8 SMT Tools and Configuration Files #
This chapter describes the most important scripts, configuration files and certificates shipped with SMT.
8.1 Important Scripts and Tools #
There are two important groups of SMT commands: The
smt command and its sub-commands are used for managing
the mirroring of updates, registration of clients, and reporting. The
systemd smt.target is used for starting,
stopping, restarting the SMT service and services that SMT depends on,
and for checking their status.
8.1.1 SMT JobQueue #
Since SUSE Linux Enterprise version 11, there is a new SMT service called SMT JobQueue for delegating jobs to the registered clients.
To enable JobQueue, the smt-client package needs
to be installed on the SMT client. The client then pulls jobs from the
server via a cron job (every 3 hours by default). The list of jobs is
maintained on the server. Jobs are not pushed directly to the clients and
processed immediately: instead, the client asks for them. Therefore, a
delay of several hours may occur.
Every job can have its parent job, which sets a dependency. The child job
only runs after the parent job successfully finished. Job timing is also
possible: a job can have a start time and an expiration time to define
its earliest execution time or the time the job expires. A job may also
be persistent. It is run repeatedly with a delay. For example, a patch
status job is a persistent job that runs once a day. For each client, a
patch status job is automatically generated after it registers
successfully against an SMT 11 server. The
patchstatus information can be queried with the
smt-client command. For already registered clients,
you can add patchstatus jobs manually with the
smt-job command.
You can edit, list, create and delete the jobs using the
smt-job command-line tool. For more details on
smt-job, see Section 8.1.2.3, “smt-job”.
When creating a software push or an update job, normally a
non-persistent patch status job is added automatically. The parent ID
is set to the ID of the new job. To disable this behavior, use the
--no-autopatchstatus option.
SMT is not intended to be a system to directly access the clients or to immediately report the results back. It is a long-term maintenance and monitoring system rather than a live interaction tool.
The client normally processes one job at a time, reports back the result, and then asks for the next job. If you create a persistent job with a time offset of only a few seconds, it is repeated forever and blocks other jobs. Therefore, adding jobs with a time offset shorter than one minute is not supported.
8.1.2 /usr/sbin/smt Commands #
The key command to manage the SMT is smt
(/usr/sbin/smt). The smt command
should be used together with certain sub-commands described in this
section. If the smt command is used alone, it prints a
list of all available sub-commands. To get help for individual
sub-commands, use smt
SUBCOMMAND --help.
The following sub-commands are available:
smt-clientsmt-delete-registrationsmt-jobsmt-list-productssmt-list-registrationssmt-mirrorsmt-scc-syncsmt-registersmt-reportsmt-repossmt-setup-custom-repossmt-stagingsmt-supportsmt-sync
There are two syntax types you can use with the smt
command: smt followed by a sub-command or a single
command consisting of smt followed by the dash and the
desired sub-command. For example, it is possible to use either
smt mirror or smt-mirror, as both
have the same meaning.
Depending on your $PATH environment variable, the
SMT smt command
(/usr/sbin/smt) may collide with the
smt command from the star
package (/usr/bin/smt). Either use the absolute
path /usr/sbin/smt, create an alias, or set your
$PATH accordingly.
Another solution is to always use the smt-
SUBCOMMAND syntax.
8.1.2.1 smt-client #
The smt-client command shows information about
registered clients. The information includes the following:
guid
host name
patch status
time stamps of the patch status
last contact with the SMT server
The smt-client supports the following options:
--verboseor-vShows detailed information about the client. The last contact date is shown as well.
--debugor-dEnables debugging mode.
--logfileor-Lwith the parameter LOGFILESpecifies the file to write the log messages to.
--hostnameor-hwith the parameter HOSTNAMELists the entries whose host name begins with HOSTNAME.
--guidor-gwith the parameter IDLists the entries whose GUID is ID.
--severityor-swith the parameter LEVELFilters the result by the patch status information. The value level can be one of
packagemanager,security,recommendedoroptional.
8.1.2.2 smt-delete-registration #
The smt-delete-registration command deletes one or
more registrations from SMT and SUSE Customer Center. It unregisters machines from
the system. The following options are available:
--guidor-gwith the parameter IDDeletes the machine with the guid ID from the system. You can use this option multiple times.
--debugor-dEnables debugging mode.
8.1.2.3 smt-job #
The smt-job script manages jobs for individual SMT
clients. You can use this command to list, create, edit and delete
jobs. The following options are available:
--listor-lLists all client jobs. This is the default if the operation mode switch is omitted.
