16 Masquerading and Firewalls #
Whenever Linux is used in a network environment, you can use the
kernel functions that allow the manipulation of network packets to
maintain a separation between internal and external network areas. The
Linux netfilter framework provides the means
to establish an effective firewall that keeps different networks
apart. Using iptables—a generic table structure for the
definition of rule sets—precisely controls the packets allowed to
pass a network interface. Such a packet filter can be set up using
SuSEfirewall2 and the corresponding YaST module.
16.1 Packet Filtering with iptables #
The components netfilter and
iptables are responsible for the filtering and
manipulation of network packets and for network address
translation (NAT). The filtering criteria and any actions associated with
them are stored in chains, which must be matched one after another by
individual network packets as they arrive. The chains to match are stored
in tables. The iptables command allows you to alter
these tables and rule sets.
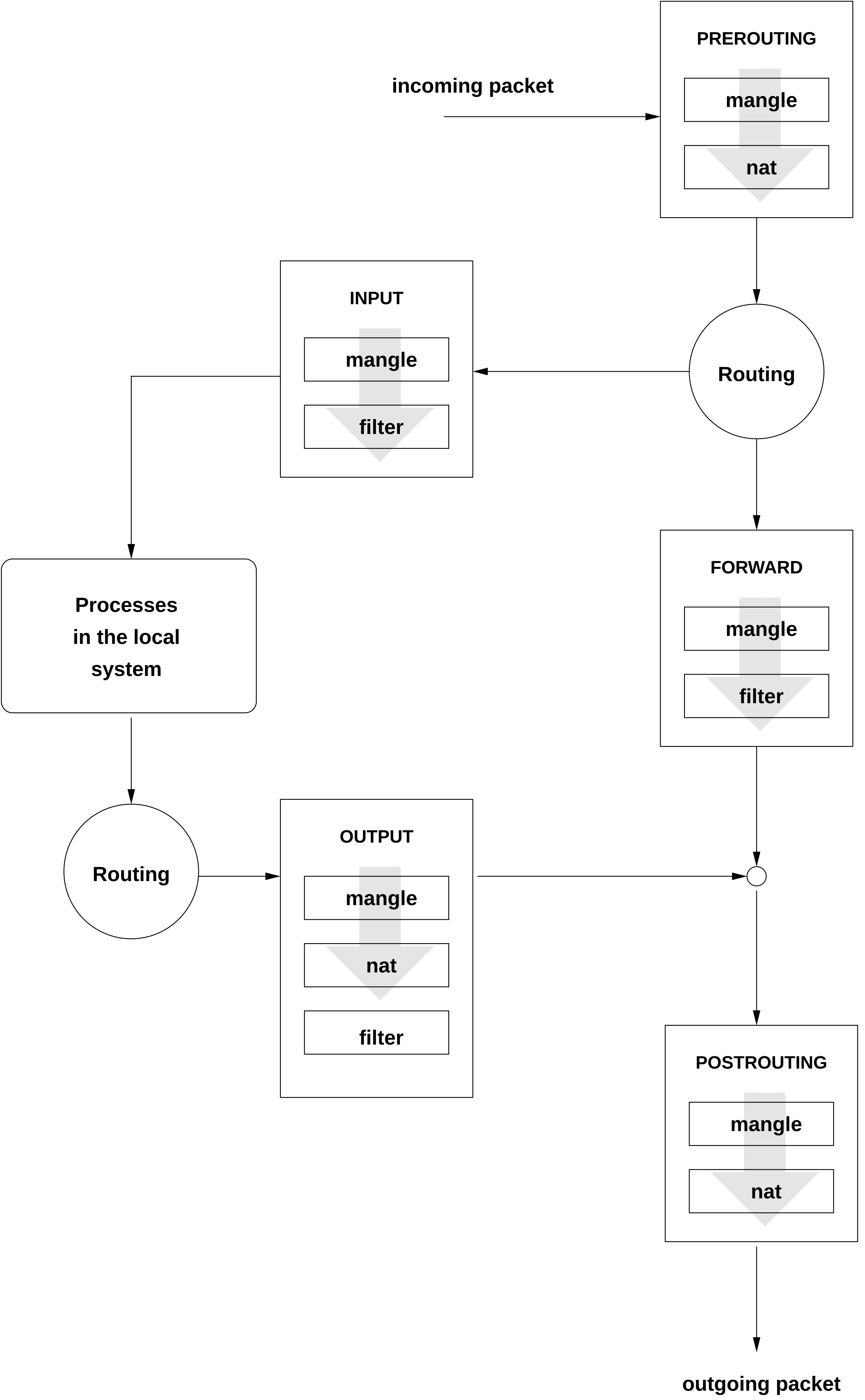
The Linux kernel maintains three tables, each for a particular category of functions of the packet filter:
- filter
This table holds the bulk of the filter rules, because it implements the packet filtering mechanism in the stricter sense, which determines whether packets are let through (
ACCEPT) or discarded (DROP), for example.- nat
This table defines any changes to the source and target addresses of packets. Using these functions also allows you to implement masquerading, which is a special case of NAT used to link a private network with the Internet.
