvirt VM Guest NUMA specification is currently only
available for QEMU/KVM.
4.6.3.2 Memory allocation control with libvirt #
If the VM Guest has a vNUMA topology (see
Section 4.6.3.1, “VM Guest virtual NUMA topology”), memory
can be pinned to host NUMA nodes using the
numatune element. This method is currently only
available for QEMU/KVM guests. See
Important: Non-vNUMA VM Guest
for how to configure non-vNUMA VM Guests.
<numatune>
<memory mode="strict"1 nodeset="1-4,^3"2/>
<memnode3 cellid="0"4 mode="strict" nodeset="1"/>
<memnode cellid="2" placement="strict"5 mode="preferred" nodeset="2"/>
</numatune>
Policies available are: | |
Specify the NUMA nodes. | |
Specify memory allocation policies for each guest NUMA node (if
this element is not defined then this will fall back and use
the | |
Addresses the guest NUMA node for which the settings are applied. | |
The placement attribute can be used to indicate the memory
placement mode for a domain process, the value can be
|
On a non-vNUMA VM Guest, pinning memory to host NUMA nodes is done like in the following example:
<numatune> <memory mode="strict" nodeset="0-1"/> </numatune>
In this example, memory is allocated from the host nodes
0 and 1. In case these
memory requirements cannot be fulfilled, starting the VM Guest
will fail. virt-install also supports this
configuration with the --numatune option.
You should avoid allocating VM Guest memory across NUMA nodes, and prevent virtual CPUs from floating across NUMA nodes.
5 VM Guest images #
Images are virtual disks used to store the operating system and data of
VM Guests. They can be created, maintained and queried with the
qemu-img command. Refer to
Section 34.2.2, “Creating, converting, and checking disk images” for more
information on the qemu-img tool and examples.
5.1 VM Guest image formats #
Certain storage formats which QEMU recognizes have their origins in
other virtualization technologies. By recognizing these formats, QEMU
can leverage either data stores or entire guests that were originally
targeted to run under these other virtualization technologies. Some
formats are supported only in read-only mode. To use them in read/write
mode, convert them to a fully supported QEMU storage format (using
qemu-img). Otherwise they can only be used as
read-only data store in a QEMU guest.
Use qemu-img info
VMGUEST.IMG to get information
about an existing image, such as: the format, the virtual size, the
physical size, snapshots if available.
It is recommended to convert the disk images to either raw or qcow2 to achieve good performance.
When you create an image, you cannot use compression
(-c) in the output file together with the encryption
option (-e).
5.1.1 Raw format #
This format is simple and easily exportable to all other emulators/hypervisors.
It provides best performance (least I/O overhead).
It occupies all allocated space on the file system.
The raw format allows to copy a VM Guest image to a physical device (
dd if=VMGUEST.RAW of=/dev/sda).It is byte-for-byte the same as what the VM Guest sees, so this wastes a lot of space.
5.1.2 qcow2 format #
Use this to have smaller images (useful if your file system does not supports holes).
It has optional AES encryption (now deprecated).
Zlib-based compression option.
Support of multiple VM snapshots (internal, external).
Improved performance and stability.
Supports changing the backing file.
Supports consistency checks.
Less performance than raw format.
- l2-cache-size
qcow2 can provide the same performance for random read/write access as raw format, but it needs a well-sized cache size. By default cache size is set to 1 MB. This will give good performance up to a disk size of 8 GB. If you need a bigger disk size, you need to adjust the cache size. For a disk size of 64 GB (64*1024 = 65536), you need 65536 / 8192B = 8 MB of cache (
-drive format=qcow2,l2-cache-size=8M).- Cluster size
The qcow2 format offers the capability to change the cluster size. The value must be between 512 KB and 2 MB. Smaller cluster sizes can improve the image file size whereas larger cluster sizes generally provide better performance.
- Preallocation
An image with preallocated metadata is initially larger but can improve performance when the image needs to grow.
- Lazy refcounts
Reference count updates are postponed with the goal of avoiding metadata I/O and improving performance. This is particularly beneficial with
cache=writethrough. This option does not batch metadata updates, but if in case of host crash, the reference count tables must be rebuilt, this is done automatically at the next open withqemu-img check -r all. Note that this takes some time.
5.1.3 qed format #
qed is a follow-on qcow (QEMU Copy On Write) format. Because qcow2 provides all the benefits of qed and more, qed is now deprecated.
5.1.4 VMDK format #
VMware 3, 4, or 6 image format, for exchanging images with that product.