--verboseor-vwith the parameter LEVELShows detailed information about a job or jobs in a list mode. The level value can be a number from 0 to 3. The higher the value, the more verbose the command is.
--createor-cCreates a new job.
--editor-eEdits an existing job.
--deleteor-dDeletes an existing job.
--guidor-gwith the parameter IDSpecifies the client's guid. This parameter can be used multiple times to create a job for more than one client.
--jobidor-jwith the parameter IDSpecifies the job ID. You need to specify job ID and client's guid when editing or deleting a job, as the same job for multiple clients has the same job ID.
--deleteallor-AidOmit either the client's GUID or the job ID in the delete operation. The missing parameter matches all respective jobs.
--typeor-twith the parameter TYPESpecifies the job type. The type can be one of
patchstatus,softwarepush,update,execute,reboot,wait,eject. On the client, only the following job types are enabled by default:patchstatus,softwarepushandupdate.--description DESCRIPTIONSpecifies a job description.
--parentIDSpecifies the job ID of the parent job. Use it to define a dependency. A job is not processed until its parent has successfully finished.
--nameor-nwith the parameter NAMESpecifies a job name.
--persistentSpecifies if a job is persistent. Non-persistent jobs are processed only once, while persistent jobs are processed again and again. Use
--timelagto define the time that elapses until the next run.--finishedSearch option for finished jobs.
--targetedtimeSpecifies the earliest execution time of a job. The job does not run exactly at that time, but a few minutes or hours after. The reason is that the client polls in a fixed interval for jobs.
--expirestimeDefines the time after which the job is no longer executed.
--timelagtimeDefines the time interval for persistent jobs.
For a complete list of available options and their explanations, see
the manual page of the smt-job command
(man smt-job).
8.1.2.3.1 Examples #
List all finished jobs:
smt-job --list --finished
Create a softwarepush job that installs
xterm and bash on client 12345
and 67890:
smt-job --create -t softwarepush -P xterm -P bash -g 12345 -g 67890
Change the timing for a persistent job with job ID 42 and guid 12345 to run every 6 hours:
smt-job --edit -j 42 -g 12345 --targeted 0000-00-00 --timelag 06:00:00
Delete all jobs with job ID 42:
smt-job --delete -jobid 42 --deleteall
8.1.2.4 smt-list-products #
The smt-list-products script lists all software
products in the SMT database. The following options are available:
--usedor-uShows only used products.
--catstator-cShows whether all repositories needed for a product are locally mirrored.
8.1.2.5 smt-list-registrations #
The smt-list-registrations script lists all
registrations. There are two options available for this command:
--verboseor-vShows detailed information about the registered devices.
--formator-fwith the parameter FORMATFormats the output in the asciitable or csv formats.
8.1.2.6 smt-mirror #
The smt-mirror command performs the mirroring
procedure and downloads repositories that are set to be mirrored.
You can run the smt-mirror with the following
options:
--cleanor-cRemoves all files no longer mentioned in the metadata from the mirror. No mirroring occurs before cleanup.
--debugor-dEnables the debugging mode.
--deepverifyTurns on verifying of all package checksums.
--hardlink SIZESearches for duplicate files with a size greater than the size specified in kilobytes. Creates hard links for them.
--directory PATHDefines the directory to work on. When using this option, the default value configured in the
smt.confconfiguration file is ignored.--dbreplfile FILEDefines a path to the *.xml file to use as database replacement. You can create this file with the
smt-scccommand.--logfileor-Lwith the parameter FILESpecifies the path to a log file.
8.1.2.7 smt-sync #
The smt-sync or smt sync command
obtains data from SUSE Customer Center and updates the local SMT database. It can
also save SUSE Customer Center data to a directory instead of the SMT database, or
read the data from such a directory instead of downloading it from
SUSE Customer Center.
For SUSE Linux Enterprise 11 clients, this script automatically determines whether
Novell Customer Center or SUSE Customer Center should be used. Then
smt-ncc-sync or smt-scc-sync is
called. For SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 clients, only smt-scc-sync is
supported.
8.1.2.8 smt-scc-sync #
The smt scc-sync command obtains data from the SUSE Customer Center
and updates the local SMT database. It can also save SUSE Customer Center data to a
directory instead of the SMT database, or read SUSE Customer Center data from a
directory instead of downloading it from SUSE Customer Center.
You can run the smt-scc-sync with the following
options:
--fromdir DIRECTORYReads SUSE Customer Center data from a directory instead of downloading it from SUSE Customer Center.
--todir DIRECTORYWrites SUSE Customer Center data to the specified directory without updating the SMT database.
