Volume Security
Harvester allows you to encrypt and decrypt virtual machine images. The encryption mechanism utilizes the Linux kernel module dm_crypt and the command-line utility cryptsetup.
Prerequisites
Prepare the following resources:
-
Secret: A Kubernetes secret is used as the passphrase of dm_crypt. You must specify the value of the
CRYPTO_KEY_VALUEfield. All other fields are fixed.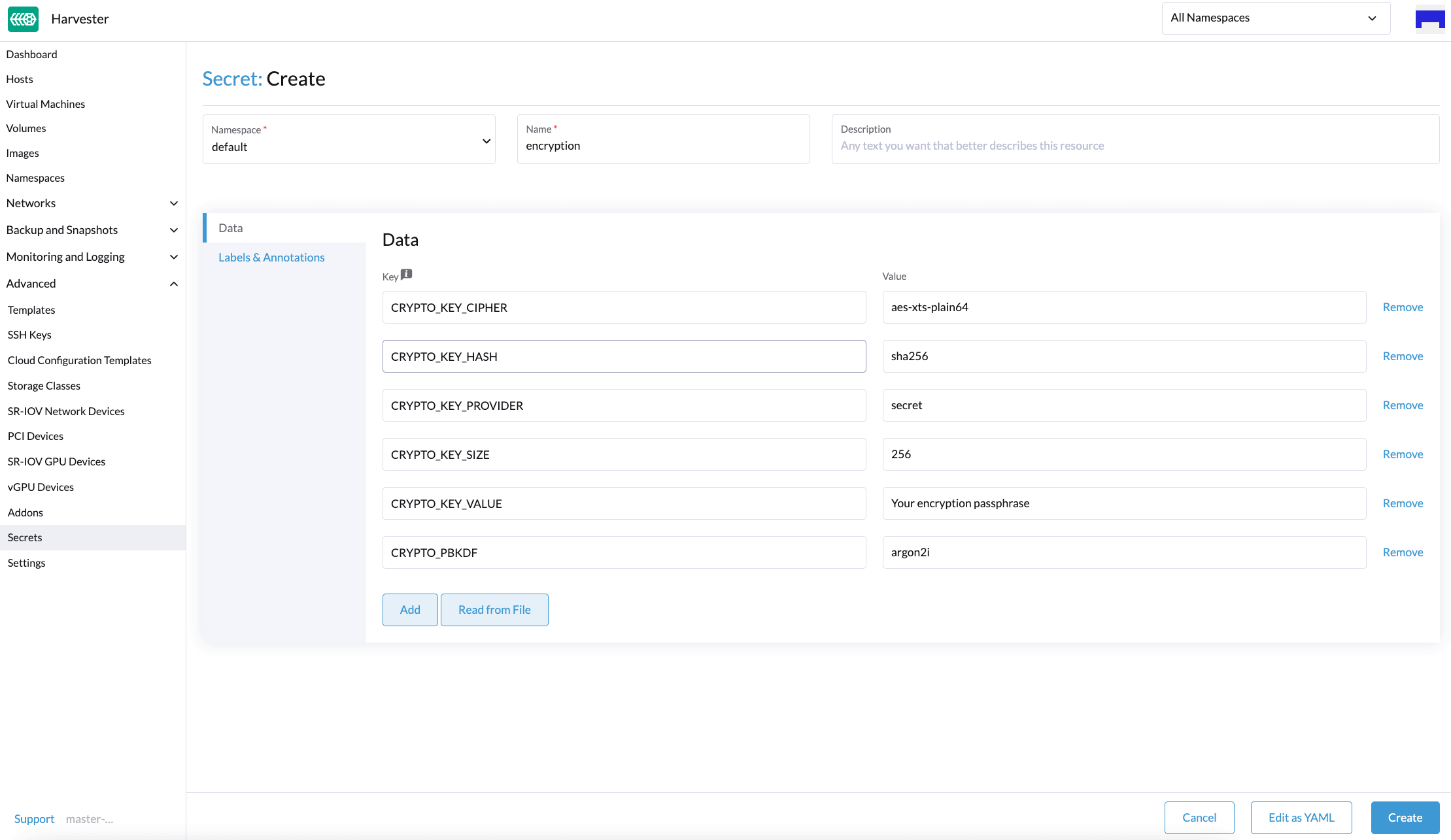
Example of a secret:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: encryption namespace: default data: CRYPTO_KEY_CIPHER: aes-xts-plain64 CRYPTO_KEY_HASH: sha256 CRYPTO_KEY_PROVIDER: secret CRYPTO_KEY_SIZE: 256 CRYPTO_KEY_VALUE: "Your encryption passphrase" CRYPTO_PBKDF: argon2iThe example contains the default YAML code for Kubernetes secrets. Aside from this, you can use encryption options for LUKS mode, which is a cryptsetup operating mode. Harvester v1.4.1 and later versions support these options, but you must verify that these are supported by your nodes.