5.2 Overlay disk images #
The qcow2 and qed formats provide a way to create a base image (also
called backing file) and overlay images on top of the base image. A
backing file is useful to be able to revert to a known state and
discard the overlay. If you write to the image, the backing image will
be untouched and all changes will be recorded in the overlay image
file. The backing file will never be modified unless you use the
commit monitor command (or qemu-img
commit).
To create an overlay image:
# qemu-img create -o1backing_file=vmguest.raw2,backing_fmt=raw3\
-f4 qcow2 vmguest.cow5
Use | |
The backing file name. | |
Specify the file format for the backing file. | |
Specify the image format for the VM Guest. | |
Image name of the VM Guest, it will only record the differences from the backing file. |
You should not change the path to the backing image, otherwise you
will need to adjust it. The path is stored in the overlay image file.
To update the path, you should make a symbolic link from the original
path to the new path and then use the qemu-img
rebase option.
#ln -sf /var/lib/images/OLD_PATH/vmguest.raw \ /var/lib/images/NEW_PATH/vmguest.raw#qemu-img rebase1 -u2 -b3 \ /var/lib/images/OLD_PATH/vmguest.raw /var/lib/images/NEW_PATH/vmguest.cow
The | |
The
| |
The backing image to be used is specified with
|
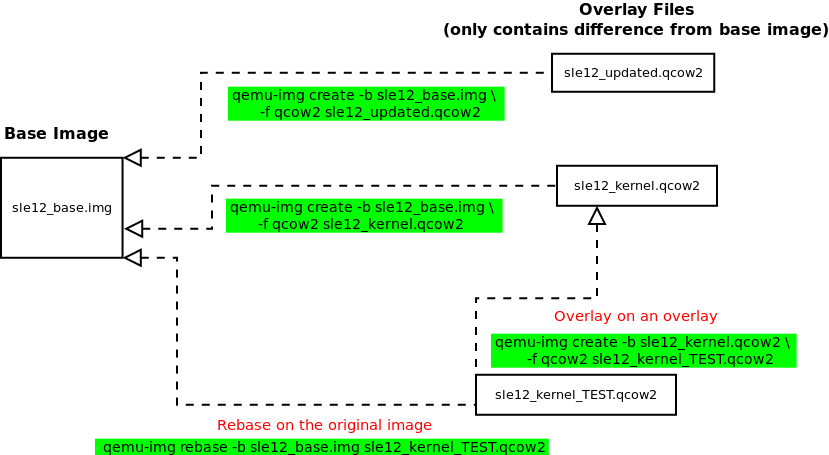
A common use is to initiate a new guest with the backing file. Let's
assume we have a sle15_base.img VM Guest ready to
be used (fresh installation without any modification). This will be our
backing file. Now you need to test a new package, on an updated system
and on a system with a different kernel. We can use
sle15_base.img to instantiate the new SUSE Linux Enterprise
VM Guest by creating a qcow2 overlay file pointing to this backing
file (sle15_base.img).
In our example we will use sle15_updated.qcow2 for
the updated system, and sle15_kernel.qcow2 for the
system with a different kernel.
To create the two thin provisioned systems use the
qemu-img command line with the -b
option:
#qemu-img create -b /var/lib/libvirt/sle15_base.img -f qcow2 \ /var/lib/libvirt/sle15_updated.qcow2 Formatting 'sle15_updated.qcow2', fmt=qcow2 size=17179869184 backing_file='sle15_base.img' encryption=off cluster_size=65536 lazy_refcounts=off nocow=off#qemu-img create -b /var/lib/libvirt/sle15_base.img -f qcow2 \ /var/lib/libvirt/sle15_kernel.qcow2 Formatting 'sle15_kernel.qcow2', fmt=qcow2 size=17179869184 backing_file='vmguest-sle15_base.img' encryption=off cluster_size=65536 lazy_refcounts=off nocow=off
The images are now usable, and you can do your test without touching
the initial sle15_base.img backing file. All
changes will be stored in the new overlay images. Additionally, you can
also use these new images as a backing file, and create a new overlay.