Tip: SUSE Manager's Subscription Matching FeatureThis data can be used by the subscription matching feature of SUSE Manager, which gives you a detailed overview of your subscription usage. For more information on the subscription matching feature, see https://documentation.suse.com/external-tree/en-us/suma/3.2/susemanager-reference/html/book.suma.reference.manual/ref.webui.audit.html#ref.webui.audit.subscription.
--createdbreplacementfileCreates a database replacement file for using
smt-mirrorwithout database.--logfileor-LLOGFILESpecifies the path to a log file.
--debugor-dEnables debugging mode.
--verboselevelor-vBITMASKSpecifies the verbosity level of log messages. Accepts a decimal number that represents a binary bitmask of one of seven verbosity levels. For example, the
--debugoption described above corresponds to the bitmask of00111111, which is63in decimal. To achieve even more verbosity, use127, which relates to the bitmask of01111111.ImportantThe
--debugand--mailoptions are mutually exclusive with the--verboseleveloption.
8.1.2.9 smt-register #
The smt-register or smt register
command registers all currently unregistered clients at the SUSE Customer Center. It
also registers all clients whose data has changed since the last
registration.
The following options are available:
--logfileor-Lwith the parameter LOGFILESpecifies the path to a log file.
--debugEnables debugging mode.
8.1.2.10 smt-report #
The smt-report or smt report
command generates a subscription report based on local calculation or
SUSE Customer Center registrations.
The following options are available:
--mailor-mActivates mailing the report to the addresses configured with the SMT Server and written in
/etc/smt.conf. The report is formatted as tables.--attachor-aAppends the report to the e-mails in CSV format. This option should only be used in combination with the
--mailoption.--quietor-qSuppresses output to STDOUT and runs
smt-reportin quiet mode.--csvor-cExports the report to multiple files in the CSV format. The first line of each *.csv file consists of the column names. The
--csvparameter should only be used in combination with the--fileparameter. If the specified file name has the.csvextension, the report is formatted as CSV (as if the--csvparameter was used).--pdfor-pExports the report in the PDF format. Use it only in combination with the
-fileoption.--xmlExports the report in the XML format. Use it only in combination with the
-fileoption. For a detailed description of the XML format, see the manual page of thesmt-reportcommand.--fileor-FExports the report to one or several files. By default, the report is written to a single file formatted as tables. Optionally, the file name or whole path may be specified after the
--file filenameparameter. If no file name is specified, a default file name containing a time stamp is used. However, SMT does not check if the file or files already exist.In the CSV mode the report is written to multiple files, therefore the specified file name expands to
[PATH/]FILENAME-reportname.extensionfor every report.--logfileor-Lwith the parameter LOGFILESpecifies path to a log file.
--debugEnables debugging mode.
8.1.2.11 smt-repos #
Use smt-repos (or smt
repositories) to list all available repositories and for
enabling, disabling and deleting repositories. The following options
are available:
--enable-mirroror-eEnables repository mirroring.
--disable-mirroror-dDisables repository mirroring.
--enable-by-prodor-pEnables repository mirroring by giving product data in the following format:
Product[,Version[,Architecture[,Release]]].--disable-by-prodor-PDisables repository mirroring by giving product data in the following format:
Product[,Version[,Architecture[,Release]]].--enable-stagingor-sEnables repository staging.
--disable-stagingor-SDisables repository staging.
--only-mirrorableor-mLists only repositories that can be mirrored.
--only-enabledor-oLists only enabled repositories.
--deleteLists repositories and deletes them from disk.
--namespace DIRNAMEDeletes the repository in the specified name space.
--verboseor-vShows detailed repository information.
8.1.2.12 smt-setup-custom-repos #
The smt-setup-custom-repos and smt
setup-custom-repos script are designed for setting up custom
repositories (repositories not present in the download server) for use
with SMT. You can use this script to add a new repository to the
SMT database or to delete a repository from the database. The script
supports the following options:
--productidPRODUCT_IDID of a product the repository belongs to. If a repository should belong to multiple products, use this option multiple times to assign the repository to all relevant products.
--nameNAMEThe name of the custom repository.
--descriptionDESCRIPTIONThe description of the custom repository.
--exturlURLThe URL for the repository to be mirrored from. Only HTTP and HTTPS protocols are supported.
--deleteIDRemoves a custom repository with a given ID from the SMT database.