- mangle
The rules held in this table make it possible to manipulate values stored in IP headers (such as the type of service).
These tables contain several predefined chains to match packets:
- PREROUTING
This chain is applied to incoming packets.
- INPUT
This chain is applied to packets destined for the system's internal processes.
- FORWARD
This chain is applied to packets that are only routed through the system.
- OUTPUT
This chain is applied to packets originating from the system itself.
- POSTROUTING
This chain is applied to all outgoing packets.
Figure 16.1, “iptables: A Packet's Possible Paths” illustrates the paths along which a network packet may travel on a given system. For the sake of simplicity, the figure lists tables as parts of chains, but in reality these chains are held within the tables themselves.
In the simplest case, an incoming packet destined for the system itself
arrives at the eth0 interface. The packet is first
referred to the PREROUTING chain of the
mangle table then to the PREROUTING
chain of the nat table. The following step, concerning
the routing of the packet, determines that the actual target of the
packet is a process of the system itself. After passing the
INPUT chains of the mangle and the
filter table, the packet finally reaches its target,
provided that the rules of the filter table are
actually matched.
16.2 Masquerading Basics #
Masquerading is the Linux-specific form of NAT (network address
translation) and can be used to connect a small LAN with the
Internet. LAN hosts use IP
addresses from the private range (see
Section 17.1.2, “Netmasks and Routing”) and on the Internet
official IP addresses are used. To be able to connect
to the Internet, a LAN host's private address is translated to an official
one. This is done on the router, which acts as the gateway between the
LAN and the Internet. The underlying principle is a simple one: The
router has more than one network interface, typically a network card and
a separate interface connecting with the Internet. While the latter links
the router with the outside world, one or several others link it with the
LAN hosts. With these hosts in the local network connected to the network
card (such as eth0) of the router, they can send any
packets not destined for the local network to their default gateway or
router.
When configuring your network, make sure both the broadcast address and the netmask are the same for all local hosts. Failing to do so prevents packets from being routed properly.
As mentioned, whenever one of the LAN hosts sends a packet destined for
an Internet address, it goes to the default router. However, the router
must be configured before it can forward such packets. For security
reasons, this is not enabled in a default installation. To enable it, set
the variable IP_FORWARD in the file
/etc/sysconfig/sysctl to
IP_FORWARD=yes.
The target host of the connection can see your router, but knows nothing about the host in your internal network where the packets originated. This is why the technique is called masquerading. Because of the address translation, the router is the first destination of any reply packets. The router must identify these incoming packets and translate their target addresses, so packets can be forwarded to the correct host in the local network.
With the routing of inbound traffic depending on the masquerading table, there is no way to open a connection to an internal host from the outside. For such a connection, there would be no entry in the table. In addition, any connection already established has a status entry assigned to it in the table, so the entry cannot be used by another connection.