# qemu-img create -b sle15_kernel.qcow2 -f qcow2 sle15_kernel_TEST.qcow2
When using qemu-img info with the option
--backing-chain, it will return all information about
the entire backing chain recursively:
# qemu-img info --backing-chain
/var/lib/libvirt/images/sle15_kernel_TEST.qcow2
image: sle15_kernel_TEST.qcow2
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 16G (17179869184 bytes)
disk size: 196K
cluster_size: 65536
backing file: sle15_kernel.qcow2
Format specific information:
compat: 1.1
lazy refcounts: false
image: sle15_kernel.qcow2
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 16G (17179869184 bytes)
disk size: 196K
cluster_size: 65536
backing file: SLE15.qcow2
Format specific information:
compat: 1.1
lazy refcounts: false
image: sle15_base.img
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 16G (17179869184 bytes)
disk size: 16G
cluster_size: 65536
Format specific information:
compat: 1.1
lazy refcounts: true5.3 Opening a VM Guest image #
To access the file system of an image, use the guestfs-tools. If you do not have this tool installed on your system you can mount an image with other Linux tools. Avoid accessing an untrusted or unknown VM Guest's image system because this can lead to security issues (for more information, read D. Berrangé's post).
5.3.1 Opening a raw image #
To be able to mount the image, find a free loop device. The following command displays the first unused loop device,
/dev/loop1in this example.#losetup -f /dev/loop1Associate an image (
SLE15.rawin this example) with the loop device:#losetup /dev/loop1 SLE15.rawCheck whether the image has successfully been associated with the loop device by getting detailed information about the loop device:
#losetup -l NAME SIZELIMIT OFFSET AUTOCLEAR RO BACK-FILE /dev/loop1 0 0 0 0 /var/lib/libvirt/images/SLE15.rawCheck the image's partitions with
kpartx:#kpartx -a1 -v2 /dev/loop1 add map loop1p1 (254:1): 0 29358080 linear /dev/loop1 2048Now mount the image partition(s) (to
/mnt/sle15mountin the following example):#mkdir /mnt/sle15mount#mount /dev/mapper/loop1p1 /mnt/sle15mount
If your raw image contains an LVM volume group you should use LVM tools to mount the partition. Refer to Section 5.3.3, “Opening images containing LVM”.
Unmount all mounted partitions of the image, for example:
#umount /mnt/sle15mountDelete partition device mappings with
kpartx:#kpartx -d /dev/loop1Detach the devices with
losetup#losetup -d /dev/loop1
5.3.2 Opening a qcow2 image #
First you need to load the
nbd(network block devices) module. The following example loads it with support for 16 block devices (max_part=16). Check withdmesgwhether the operation was successful:#modprobe nbd max_part=16#dmesg | grep nbd [89155.142425] nbd: registered device at major 43Connect the VM Guest image (for example
SLE15.qcow2) to an NBD device (/debv/nbd0in the following example) with theqemu-nbdcommand. Make sure to use a free NBD device:#qemu-nbd -c1 /dev/nbd02 SLE15.qcow23Tip: Checking for a free NBD deviceTo check whether an NBD device is free, run the following command:
#lsof /dev/nbd0 COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME qemu-nbd 15149 root 10u BLK 43,0 0t0 47347 /dev/nbd0If the command produces an output like in the example above, the device is busy (not free). This can also be confirmed by the presence of the
/sys/devices/virtual/block/nbd0/pidfile.Inform the operating system about partition table changes with
partprobe:#partprobe /dev/nbd0 -s /dev/nbd0: msdos partitions 1 2#dmesg | grep nbd0 | tail -1 [89699.082206] nbd0: p1 p2In the example above, the
SLE15.qcow2contains two partitions:/dev/nbd0p1and/dev/nbd0p2. Before mounting these partitions, usevgscanto check whether they belong to an LVM volume:#vgscan -v Wiping cache of LVM-capable devices Wiping internal VG cache Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while... Using volume group(s) on command line. No volume groups found.If no LVM volume has been found, you can mount the partition with
mount:#mkdir /mnt/nbd0p2 # mount /dev/nbd0p1 /mnt/nbd0p2Refer to Section 5.3.3, “Opening images containing LVM” for information on how to handle LVM volumes.
Unmount all mounted partitions of the image, for example:
#umount /mnt/nbd0p2Disconnect the image from the
/dev/nbd0device.#qemu-nbd -d /dev/nbd0
5.3.3 Opening images containing LVM #
If your VM Host Server uses VG name system, and the
guest image also uses VG name system, LVM will
complain during its activation. A workaround is to temporarily
rename the guest VG, while a correct approach is to use different
VG names for the guests than for the VM Host Server.
