About This Guide #
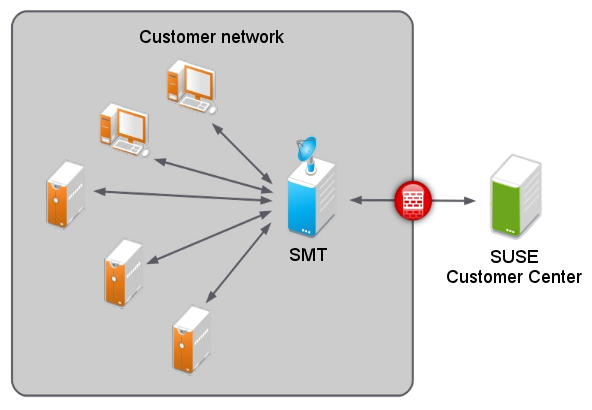
Subscription Management Tool (SMT) for SUSE Linux Enterprise 12 SP5 allows enterprise customers to optimize the management of SUSE Linux Enterprise software updates and subscription entitlements. It establishes a proxy system for SUSE® Customer Center with repository (formerly known as catalog) and registration targets. This helps you centrally manage software updates within the firewall on a per-system basis, while maintaining your corporate security policies and regulatory compliance.
SMT allows you to provision updates for all of your devices running a product based on SUSE Linux Enterprise. By downloading these updates once and distributing them throughout the enterprise, you can set more restrictive firewall policies. This also reduces bandwidth usage, as there is no need to download the same updates for each device. SMT is fully supported and available as a download for customers with an active SUSE Linux Enterprise product subscription.
Subscription Management Tool provides functionality that can be useful in many situations, including the following:
You want to update both SUSE Linux Enterprise and Red Hat Enterprise Linux servers.
You want to get a detailed overview of your company's license compliance.
Not all machines in your environment can be connected to SUSE Customer Center to register and retrieve updates for bandwidth or security reasons.
There are SUSE Linux Enterprise hosts that are restricted and difficult to update without putting in place a custom update management solution.
You need to integrate additional software update external or internal repositories into your update solution.
You are looking for a turnkey box staging solution for testing updates before releasing them to the clients.
You want to have a quick overview of the patch status of your SUSE Linux Enterprise servers and desktops.
1 Overview #
The Subscription Management Tool Guide is divided into the following chapters:
- SMT Installation
Introduction to the SMT installation process and the SMT Configuration Wizard. You will learn how to install the SMT add-on on your base system during the installation process or on an already installed base system.
- SMT Server Configuration
Description of the YaST configuration module SMT Server. This chapter explains how to set and configure organization credentials, SMT database passwords, and e-mail addresses to send SMT reports, or set the SMT job schedule, and activate or deactivate the SMT service.
- Mirroring Repositories on the SMT Server
Explanation of how to mirror the installation and update sources with YaST.
- Managing Repositories with YaST SMT Server Management
Description of how to register client machines on SUSE Customer Center. The client machines must be configured to use SMT.
- SMT Reports
In-depth look at generated reports based on SMT data. Generated reports contain statistics of all registered machines and products used and of all active, expiring, or missing subscriptions.
- SMT Tools and Configuration Files
Description of the most important scripts, configuration files and certificates supplied with SMT.
- Configuring Clients to Use SMT
Introduction to configuring any client machine to register against SMT and download software updates from there instead of communicating directly with the SUSE Customer Center.
2 Available documentation #
- Online documentation
Our documentation is available online at . Browse or download the documentation in various formats.
Note: Latest updatesThe latest updates are usually available in the English-language version of this documentation.
- SUSE Knowledgebase
If you run into an issue, check out the Technical Information Documents (TIDs) that are available online at https://www.suse.com/support/kb/. Search the SUSE Knowledgebase for known solutions driven by customer need.
- In your system
For offline use, the release notes are also available under
/usr/share/doc/release-noteson your system. The documentation for individual packages is available at/usr/share/doc/packages.Many commands are also described in their manual pages. To view them, run
man, followed by a specific command name. If themancommand is not installed on your system, install it withsudo zypper install man.
3 Improving the documentation #
Your feedback and contributions to this documentation are welcome. The following channels for giving feedback are available:
- Bug reports
Report issues with the documentation at .
To simplify this process, click the icon next to a headline in the HTML version of this document. This preselects the right product and category in Bugzilla and adds a link to the current section. You can start typing your bug report right away.
A Bugzilla account is required.
- Contributions
To contribute to this documentation, click the icon next to a headline in the HTML version of this document. This will take you to the source code on GitHub, where you can open a pull request.