As a consequence of all this, you might experience some problems with several application protocols, such as ICQ, cucme, IRC (DCC, CTCP), and FTP (in PORT mode). Web browsers, the standard FTP program, and many other programs use the PASV mode. This passive mode is much less problematic as far as packet filtering and masquerading are concerned.
16.3 Firewalling Basics #
Firewall is probably the term most widely used to describe a mechanism that provides and manages a link between networks while also controlling the data flow between them. Strictly speaking, the mechanism described in this section is called a packet filter. A packet filter regulates the data flow according to certain criteria, such as protocols, ports, and IP addresses. This allows you to block packets that, according to their addresses, are not supposed to reach your network. To allow public access to your Web server, for example, explicitly open the corresponding port. However, a packet filter does not scan the contents of packets with legitimate addresses, such as those directed to your Web server. For example, if incoming packets were intended to compromise a CGI program on your Web server, the packet filter would still let them through.
A more effective but more complex mechanism is the combination of several types of systems, such as a packet filter interacting with an application gateway or proxy. In this case, the packet filter rejects any packets destined for disabled ports. Only packets directed to the application gateway are accepted. This gateway or proxy pretends to be the actual client of the server. In a sense, such a proxy could be considered a masquerading host on the protocol level used by the application. One example for such a proxy is Squid, an HTTP and FTP proxy server. To use Squid, the browser must be configured to communicate via the proxy. Any HTTP pages or FTP files requested are served from the proxy cache and objects not found in the cache are fetched from the Internet by the proxy.
The following section focuses on the packet filter that comes with SUSE Linux Enterprise Server. For further information about packet filtering and firewalling, read the Firewall HOWTO.
16.4 SuSEfirewall2 #
SuSEfirewall2 is a script that reads the variables set in
/etc/sysconfig/SuSEfirewall2 to generate a
set of iptables rules. It defines three security zones, although only the
first and the second one are considered in the following sample
configuration:
Given that there is no way to control what is happening on the external network, the host needs to be protected from it. Usually, the external network is the Internet, but it could be another insecure network, such as a Wi-Fi.
This refers to the private network, usually the LAN. If the hosts on this network use IP addresses from the private range (see Section 17.1.2, “Netmasks and Routing”), enable network address translation (NAT), so hosts on the internal network can access the external one. All ports are open in the internal zone. The main benefit of putting interfaces into the internal zone (rather than stopping the firewall) is that the firewall still runs, so when you add new interfaces, they will be put into the external zone by default. That way an interface is not accidentally “open” by default.
While hosts located in this zone can be reached both from the external and the internal network, they cannot access the internal network themselves. This setup can be used to put an additional line of defense in front of the internal network, because the DMZ systems are isolated from the internal network.
By default, all network interfaces are set to no zone
assigned. This mode behaves as the External Zone profile.
Any kind of network traffic not explicitly allowed by the filtering rule set is suppressed by iptables. Therefore, each of the interfaces with incoming traffic must be placed into one of the three zones. For each of the zones, define the services or protocols allowed. The rule set is only applied to packets originating from remote hosts. Locally generated packets are not captured by the firewall.
The configuration can be performed with YaST (see
Section 16.4.1, “Configuring the Firewall with YaST”). It can also be made
manually in the file
/etc/sysconfig/SuSEfirewall2, which is well
commented. Additionally, several example scenarios are available in
/usr/share/doc/packages/SuSEfirewall2/EXAMPLES.
16.4.1 Configuring the Firewall with YaST #
16.4.1.1 Opening Ports #
In case your network interfaces are located in a firewall zone where network traffic is blocked on most ports, services that manage their network traffic via a blocked port will not work. For example, SSH is a popular service that uses port 22. By default, this port is blocked on interfaces located in the external or demilitarized zone. To make SSH work, you need to open port 22 in the firewall configuration. This can be done with the YaST module .