To set up a new repository, use the following command:
smt-setup-custom-repos --productid PRODUCT_ID \ --name NAME --exturl URL
For example:
smt-setup-custom-repos --productid 434 \ --name My_Catalog --exturl http://my.example.com/My_Catalog
To remove a configured repository, use the following command:
smt-setup-custom-repos --delete ID
For example:
smt-setup-custom-repos --delete 1cf336d819e8e5904f4d4b05ee081971a0cc8afc
8.1.2.13 smt-staging #
A patch is an update of a package or group of
packages. The term update and
patch are often interchangeable. With the
smt-staging script, you can set up patch filters for
update repositories. It can also help you generate both testing
repositories and repositories for the production environment.
The first argument of smt-staging is always the
command. It must be followed by a
repository. The repository can be specified
by Name and
Target from the table scheme returned by the
smt-repos command. Alternatively, it can be
specified by its Repository ID which can be obtained
by running the command smt-repos -v. The
smt-staging script supports the following commands:
listupdatesLists available patches and their allowed and forbidden status.
allow/forbidAllows or forbids specified patches.
createrepoGenerates both testing and production repository with allowed patches.
statusGives information about both testing and production snapshots, and patch counts.
listgroupsLists staging groups.
There is always one group available with the name “default”. The default group has the path
repo/full,repo/testingandrepo. New paths can be specified when creating a new group.creategroupCreates a staging group. Required parameters are: group name, testing directory name, and production directory name.
removegroupRemoves a staging group. The group name parameter is required.
The following options apply to any smt-staging
command:
--logfileor-Lfile pathWrites log information to the specified file. It is created if it does not already exist.
--debugor-dTurns on the debugging output and log.
--verboseor-vTurns more detailed output on.
The following options apply to specific smt-staging
commands:
--patchPATCH_IDSpecifies a patch by its ID. You can get a list of available patches with the
listupatescommand. This option can be used multiple times. Use it with theallow,forbid, andlistupdatescommands. When used withlistupdates, the command prints detailed information about the specified patches.--categoryCATEGORYSpecifies the patch category. The following categories are available:
security,recommendedandoptional. Use it in combination with theallow,forbid, andlistupdatescommands.--allAllows or forbids all patches in the
alloworforbidcommands.--individuallyAllows or forbids multiple patches (for example, by category) one by one, similar to the
--patchoption used with each of the patches.--testingGenerates a repository for testing when used in combination with the
createrepocommand. The repository is generated from the full unfiltered local mirror of the remote repository. It is written into the<MirrorTo>/repo/testingdirectory, whereMirrorTois the value obtained fromsmt.conf.--productionGenerates a repository for production when used in combination with the
createrepocommand. The repository is generated from the testing repository. It is written into the<MirrorTo>/repodirectory, whereMirrorTois the value obtained fromsmt.conf. If the testing repository does not exist, the production repository is generated from the full unfiltered local mirror of the remote repository.--groupGROUPSpecifies on which group the command should work. The default for
--groupis the namedefault.--nohardlinkPrevents creating hard links instead of copying files when creating a repository with the
createrepocommand. If not specified, hard links are created instead.--nodescSkips patch descriptions and summaries—to save certain screen space and make the output more readable.
--sort-by-versionSorts the
listupdatestable by patch version. The higher the version, the newer the patch should be.--sort-by-categorySorts the
listupdatestable by patch category.
8.1.2.14 smt-support #
The smt-support command manages uploaded support
data often coming from the supportconfig tool. You
can forward the data to SUSE, either selectively or in full. This
command supports the following options:
--incomingor-iwith the parameter DIRECTORYSpecifies the directory where the supportconfig archives are uploaded. You can also set this option with the
SMT_INCOMINGenvironment variable. The defaultSMT_INCOMINGdirectory is/var/spool/smt-support.--listor-lLists the uploaded supportconfig archives in the incoming directory.
--removeor-rwith the parameter ARCHIVEDeletes the specified archive.
--emptyor-RDeletes all archives in the incoming directory.
--uploador-uwith the parameter ARCHIVEUploads the specified archive to SUSE. If you specify
-s,-n,-c,-p, and-eoptions, the archive is repackaged with contact information.--uploadallor-UUploads all archives in the incoming directory to SUSE.
--srnumor-swith the parameter SR_NUMBERSpecifies the Novell Service Request 12-digit number.
--nameor-nwith the parameter NAMESpecifies the first and last name of the contact, in quotes.
--companyor-cwith the parameter COMPANYSpecifies the company name.
--storeidor-dwith the parameter IDSpecifies the store ID, if applicable.
--terminalidor-twith the parameter IDSpecifies the terminal ID, if applicable.
--phoneor-pwith the parameter PHONESpecifies the phone number of the contact person.
--emailor-ewith the parameter E-MAIL_ADDRESSSpecifies the e-mail address of the contact.