A GitHub account is required.
Note: only available for EnglishThe icons are only available for the English version of each document. For all other languages, use the icons instead.
For more information about the documentation environment used for this documentation, see the repository's README.
You can also report errors and send feedback concerning the documentation to <doc-team@suse.com>. Include the document title, the product version, and the publication date of the document. Additionally, include the relevant section number and title (or provide the URL) and provide a concise description of the problem.
4 Documentation conventions #
The following notices and typographic conventions are used in this document:
/etc/passwd: Directory names and file namesPLACEHOLDER: Replace PLACEHOLDER with the actual value
PATH: An environment variablels,--help: Commands, options, and parametersuser: The name of a user or grouppackage_name: The name of a software package
Alt, Alt–F1: A key to press or a key combination. Keys are shown in uppercase as on a keyboard.
, › : menu items, buttons
AMD/Intel This paragraph is only relevant for the AMD64/Intel 64 architectures. The arrows mark the beginning and the end of the text block.
IBM Z, POWER This paragraph is only relevant for the architectures
IBM ZandPOWER. The arrows mark the beginning and the end of the text block.Chapter 1, “Example chapter”: A cross-reference to another chapter in this guide.
Commands that must be run with
rootprivileges. You can also prefix these commands with thesudocommand to run them as a non-privileged user:root #commandtux >sudocommandCommands that can be run by non-privileged users:
tux >commandCommands can be split into two or multiple lines by a backslash character (
\) at the end of a line. The backslash informs the shell that the command invocation will continue after the end of the line:tux >echoa b \ c dA code block that shows both the command (preceded by a prompt) and the respective output returned by the shell:
tux >commandoutputNotices
Warning: Warning noticeVital information you must be aware of before proceeding. Warns you about security issues, potential loss of data, damage to hardware, or physical hazards.
Important: Important noticeImportant information you should be aware of before proceeding.
Note: Note noticeAdditional information, for example about differences in software versions.
Tip: Tip noticeHelpful information, like a guideline or a piece of practical advice.
Compact Notices
Additional information, for example about differences in software versions.
Helpful information, like a guideline or a piece of practical advice.
5 Support #
Find the support statement for SUSE Linux Enterprise Server and general information about technology previews below. For details about the product lifecycle, see https://www.suse.com/lifecycle. For the virtualization support status, see Chapter 7, Supported Hosts, Guests, and Features.
If you are entitled to support, find details on how to collect information for a support ticket at https://documentation.suse.com/sles-15/html/SLES-all/cha-adm-support.html.
5.1 Support statement for SUSE Linux Enterprise Server #
To receive support, you need an appropriate subscription with SUSE. To view the specific support offers available to you, go to https://www.suse.com/support/ and select your product.
The support levels are defined as follows:
- L1
Problem determination, which means technical support designed to provide compatibility information, usage support, ongoing maintenance, information gathering and basic troubleshooting using available documentation.
- L2
Problem isolation, which means technical support designed to analyze data, reproduce customer problems, isolate a problem area and provide a resolution for problems not resolved by Level 1 or prepare for Level 3.
- L3
Problem resolution, which means technical support designed to resolve problems by engaging engineering to resolve product defects which have been identified by Level 2 Support.
For contracted customers and partners, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server is delivered with L3 support for all packages, except for the following:
Technology previews.
Sound, graphics, fonts, and artwork.
Packages that require an additional customer contract.
Some packages shipped as part of the module Workstation Extension are L2-supported only.
Packages with names ending in -devel (containing header files and similar developer resources) will only be supported together with their main packages.
SUSE will only support the usage of original packages. That is, packages that are unchanged and not recompiled.
5.2 Technology previews #
Technology previews are packages, stacks, or features delivered by SUSE to provide glimpses into upcoming innovations. Technology previews are included for your convenience to give you a chance to test new technologies within your environment. We would appreciate your feedback. If you test a technology preview, please contact your SUSE representative and let them know about your experience and use cases. Your input is helpful for future development.
Technology previews have the following limitations:
Technology previews are still in development. Therefore, they may be functionally incomplete, unstable, or otherwise not suitable for production use.
Technology previews are not supported.
Technology previews may only be available for specific hardware architectures.
Details and functionality of technology previews are subject to change. As a result, upgrading to subsequent releases of a technology preview may be impossible and require a fresh installation.
SUSE may discover that a preview does not meet customer or market needs, or does not comply with enterprise standards. Technology previews can be removed from a product at any time. SUSE does not commit to providing a supported version of such technologies in the future.
For an overview of technology previews shipped with your product, see the release notes at https://www.suse.com/releasenotes.