Option Possible Values CRYPTO_KEY_CIPHER
aes-xts-plain, aes-xts-plain64, aes-cbc-plain, aes-cbc-plain64, aes-cbc-essiv:sha256
CRYPTO_KEY_HASH
sha256, sha384, sha512
CRYPTO_KEY_SIZE
256, 384, 512
CRYPTO_PBKDF
argon2i, argon2id, pbkdf2
You can create a secret in the system namespace using kubectl or the Harvester UI (Edit as YAML feature). Resources in the system namespace are not displayed on the Harvester UI Secrets screen.
-
StorageClass: Images are encrypted using Longhorn, so required fields must be passed to the Longhorn CSI Driver. You can specify the encryption secret when creating a StorageClass. For more information, see Image StorageClass.
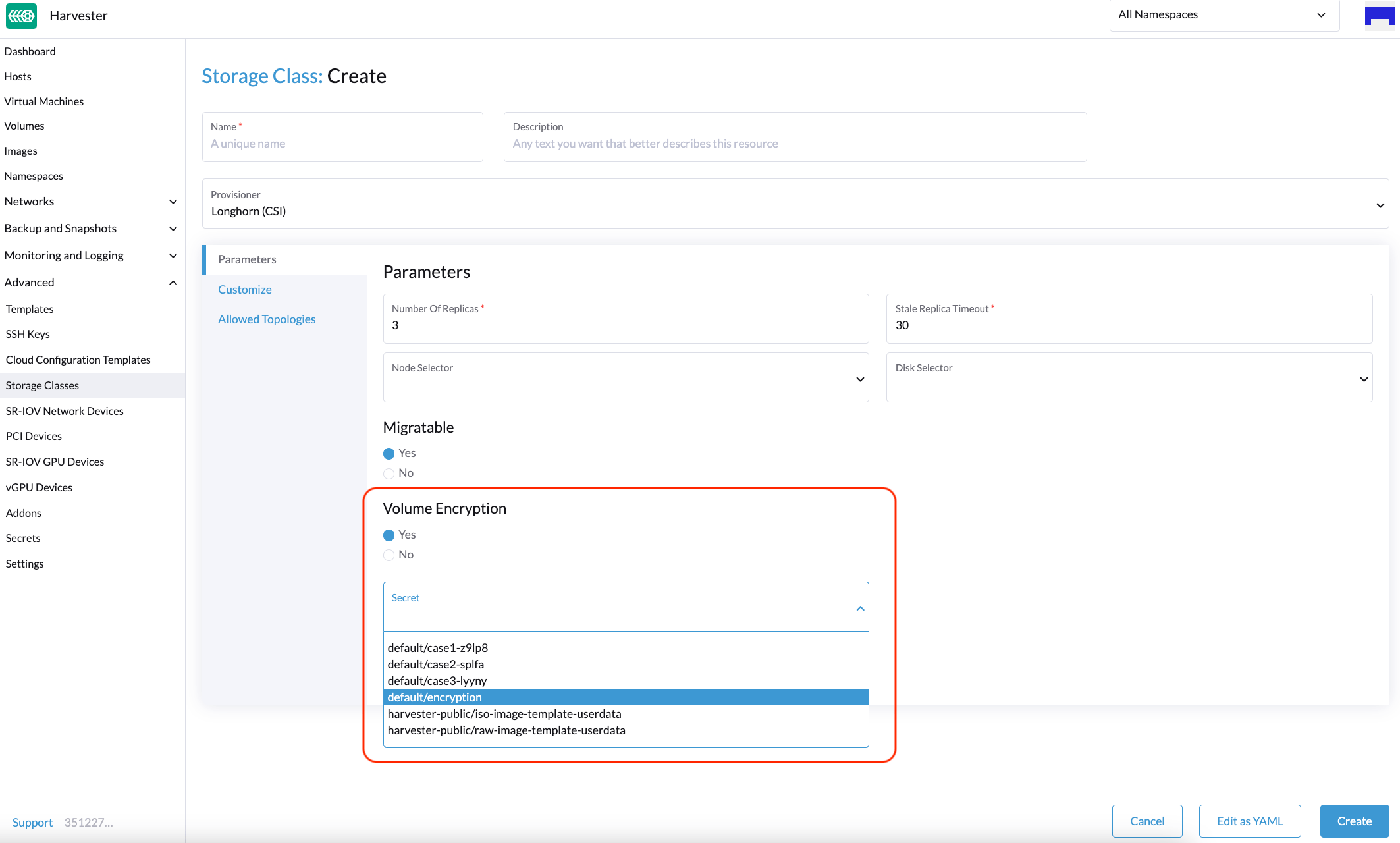
Example of a StorageClass:
allowVolumeExpansion: true apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1 kind: StorageClass metadata: name: encryption parameters: csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-name: encryption csi.storage.k8s.io/node-publish-secret-namespace: default csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: encryption csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: default csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: encryption csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: default encrypted: "true" migratable: "true" numberOfReplicas: "3" staleReplicaTimeout: "2880" provisioner: driver.longhorn.io reclaimPolicy: Delete volumeBindingMode: ImmediateYou can create a secret in the system namespace using the Harvester UI (Edit as YAML feature) and kubectl. Resources in the system namespace are not displayed on the Harvester UI Secrets screen.