After the installation, YaST automatically starts a firewall on all configured interfaces. If a server is configured and activated on the system, YaST can modify the automatically generated firewall configuration with the options or in the server configuration modules. Some server module dialogs include a button for activating additional services and ports. The YaST firewall configuration module can be used to activate, deactivate, or reconfigure the firewall.
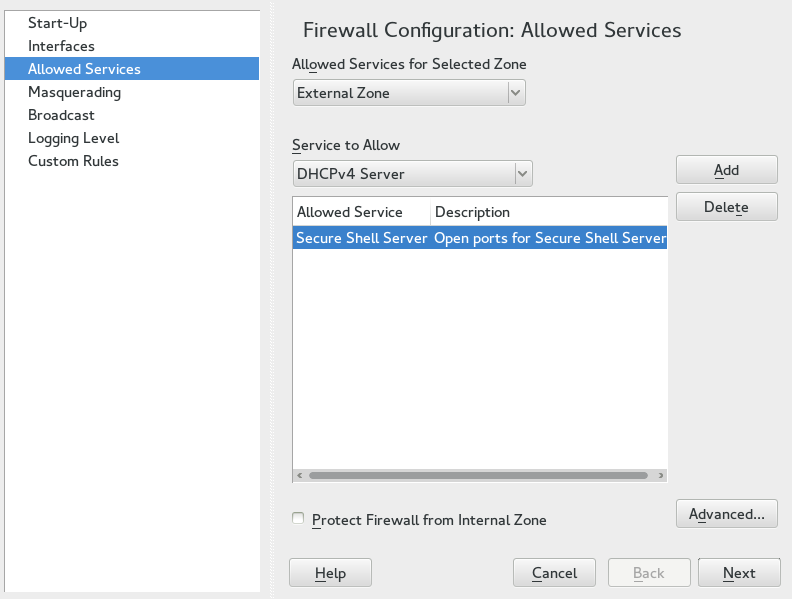
Open › › and switch to the tab.
Select a zone at in which to open the port. It is not possible to open a port for several zones at once.
Select a service from and choose to add it to the list of . The port this service uses will be unblocked.
In case your service is not listed, you need to manually specify the port(s) to unblock. Choose to open a dialog where you can specify TCP, UPD, RPC ports and IP protocols. Refer to the help section in this dialog for details.
Choose to display a summary of your changes. Modify them by choosing or apply them by choosing .
16.4.2 Configuring Manually #
The following paragraphs provide step-by-step instructions for a
successful configuration. Each configuration item is marked
whether it is relevant to firewalling or masquerading. Use port range
(for example, 500:510) whenever appropriate. Aspects
related to the DMZ (demilitarized zone) as mentioned in the
configuration file are not covered here. They are applicable only to a
more complex network infrastructure found in larger organizations
(corporate networks), which require extensive configuration and in-depth
knowledge about the subject.
To enable SuSEfirewall2, use sudo systemctl enable
SuSEfirewall2 or use the YaST module
Services Manager.
FW_DEV_EXT(firewall, masquerading)The device linked to the Internet. For a modem connection, enter
ppp0. DSL connections usedsl0. Specifyautoto use the interface that corresponds to the default route.FW_DEV_INT(firewall, masquerading)The device linked to the internal, private network (such as
eth0). Leave this blank if there is no internal network and the firewall protects only the host on which it runs.FW_ROUTE(firewall, masquerading)If you need the masquerading function, set this to
yes. Your internal hosts will not be visible to the outside, because their private network addresses (for example192.168.x.x) are ignored by Internet routers.For a firewall without masquerading, set this to
yesif you want to allow access to the internal network. Your internal hosts need to use officially registered IP addresses in this case. Normally, however, you should not allow access to your internal network from the outside.FW_MASQUERADE(masquerading)Set this to
yesif you need the masquerading function. This provides a virtually direct connection to the Internet for the internal hosts. It is more secure to have a proxy server between the hosts of the internal network and the Internet. Masquerading is not needed for services that a proxy server provides.FW_MASQ_NETS(masquerading)Specify the hosts or networks to masquerade, leaving a space between the individual entries. For example:
FW_MASQ_NETS="192.168.0.0/24 192.168.10.1"
FW_PROTECT_FROM_INT(firewall)Set this to
yesto protect your firewall host from attacks originating in your internal network. Services are only available to the internal network if explicitly enabled. Also seeFW_SERVICES_INT_TCPandFW_SERVICES_INT_UDP.FW_SERVICES_EXT_TCP(firewall)Enter the TCP ports that should be made available. Leave this blank for a normal workstation at home that should not offer any services.