To check images for LVM groups, use
vgscan -v. If an image contains LVM groups, the output of the command looks like the following:#vgscan -v Wiping cache of LVM-capable devices Wiping internal VG cache Reading all physical volumes. This may take a while... Finding all volume groups Finding volume group "system" Found volume group "system" using metadata type lvm2The
systemLVM volume group has been found on the system. You can get more information about this volume withvgdisplay VOLUMEGROUPNAME(in our case VOLUMEGROUPNAME issystem). You should activate this volume group to expose LVM partitions as devices so the system can mount them. Usevgchange:#vgchange -ay -v Finding all volume groups Finding volume group "system" Found volume group "system" activation/volume_list configuration setting not defined: Checking only host tags for system/home Creating system-home Loading system-home table (254:0) Resuming system-home (254:0) Found volume group "system" activation/volume_list configuration setting not defined: Checking only host tags for system/root Creating system-root Loading system-root table (254:1) Resuming system-root (254:1) Found volume group "system" activation/volume_list configuration setting not defined: Checking only host tags for system/swap Creating system-swap Loading system-swap table (254:2) Resuming system-swap (254:2) Activated 3 logical volumes in volume group system 3 logical volume(s) in volume group "system" now activeAll partitions in the volume group will be listed in the
/dev/mapperdirectory. You can simply mount them now.#ls /dev/mapper/system-* /dev/mapper/system-home /dev/mapper/system-root /dev/mapper/system-swap#mkdir /mnt/system-root#mount /dev/mapper/system-root /mnt/system-root#ls /mnt/system-root/ bin dev home lib64 mnt proc root sbin srv tmp var boot etc lib lost+found opt read-write run selinux sys usr
Unmount all partitions (with
umount)#umount /mnt/system-rootDeactivate the LVM volume group (with
vgchange -an VOLUMEGROUPNAME)#vgchange -an -v system Using volume group(s) on command line Finding volume group "system" Found volume group "system" Removing system-home (254:0) Found volume group "system" Removing system-root (254:1) Found volume group "system" Removing system-swap (254:2) Deactivated 3 logical volumes in volume group system 0 logical volume(s) in volume group "system" now activeNow you have two choices:
Important: Check for a successful unmountYou should double-check that unmounting succeeded by using a system command like
losetup,qemu-nbd,mountorvgscan. If this is not the case you may have trouble using the VM Guest because its system image is used in different places.
6 VM Guest configuration #
6.1 Virtio driver #
To increase VM Guest performance it is recommended to use
paravirtualized drivers within the VM Guests. The virtualization
standard for such drivers for KVM are the virtio
drivers, which are designed for running in a virtual environment. Xen
uses similar paravirtualized device drivers (like
VMDP
in a Windows* guest).
6.1.1 virtio blk #
virtio_blk is the virtio block device for disk. To
use the virtio blk driver for a block device,
specify the bus='virtio' attribute in
the disk definition:
<disk type='....' device='disk'>
....
<target dev='vda' bus='virtio'/>
</disk>
virtio disk devices are named
/dev/vd[a-z][1-9]. If you migrate a Linux guest
from a non-virtio disk you need to adjust the
root= parameter in the GRUB configuration, and
regenerate the initrd file. Otherwise the
system cannot boot. On VM Guests with other operating systems, the
boot loader may need to be adjusted or reinstalled accordingly,
too.
virtio disks with qemu-system-ARCH
When running qemu-system-ARCH, use the
-drive option to add a disk to the VM Guest. See
Section 34.1, “Basic installation with qemu-system-ARCH” for an example. The
-hd[abcd] option will not work for virtio disks.
6.1.2 virtio net #
virtio_net is the virtio network device. The
kernel modules should be loaded automatically in the guest at boot
time. You need to start the service to make the network available.
<interface type='network'>
...
<model type='virtio' />
</interface>6.1.3 virtio balloon #
The virtio balloon is used for host memory over-commits for guests.
For Linux guests, the balloon driver runs in the guest kernel,
whereas for Windows guests, the balloon driver is in the VMDP
package. virtio_balloon is a PV driver to give or
take memory from a VM Guest.
Inflate balloon: Return memory from guest to host kernel (for KVM) or to hypervisor (for Xen)
Deflate balloon: Guest will have more available memory
It is controlled by the currentMemory and
memory options.
<memory unit='KiB'>16777216</memory>
<currentMemory unit='KiB'>1048576</currentMemory>
[...]