Encrypted Volumes
You can create an encrypted volume using an encrypted StorageClass on the following UI locations:
-
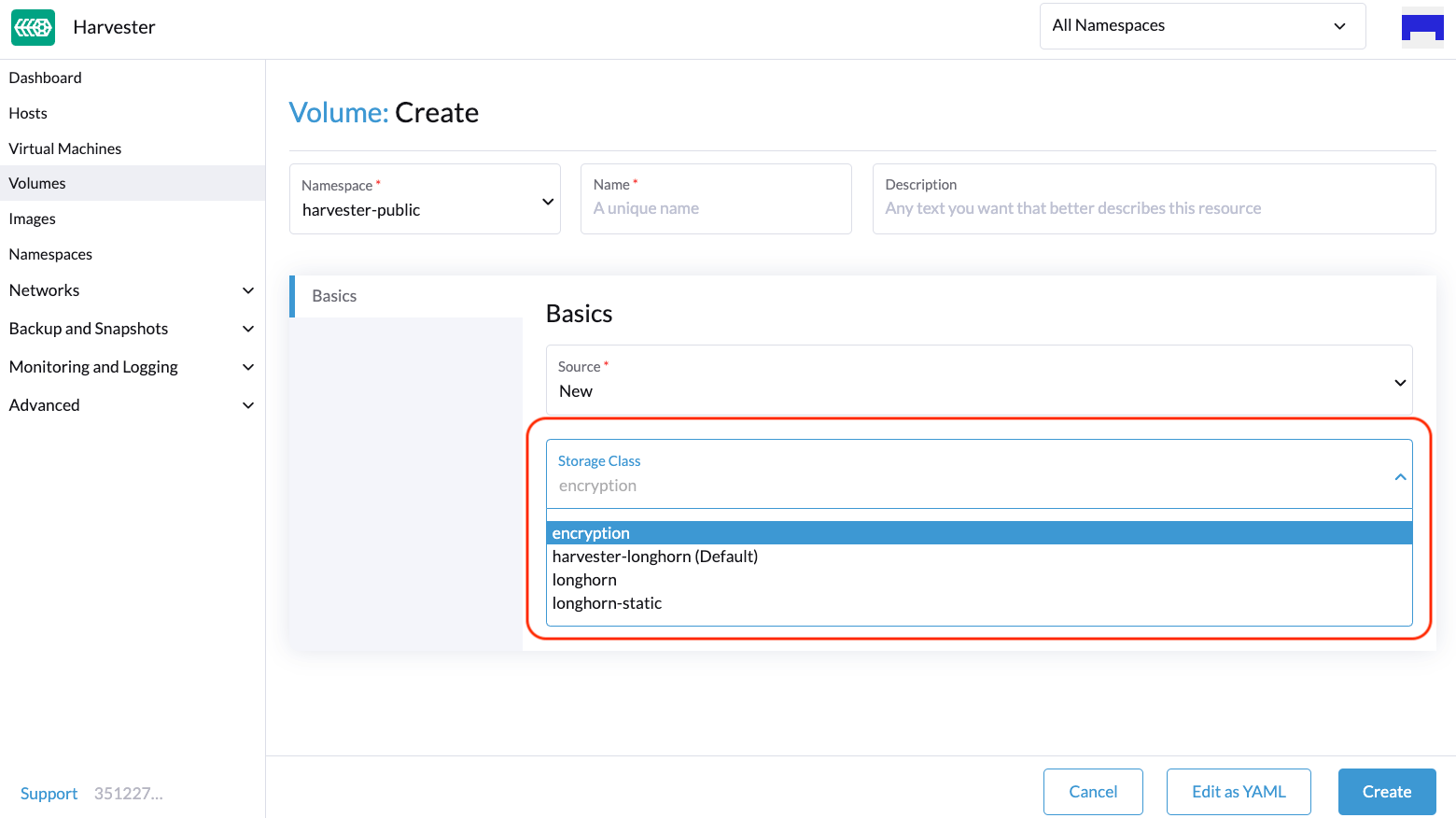
Volumes: Create screen
-
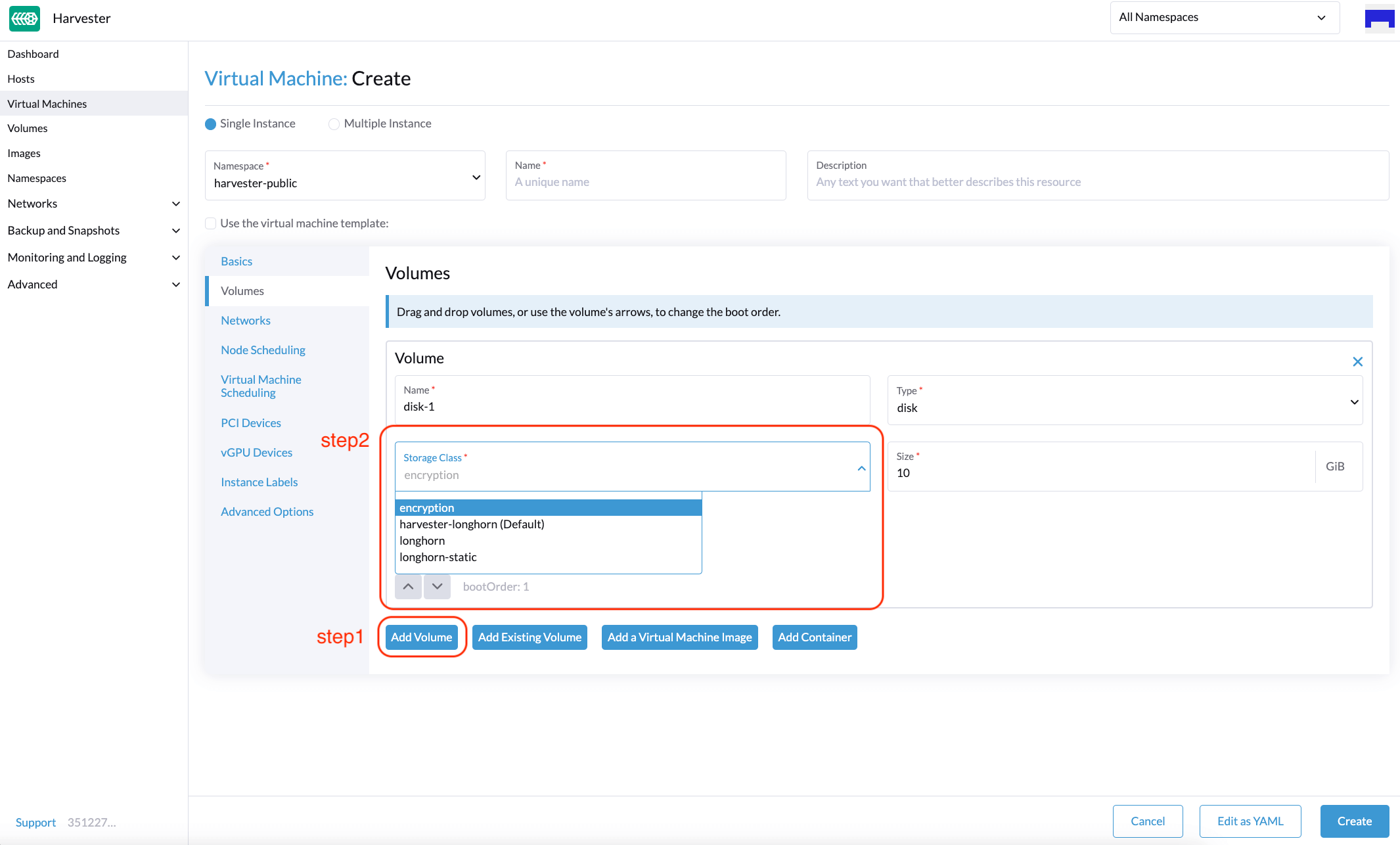
Volumes tab on the Virtual Machine: Create screen
Advanced Usage with Rancher Integration
The secret is an unencrypted Base64-encoded string. To keep the secret safe, you can use projects and namespaces to isolate permissions. For more information, see Multi-Tenancy.