8.1.3 SMT systemd Commands #
You can manage SMT-related services with the standard systemd
commands:
systemctl start smt.targetStarts the SMT services.
systemctl stop smt.targetStops the SMT services.
systemctl status smt.targetChecks the status of the SMT services. Checks whether httpd, MariaDB, and cron are running.
systemctl restart smt.targetRestarts the SMT services.
systemctl try-restart smt.targetChecks whether the SMT services are enabled and if so, restarts them.
You can enable and disable SMT with the YaST SMT Server module.
8.2 SMT Configuration Files #
The main SMT configuration file is /etc/smt.conf.
You can set most of the options with the YaST SMT Server module.
Another important configuration file is
/etc/smt.d/smt-cron.conf, which contains parameters
for commands launched as SMT scheduled jobs.
8.2.1 /etc/smt.conf #
The /etc/smt.conf file has several sections. The
[NU] section contains the update credentials and URL.
The [DB] section contains the configuration of the
MariaDB database for SMT. The [LOCAL] section includes
other configuration data. The [REPORT] section
contains the configuration of SMT reports.
The /etc/smt.conf file contains passwords
in clear text. Its default permissions (640, root, wwwrun)
make its content easily accessible with scripts running on the
Apache server. Be careful with running other software on the
SMT Apache server. The best policy is to use this server only
for SMT.
8.2.1.1 [NU] Section of /etc/smt.conf #
The following options are available in the [NU] section:
NUUrlURL of the update service. Usually it should contain the
https://updates.suse.com/URL.NURegUrlURL of the update registration service. It is used by
smt-sync. If this option is missing, the URL from/etc/SUSEConnectis used as a fallback.NUUserNUUsershould contain the user name for update service. For information about getting organization credentials, see Section 4.1, “Mirroring Credentials”. You can set this value with the SMT Server.NUPassNUPassis the password for the user defined inNUUser. For information about getting organization credentials, see Section 4.1, “Mirroring Credentials”. You can set this value with the SMT Server.ApiTypeApiTypeis the type of service SMT uses; it can be eitherNCCfor Novell Customer Center orSCCfor SUSE Customer Center. The only supported value for SMT 12 isSCC.
8.2.1.2 [DB] Section of /etc/smt.conf #
The three options defined in the [DB] section are used for configuring the database for SMT. Currently, only MariaDB is supported by SMT.
configThe first parameter of the DBI->connect Perl method used for connection to the MariaDB database. The value should be in the form
dbi:mysql:database=SMT;host=LOCALHOST
where SMT is the name of the database and LOCALHOST is the host name of the database server.
userThe user for the database. The default value is
smt.passThe password for the database user. You can set the password with the YaST SMT Server module.
8.2.1.3 [LOCAL] Section of /etc/smt.conf #
The following options are available in the [LOCAL]
section:
urlThe base URL of the SMT server which is used to construct URLs of the repositories available on the server. This value should be set by YaST automatically during installation. The format of this option should be:
https://server.domain.tld/.You can change the URL manually. For example, the administrator may choose to use the
http://scheme instead ofhttps://for performance reasons. Another reason may be using an alias (configured with CNAME in DNS) instead of the host name of the server. For example,http://smt.domain.tld/instead ofhttp://server1.domain.tld/.nccEmailE-mail address used for registration at the SUSE Customer Center. The SMT administrator can set this value with the YaST SMT Server module.
MirrorToDetermines the path to mirror to.
MirrorAllIf the
MirrorAlloption is set totrue, thesmt-syncscript will set all repositories that can be mirrored to be mirrored (DOMIRROR flag).MirrorSRCIf the
MirrorSRCoption is set totrue, source RPM packages are mirrored.Note: Default Value Changed with SMT 11 SP2With SMT 11 SP2, the preset default value was changed to
false. If you also want SMT to mirror source RPM packages on new installations, setMirrorSRCtotrue.Upgraded systems are not affected.
forwardRegistrationFor SMT 11, this option determined whether the clients registered at SMT should be registered at Novell Customer Center, too. This option does not work with SUSE Customer Center yet.