<devices>
<memballoon model='virtio'/>
</devices>
You can also use virsh to change it:
> virsh setmem DOMAIN_ID MEMORY in KB6.1.4 Checking virtio presence #
You can check the virtio block PCI with:
> find /sys/devices/ -name virtio*
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:06.0/virtio0
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/virtio1
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.0/virtio2
To find the block device associated with vdX:
> find /sys/devices/ -name virtio* -print -exec ls {}/block 2>/dev/null \;
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:06.0/virtio0
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/virtio1
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.0/virtio2
vdaTo get more information on the virtio block:
> udevadm info -p /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.0/virtio2
P: /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.0/virtio2
E: DEVPATH=/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.0/virtio2
E: DRIVER=virtio_blk
E: MODALIAS=virtio:d00000002v00001AF4
E: SUBSYSTEM=virtioTo check all virtio drivers being used:
> find /sys/devices/ -name virtio* -print -exec ls -l {}/driver 2>/dev/null \;
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:06.0/virtio0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jun 17 15:48 /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:06.0/virtio0/driver -> ../../../../bus/virtio/drivers/virtio_console
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/virtio1
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jun 17 15:47 /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:07.0/virtio1/driver -> ../../../../bus/virtio/drivers/virtio_balloon
/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.0/virtio2
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jun 17 14:35 /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:08.0/virtio2/driver -> ../../../../bus/virtio/drivers/virtio_blk6.1.5 Find device driver options #
Virtio devices and other drivers have various options. To list all of
them, use the help parameter of
theqemu-system-ARCH command.
> qemu-system-x86_64 -device virtio-net,help
virtio-net-pci.ioeventfd=on/off
virtio-net-pci.vectors=uint32
virtio-net-pci.indirect_desc=on/off
virtio-net-pci.event_idx=on/off
virtio-net-pci.any_layout=on/off
.....6.2 Cirrus video driver #
To get 16-bit color, high compatibility and better performance it is
recommended to use the cirrus video driver.
libvirt
libvirt ignores the vram value because video
size has been hardcoded in QEMU.
<video> <model type='cirrus' vram='9216' heads='1'/> </video>
6.3 Better entropy #
Virtio RNG (random number generator) is a paravirtualized device that
is exposed as a hardware RNG device to the guest. On the host side, it
can be wired up to one of several sources of entropy (including a real
hardware RNG device and the host's /dev/random) if
hardware support does not exist. The Linux kernel contains the guest
driver for the device from version 2.6.26 and higher.
The system entropy is collected from various non-deterministic hardware events and is mainly used by cryptographic applications. The virtual random number generator device (paravirtualized device) allows the host to pass through entropy to VM Guest operating systems. This results in a better entropy in the VM Guest.
To use Virtio RNG, add an RNG device in
virt-manager or directly in the VM Guest's XML
configuration:
<devices>
<rng model='virtio'>
<backend model='random'>/dev/random</backend>
</rng>
</devices>
The host now should used /dev/random:
> lsof /dev/random
qemu-syst 4926 qemu 6r CHR 1,8 0t0 8199 /dev/randomOn the VM Guest, the source of entropy can be checked with:
> cat /sys/devices/virtual/misc/hw_random/rng_availableThe current device used for entropy can be checked with:
> cat /sys/devices/virtual/misc/hw_random/rng_current
virtio_rng.0You should install the rng-tools package on the VM Guest, enable the service, and start it. Under SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 15, do the following:
#zypper in rng-tools#systemctl enable rng-tools#systemctl start rng-tools
6.4 Disable unused tools and devices #
Per host, use one virtualization technology only. For example, do not use KVM and Xen on the same host. Otherwise, you may find yourself with a reduced amount of available resources, increased security risk and a longer software update queue. Even when the amount of resources allocated to each of the technologies is configured carefully, the host may suffer from reduced overall availability and degraded performance.
Minimize the amount of software and services available on hosts. Most default installations of operating systems are not optimized for VM usage. Install what you really need and remove all other components in the VM Guest.
Windows* Guest:
Disable the screen saver
Remove all graphical effects
Disable indexing of hard disks if not necessary
Check the list of started services and disable the ones you do not need
Check and remove all unneeded devices
Disable system update if not needed, or configure it to avoid any delay while rebooting or shutting down the host
Check the Firewall rules
Schedule backups and anti-virus updates appropriately
Install the VMDP paravirtualized driver for best performance
Check the operating system recommendations, such as on the Microsoft Windows* 7 better performance Web page.
Linux Guest:
Remove or do not start the X Window System if not necessary
Check the list of started services and disable the ones you do not need
Check the OS recommendations for kernel parameters that enable better performance
Only install software that you really need
Optimize the scheduling of predictable tasks (system updates, hard disk checks, etc.)