FW_SERVICES_EXT_UDP(firewall)Leave this blank unless you run a UDP service and want to make it available to the outside. The services that use UDP include DNS servers, IPsec, TFTP, DHCP and others. In that case, enter the UDP ports to use.
FW_SERVICES_ACCEPT_EXT(firewall)List services to allow from the Internet. This is a more generic form of the
FW_SERVICES_EXT_TCPandFW_SERVICES_EXT_UDPsettings, and more specific thanFW_TRUSTED_NETS. The notation is a space-separated list ofNET,PROTOCOL[,DPORT][,SPORT], for example0/0,tcp,22or0/0,tcp,22,,hitcount=3,blockseconds=60,recentname=ssh, which means: allow a maximum of three SSH connects per minute from one IP address.FW_SERVICES_INT_TCP(firewall)With this variable, define the services available for the internal network. The notation is the same as for
FW_SERVICES_EXT_TCP, but the settings are applied to the internal network. The variable only needs to be set ifFW_PROTECT_FROM_INTis set toyes.FW_SERVICES_INT_UDP(firewall)See
FW_SERVICES_INT_TCP.FW_SERVICES_ACCEPT_INT(firewall)List services to allow from internal hosts. See
FW_SERVICES_ACCEPT_EXT.FW_SERVICES_ACCEPT_RELATED_*(firewall)This is how the SuSEfirewall2 implementation considers packets
RELATEDby netfilter.For example, to allow finer grained filtering of Samba broadcast packets,
RELATEDpackets are not accepted unconditionally. Variables starting withFW_SERVICES_ACCEPT_RELATED_allow restrictingRELATEDpackets handling to certain networks, protocols and ports.This means that adding connection tracking modules (conntrack modules) to
FW_LOAD_MODULESdoes not automatically result in accepting the packets tagged by those modules. Additionally, you must set variables starting withFW_SERVICES_ACCEPT_RELATED_to a suitable value.FW_CUSTOMRULES(firewall)Uncomment this variable to install custom rules. Find examples in
/etc/sysconfig/scripts/SuSEfirewall2-custom.
After configuring the firewall, test your setup. The
firewall rule sets are created by entering systemctl start
SuSEfirewall2 as
root. Then use
telnet, for example, from an external host to see
whether the connection is actually denied. After that, review the output
of journalctl (see Chapter 16, journalctl: Query the systemd Journal),
where you should see something like this:
Mar 15 13:21:38 linux kernel: SFW2-INext-DROP-DEFLT IN=eth0 OUT= MAC=00:80:c8:94:c3:e7:00:a0:c9:4d:27:56:08:00 SRC=192.168.10.0 DST=192.168.10.1 LEN=60 TOS=0x10 PREC=0x00 TTL=64 ID=15330 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=48091 DPT=23 WINDOW=5840 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0 OPT (020405B40402080A061AFEBC0000000001030300)
Other packages to test your firewall setup are Nmap (portscanner) or
OpenVAS (Open Vulnerability Assessment System). The documentation of
Nmap is found at /usr/share/doc/packages/nmap after
installing the package and the documentation of openVAS resides at
http://www.openvas.org.
16.5 For More Information #
The most up-to-date information and other documentation about the
SuSEfirewall2 package is found in
/usr/share/doc/packages/SuSEfirewall2. The
home page of the netfilter and iptables project,
http://www.netfilter.org, provides a large
collection of documents in many languages.