rndRegisterSpecify a delay in seconds before the clients are registered at SUSE Customer Center. The value is a random number between
0and450, generated by the YaST SMT Server module. The purpose of this random delay is to prevent a high load on the SUSE Customer Center server that would occur if all smt-register cron jobs connected at the same time.mirror_preunlock_hookSpecify the path to the script that will be run before the
smt-mirrorscript removes its lock.mirror_postunlock_hookSpecify the path to the script that will be run after the
smt-mirrorscript removes its lock.HTTPProxyIf you do not want to use global proxy settings, specify the proxy to be used for HTTP connection here. Use the following form:
http://PROXY.example.com:3128.If the proxy settings are not configured in
/etc/smt.conf, the global proxy settings configured in/etc/syconfig/proxyare used. You can configure the global proxy settings with the YaST Proxy module.HTTPSProxyIf you do not want to use global proxy settings, specify the proxy to be used for HTTPS connection here. Use the form:
https://PROXY.example.com:3128.If the proxy settings are not configured in
/etc/smt.conf, the global proxy settings configured in/etc/syconfig/proxyare used. You can configure the global proxy settings with the YaST Proxy module.ProxyUserIf your proxy requires authentication, specify a user name and password here, using the
USERNAME:PASSWORDformat.If the proxy settings are not configured in
/etc/smt.conf, the global proxy settings configured in/etc/syconfig/proxyare used. You can configure the global proxy settings with the YaST Proxy module.Tip: Global User Authentication SettingIf you configure the global proxy settings with YaST, manually copy
/root/.curlrcto the home directory of thesmt. Adjust the permissions with the following commands asroot:cp /root/.curlrc /var/lib/smt/ chown smt:www /var/lib/smt/.curlrc
requiredAuthTypeSpecify an authentication type to access the repository. There are three possible types:
none- no authentication is required. This is the default value.lazy- only user name and password are checked. A valid user can access all repositories.strict- checks also if the user has access to the repository.
smtUserSpecify a user name of a Unix user under which all smt commands will run.
signingKeyIDSpecify the ID of the GPG key to sign modified repositories. The user specified under
smtUserneeds to have access to the key. If this option is not set, the modified repositories will be unsigned.
8.2.1.4 [REST] Section of /etc/smt.conf #
The following options are available in the [REST]
section:
enableRESTAdminAccessIf set to 1, turns administrative access to the SMT RESTService on. Default value is 0.
RESTAdminUserSpecify the user name that the REST-Admin uses to log in. Default value is RESTroot.
RESTAdminPasswordSpecify the password for the REST-Admin user. The option has no default value. An empty password is invalid.
8.2.1.5 [JOBQUEUE] Section of /etc/smt.conf #
The following options are available in the [JOBQUEUE]
section:
maxFinishedJobAgeSpecify the maximum age of finished non-persistent jobs in days. Default value is 8.
jobStatusIsSuccessSpecify a comma separated list of JobQueue status IDs that should be interpreted as successful. For more information about possible status IDs, see
smt-job --help. Leaving this option empty is interpreted as default (1,4).
8.2.1.6 [REPORT] Section of /etc/smt.conf #
The following options are available in the [REPORT]
section:
reportEmailA comma separated list of e-mail addresses to send SMT status reports to. You can set this list with the YaST SMT Server module.
reportEmailFromFromfield of report e-mails. If not set, the defaultroot@HOSTNAME.DOMAINNAMEwill be used.mailServerRelay mail server. If empty, e-mails are sent directly.
mailServerPortPort of the relay mail server set in
mailServer.mailServerUserUser name for authentication to the mail server set in
mailServer.mailServerPasswordPassword for authentication to the mail server set in
mailServer.
8.2.1.7 Example /etc/smt.conf #
[NU] NUUrl=https://updates.suse.com/ NURegUrl=https://scc.suse.com/connect NUUser = exampleuser NUPass = examplepassword ApiType = SCC [DB] config = dbi:mysql:database=smt;host=localhost user = smt pass = smt [LOCAL] # Default should be http://server.domain.top/ url = http://smt.example.com/ # This email address is used for registration at SCC nccEmail = exampleuser@example.com MirrorTo = /srv/www/htdocs MirrorAll = false MirrorSRC = false forwardRegistration = true rndRegister = 127 # The hook script that should be called before the smt-mirror script removes its lock mirror_preunlock_hook = # The hook script that should be called after the smt-mirror script removed its lock mirror_postunlock_hook = # specify proxy settings here, if you do not want to use the global proxy settings # If you leave these options empty the global options are used. # # specify which proxy you want to use for HTTP connection # in the form http://proxy.example.com:3128 HTTPProxy = # specify which proxy you want to use for HTTPS connection # in the form http://proxy.example.com:3128 HTTPSProxy = # specify username and password if your proxy requires authentication # in the form username:password ProxyUser = # # require