6.5 Updating the guest machine type #
QEMU machine types define details of the architecture that are particularly relevant for migration and session management. As changes or improvements to QEMU are made, new machine types are added. Old machine types are still supported for compatibility reasons, but to take advantage of improvements, we recommend to always migrate to the latest machine type when upgrading.
Changing the guest's machine type for a Linux guest will mostly be transparent. For Windows* guests, we recommend to take a snapshot or backup of the guest—in case Windows* has issues with the changes it detects and subsequently the user decides to revert to the original machine type the guest was created with.
Refer to Section 15.2, “Changing the machine type” for documentation.
7 VM Guest-specific configurations and settings #
This section applies to QEMU / KVM hypervisor only.
7.1 ACPI testing #
The ability to change a VM Guest's state heavily depends on the operating system. It is very important to test this feature before any use of your VM Guests in production. For example, most Linux operating systems disable this capability by default, so this requires you to enable this operation (mostly through Polkit).
ACPI must be enabled in the guest for a graceful shutdown to work. To check if ACPI is enabled, run:
> virsh dumpxml VMNAME | grep acpi
If nothing is printed, ACPI is not enabled for your machine. Use
virsh edit to add the following XML under
<domain>:
<features> <acpi/> </features>
If ACPI was enabled during a Windows Server* guest installation, it is not sufficient to turn it on in the VM Guest configuration only. For more information, see https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/309283.
Regardless of the VM Guest's configuration, a graceful shutdown is always possible from within the guest operating system.
7.2 Keyboard layout #
Though it is possible to specify the keyboard layout from a
qemu-system-ARCH command, it is recommended to
configure it in the libvirt XML file. To change the keyboard layout
while connecting to a remote VM Guest using vnc, you should edit the
VM Guest XML configuration file. For example, to add an
en-us keymap, add in the
<devices> section:
<graphics type='vnc' port='-1' autoport='yes' keymap='en-us'/>
Check the vncdisplay configuration and connect to
your VM Guest:
> virsh vncdisplay sles15 127.0.0.1:07.3 Spice default listen URL #
If no network interface other than lo is assigned an
IPv4 address on the host, the default address on which the spice server
listens will not work. An error like the following one will occur:
> virsh start sles15
error: Failed to start domain sles15
error: internal error: process exited while connecting to monitor: ((null):26929): Spice-Warning **: reds.c:2330:reds_init_socket: getaddrinfo(127.0.0.1,5900): Address family for hostname not supported
2015-08-12T11:21:14.221634Z qemu-system-x86_64: failed to initialize spice server
To fix this, you can change the default spice_listen
value in /etc/libvirt/qemu.conf using the local
IPv6 address ::1. The spice
server listening address can also be changed on a per VM Guest basis,
use virsh edit to add the listen XML attribute to
the graphics type='spice' element:
<graphics type='spice' listen='::1' autoport='yes'/>>
7.4 XML to QEMU command line #
Sometimes it could be useful to get the QEMU command line to launch the VM Guest from the XML file.
> virsh domxml-to-native1 qemu-argv2 SLE15.xml3Convert the XML file in domain XML format to the native guest configuration | |
For the QEMU/KVM hypervisor, the format argument needs to be qemu-argv | |
Domain XML file to use |
>sudovirsh domxml-to-native qemu-argv /etc/libvirt/qemu/SLE15.xml LC_ALL=C PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin \ QEMU_AUDIO_DRV=none /usr/bin/qemu-system-x86_64 -name SLE15 -machine \ pc-i440fx-2.3,accel=kvm,usb=off -cpu SandyBridge -m 4048 -realtime \ mlock=off -smp 4,sockets=4,cores=1,threads=1 -uuid 8616d00f-5f05-4244-97cc-86aeaed8aea7 \ -no-user-config -nodefaults -chardev socket,id=charmonitor,path=/var/lib/libvirt/qemu/SLE15.monitor,server,nowait \ -mon chardev=charmonitor,id=monitor,mode=control -rtc base=utc,driftfix=slew \ -global kvm-pit.lost_tick_policy=discard -no-hpet \ -no-shutdown -global PIIX4_PM.disable_s3=1 -global PIIX4_PM.disable_s4=1 \ -boot strict=on -device ich9-usb-ehci1,id=usb,bus=pci.0,addr=0x4.0x7 \ -device ich9-usb-uhci1,masterbus=usb.0,firstport=0,bus=pci.0,multifunction=on,addr=0x4 \ -device ich9-usb-uhci2,masterbus=usb.0,firstport=2,bus=pci.0,addr=0x4.0x1 \ -device ich9-usb-uhci3,masterbus=usb.0,firstport=4,bus=pci.0,addr=0x4.0x2 \ -drive file=/var/lib/libvirt/images/SLE15.qcow2,if=none,id=drive-virtio-disk0,format=qcow2,cache=none \ -device virtio-blk-pci,scsi=off,bus=pci.0,addr=0x6,drive=drive-virtio-disk0,id=virtio-disk0,bootindex=2 \ -drive if=none,id=drive-ide0-0-1,readonly=on,format=raw \ -device ide-cd,bus=ide.0,unit=1,drive=drive-ide0-0-1,id=ide0-0-1 -netdev tap,id=hostnet0 \ -device virtio-net-pci,netdev=hostnet0,id=net0,mac=52:54:00:28:04:a9,bus=pci.0,addr=0x3,bootindex=1 \ -chardev pty,id=charserial0 -device isa-serial,chardev=charserial0,id=serial0 \ -vnc 127.0.0.1:0 -device cirrus-vga,id=video0,bus=pci.0,addr=0x2 \ -device virtio-balloon-pci,id=balloon0,bus=pci.0,addr=0x5 -msg timestamp=on
7.5 Change kernel parameters at boot time #
7.5.1 SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 #
To change the value for SLE 11 products at boot time, you need to
modify your /boot/grub/menu.lst file by adding
the OPTION=parameter. Then reboot your system.
7.5.2 SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 and 15 #
To change the value for SLE 12 and 15 products at boot time, you
need to modify your /etc/default/grub file. Find
the variable starting with
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT and add at the end
OPTION=parameter (or change it with the correct
value if it is already available).
Now you need to regenerate your grub2
configuration:
# grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
Then reboot your system.
7.6 Add a device to an XML configuration #
To create a new VM Guest based on an XML file, you can specify the
QEMU command line using the special tag
qemu:commandline. For example, to add a
virtio-balloon-pci, add this block at the end of the XML configuration
file (before the </domain> tag):
<qemu:commandline>
<qemu:arg value='-device'/>
<qemu:arg value='virtio-balloon-pci,id=balloon0'/>
</qemu:commandline>7.7 Adding and removing CPUs #
Some virtualization environments allow adding or removing CPUs while the virtual machine is running.
For the safe removal of CPUs, deactivate them first by executing
#echo 0 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuX/online
Replace X with the CPU number. To bring a CPU back online, execute
#echo 1 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuX/online
7.8 SCSI persistent reservation on a multipathed device #
SCSI persistent reservations allow restricting access to block devices in a shared storage setup. This avoids improper multiple parallel accesses to the same block device from software components on local or remote hosts, which could lead to device damage and data corruption.
Find more information on managing storage multipath I/O in 第18章 「デバイスのマルチパスI/Oの管理」. Find more information about SCSI persistent reservations in 18.4.6項 「mpathpersistユーティリティ」.
For the virtualization scenario, QEMU's SCSI passthrough devices
scsi-block and scsi-generic
support passing guest persistent reservation requests to a privileged
external helper program qemu-pr-helper. It needs to
start before QEMU and creates a listener socket that accepts incoming
connections for communication with QEMU.
We recommend using the multipath alias instead of
wwid. It is useful in the VM Guest live migration
scenario, because it makes sure that the storage paths are identical
between the source and destination hosts.
In the VM Host Server, create a multipath environment. For more information, refer to 18.5項 「マルチパス処理用システムの設定」 and 18.6項 「マルチパス設定」.
In the VM Host Server, configure the
<reservations/>sub-element of the<source/>element of the<disk/>element for the passed-through lun in yourlibvirtdomain configuration. Refer tolibvirtDomain XML format.In the VM Guest, install the sg3_utils package and reserve the SCSI disks on demand by the
sg_persistcommand.