authentication to access the repository? # Three possible authtypes can be configured here # 1) none : no authentication required (default) # 2) lazy : check only username and password. A valid user has access to all repositories # 3) strict : check also if this user has access to the repository. # requiredAuthType = none # # the smt commands should run with this unix user # smtUser = smt # # ID of the GPG key to be used to sign modified (filtered) repositories. # The key must be accessible by the user who runs SMT, i.e. the user specified # in the 'smtUser' configuration option. # # If empty, the modified repositories will be unsigned. # signingKeyID = # # This string is sent in HTTP requests as UserAgent. # If the key UserAgent does not exist, a default is used. # If UserAgent is empty, no UserAgent string is set. # #UserAgent= # Organization credentials for this SMT server. # These are currently only used to get list of all available repositories # from https://your.smt.url/repo/repoindex.xml # Note: if authenticated as a client machine instead of these mirrorUser, # the above URL returns only repositories relevant for that client. mirrorUser = mirrorPassword = [REST] # Enable administrative access to the SMT RESTService by setting enableRESTAdminAccess=1 # default: 0 enableRESTAdminAccess = 0 # Define the username the REST-Admin uses for login # default: RESTroot RESTAdminUser = RESTroot # Define the password for the REST-Admin (note: empty password is invalid) # default: <empty> RESTAdminPassword = [JOBQUEUE] # maximum age of finished (non-persistent) jobs in days # default: 8 maxFinishedJobAge = 8 # comma separated list of JobQueue status IDs that should be interpreted as successful # See smt-job --help for more information about possible Status IDs # Please note: An empty string will be interpreted as default (1,4). # default: 1,4 # useful: 1,4,6 jobStatusIsSuccess = 1,4 [REPORT] # comma separated list of eMail addresses where the status reports will be sent to reportEmail = exampleuser@example.com # from field of report mails - if empty it defaults to "root@<hostname>.<domainname>" reportEmailFrom = # relay mail server - leave empty if mail should be sent directly mailServer = mailServerPort = # mail server authentication - leave empty if not required mailServerUser = mailServerPassword =
8.2.2 /etc/smt.d/smt-cron.conf #
The /etc/smt.d/smt-cron.conf configuration file
contains options of the SMT commands launched as SMT scheduled jobs
set with YaST (see Section 3.5, “Setting the SMT Job Schedule with YaST”). Cron is used
to launch these scheduled jobs. The cron table is located in the
/etc/cron.d/novell.com-smt file.
SCC_SYNC_PARAMSContains parameters of the
smt scc-synccommand, if called as part of an SMT scheduled job via cron. The default value is"-L /var/log/smt/smt-sync.log --mail".MIRROR_PARAMSContains parameters of the
smt mirrorcommand, if called as part of an SMT scheduled job via cron. The default value is"-L /var/log/smt/smt-mirror.log --mail".REGISTER_PARAMSContains parameters of the
smt registercommand, if called as part of an SMT scheduled job via cron. The default value is"-r -L /var/log/smt/smt-register.log --mail".REPORT_PARAMSContains parameters of the
smt reportcommand, if called as part of an SMT scheduled job via cron. The default value is"--mail --attach -L /var/log/smt/smt-report.log".JOBQUEUECLEANUP_PARAMSContains parameters for smt jobqueue cleanup, if called as a part of an SMT scheduled job via cron. The default value is
"--mail -L /var/log/smt/smt-jobqueuecleanup.log".
8.3 Server Certificates #
For communication between the SMT server and client machines, the encrypted HTTPS protocol is used, requiring a server certificate. If the certificate is not available, or if clients are not configured to use the certificate, the communication between server and clients will fail.
Every client must be able to verify the server certificate by trusting the CA
(certificate authority) certificate that signed the server certificate.
Therefore, the SMT server provides a copy of the CA at
/srv/www/htdocs/smt.crt. This CA can be downloaded from
every client via the URL
http://FQDN/smt.crt. The copy is
created by the /usr/lib/SMT/bin/smt-maintenance script.
Whenever SMT is started with systemctl start smt.target,
it checks the certificate. If a new CA certificate exists, it is copied again.
Therefore, whenever the CA certificate is missing or changed, restart SMT
using the systemctl restart smt.target command.
When the SMT Server module applies configuration changes, it checks for the existence of the common server certificate. If the certificate does not exist, YaST asks whether the certificate should be created. If the user confirms, the YaST CA Management module is started.
8.3.1 Certificate Expiration #
The common server certificate SMT uses is valid for one year. After that time, a new certificate is needed. Either generate a new certificate using YaST CA Management module or import a new certificate using the YaST Common Server Certificate module. Both options are described in the following sections.
As long as the same CA certificate is used, there is no need to update certificates on the client machines. The generated CA certificate is valid for 10 years.
8.3.2 Creating a New Common Server Certificate #
To create a new common server certificate with YaST, proceed as follows:
Start YaST and select › . Alternatively, start the YaST CA Management module from a command line by entering
yast2 ca_mgmasroot.Select the required CA and click .
Enter the password if entering a CA for the first time. YaST displays the CA key information in the tab.
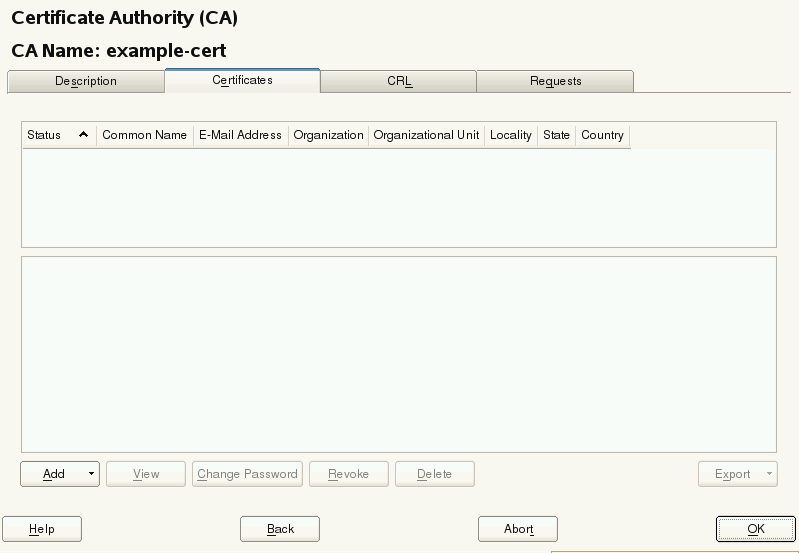
Click the tab (see Figure 8.1, “Certificates of a CA”) and select › .
Figure 8.1: Certificates of a CA #Enter the fully qualified domain name of the server as . Add a valid e-mail address of the server administrator. Other fields, such as , , , and are optional. Click to proceed.
Important: Host Name in Server CertificateThe server certificate must contain the correct host name. If the client requests server
https://some.hostname/, thensome.hostnamemust be part of the certificate. The host name must either be used as the , see Step 5, or as the , see Step 7:DNS:some.hostnameandIP:<ipaddress>.Enter a for the private key of the certificate and re-enter it in the next field to verify it.
If you want to define a , click , select from the list and click .
Important: Subject Alternative NameIf is in the server certificate, then it needs to contain the DNS entry. If is present, the (CN) is not checked anymore.
If you want to keep the default values for the other options, like and , click . An overview of the certificate to be created is shown.
Click to generate the certificate.
To export the new certificate as the common server certificate, select it in the tab and select › .
After having created a new certificate, restart SMT using the
systemctl restart smt.targetcommand. Restarting SMT ensures that the new certificate is copied from/etc/ssl/certs/YaST-CA.pemto/srv/www/htdocs/smt.crt, the copy SMT uses. Restarting SMT also restarts the Web server.
For detailed information about managing certification and further usage of the YaST CA Management module and the Common Server Certificate module, refer to the Security and Hardening Guide. It is available from https://documentation.suse.com/sles/.
8.3.3 Importing a Common Server Certificate #
You can import an own common server certificate from a file. The certificate to be imported needs to be in the PKCS12 format with CA chain. Common server certificates can be imported with the YaST Common Server Certificate module.
To import an own certificate with YaST, proceed as follows:
Start YaST and select › . Alternatively, start the YaST Common Server Certificate module from the command line by entering
yast2 common_certasroot.The description of the currently used common server certificate is shown in the dialog that opens.
Click and select the file containing the certificate to be imported. Specify the certificate password in the field.
Click . If the certificate is successfully imported, close YaST with .
After having created a new certificate, restart SMT using the
systemctl restart smt.targetcommand. Restarting SMT ensures that the new certificate is copied from/etc/ssl/certs/YaST-CA.pemto/srv/www/htdocs/smt.crt, the copy SMT uses. Restarting SMT also restarts the Web server.
8.3.4 Synchronizing Time between SMT Server and Clients #
The synchronization of time between the SMT server and clients is highly recommended. Each server certificate has a validity period. If the client happens to be set to a time outside of this period, the certificate validation on the client side fails.
Therefore, it is advisable to keep the time on the server and clients
synchronized. You can easily synchronize the time using NTP (network time
protocol). Use yast2 ntp-client to configure an NTP
client. Find detailed information about NTP in the Administration Guide.