In the VM Host Server, verify that the
multipathd.serviceis running, and that a multipathed disk exists and is named, for example,storage1.>sudosystemctl status multipathd.service ● multipathd.service - Device-Mapper Multipath Device Controller Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/multipathd.service; enabled; preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Sat 2023-08-26 21:34:13 CST; 1 week 1 day ago TriggeredBy: ○ multipathd.socket Main PID: 79411 (multipathd) Status: "up" Tasks: 7 CPU: 1min 43.514s CGroup: /system.slice/multipathd.service └─79411 /sbin/multipathd -d -s>sudomultipath -ll storage1 (36589cfc000000537c47ad3eb2b20216e) dm-6 TrueNAS,iSCSI Disk size=50G features='0' hwhandler='1 alua' wp=rw |-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=50 status=active | `- 16:0:0:0 sdg 8:96 active ready running `-+- policy='service-time 0' prio=50 status=enabled `- 17:0:0:0 sdh 8:112 active ready runningIn the VM Host Server, add a <disk/> element in the VM Guest configuration file by running
virsh edit.<disk type='block' device='lun'1> <driver name='qemu' type='raw'/> <source dev='/dev/mapper/storage1'> <reservations2 managed='yes'3/> </source> <target dev='sda' bus='scsi'/> <address type='drive' controller='0' bus='0' target='0' unit='0'4/> </disk>
To support persistent reservations, the disks must be marked as
lunwith typeblockso that QEMU does SCSI passthrough.If present, it enables persistent reservations for SCSI based disks. The element has one mandatory attribute
managedwith accepted valuesyesandno.If
managedisyes,libvirtprepares and manages any resources needed.When the value of the attribute
managedisno, then the hypervisor acts as a client and the path to the server socket must be provided in the child element source, which currently accepts only the following attributes:- type
The only valid option is
unix.- path
The path to the server socket.
- mode
The role of the hypervisor. Valid is
client.
Verify that the virtio-scsi HBA that the disk attaches already exists and has available units (the maximum count of units per virtio-scsi HBA is 7). Otherwise, you need to manually add a virtio-scsi HBA to avoid automatically adding the LSI HBA by
libvirt. For example:<controller type='scsi' index='0' model='virtio-scsi'> <address type='pci' domain='0x0000' bus='0x03' slot='0x00' function='0x0'/> </controller>
>sudovirsh domblklist sles15sp5 Target Source --------------------------------------------- vda /mnt/images/sles15sp5/disk0.qcow2 sda /dev/mapper/storage1In the VM Host Server, start the VM Guest.
libvirtlaunches a qemu-pr-helper instance as the server role for the VM Guest sles15sp5, then launches the VM Guest sles15sp5 as the client role.>sudovirsh start sles15sp5 Domain 'sles15sp5' started>sudovirsh list Id Name State --------------------------- 4 sles15sp5 running>sudops -eo pid,args | grep -v grep | grep qemu-pr-helper 37063 /usr/bin/qemu-pr-helper -k /var/lib/libvirt/qemu/domain-4-sles15sp5/pr-helper0.sock>sudovirsh dumpxml sles15sp5 | grep -A11 "<disk type='block' device='lun'> <disk type='block' device='lun'> <driver name='qemu' type='raw'/> <source dev='/dev/mapper/storage1' index='1'> <reservations managed='yes'> <source type='unix' path='/var/lib/libvirt/qemu/domain-4-sles15sp5/pr-helper0.sock' mode='client'/> </reservations> </source> <backingStore/> <target dev='sda' bus='scsi'/> <alias name='scsi0-0-0-0'/> <address type='drive' controller='0' bus='0' target='0' unit='0'/> </disk>In the VM Guest, reserve the scsi disk, for example,
sda, with the key123abc.>lsblk NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS sda 8:0 0 50G 0 disk vda 253:0 0 20G 0 disk ├─vda1 253:1 0 8M 0 part ├─vda2 253:2 0 2G 0 part [SWAP] └─vda3 253:3 0 18G 0 part />sudosg_persist --verbose --out --register --param-sark=123abc /dev/sda inquiry cdb: [12 00 00 00 24 00] TrueNAS iSCSI Disk 0123 Peripheral device type: disk Persistent reservation out cdb: [5f 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 18 00] PR out: command (Register) successful>sudosg_persist --verbose --in -k /dev/sda inquiry cdb: [12 00 00 00 24 00] TrueNAS iSCSI Disk 0123 Peripheral device type: disk Persistent reservation in cdb: [5e 00 00 00 00 00 00 20 00 00] PR generation=0x5, 2 registered reservation keys follow: 0x123abc 0x123abcIn the VM Guest, release the
sdadisk with the key123abc.>sudosg_persist --verbose --out --clear --param-rk=123abc /dev/sda inquiry cdb: [12 00 00 00 24 00] TrueNAS iSCSI Disk 0123 Peripheral device type: disk Persistent reservation out cdb: [5f 03 00 00 00 00 00 00 18 00] PR out: command (Clear) successful>sudosg_persist --verbose --in -k /dev/sda inquiry cdb: [12 00 00 00 24 00] TrueNAS iSCSI Disk 0123 Peripheral device type: disk Persistent reservation in cdb: [5e 00 00 00 00 00 00 20 00 00] PR generation=0x6, there are NO registered reservation keys