11 Setting Up Hardware Components with YaST #
YaST allows you to configure hardware items such as audio hardware, your system keyboard layout or printers.
Graphics card, monitor, mouse and keyboard can be configured with GNOME tools.
11.1 Setting Up Your System Keyboard Layout #
The YaST module lets you define the default keyboard layout for the system (also used for the console). Users can modify the keyboard layout in their individual X sessions, using the desktop's tools.
Start the YaST dialog by clicking › in YaST. Alternatively, start the module from the command line with
sudo yast2 keyboard.Select the desired from the list.
Optionally, you can also define the keyboard repeat rate or keyboard delay rate in the .
Try the selected settings in the text box.
If the result is as expected, confirm your changes and close the dialog. The settings are written to
/etc/sysconfig/keyboard.
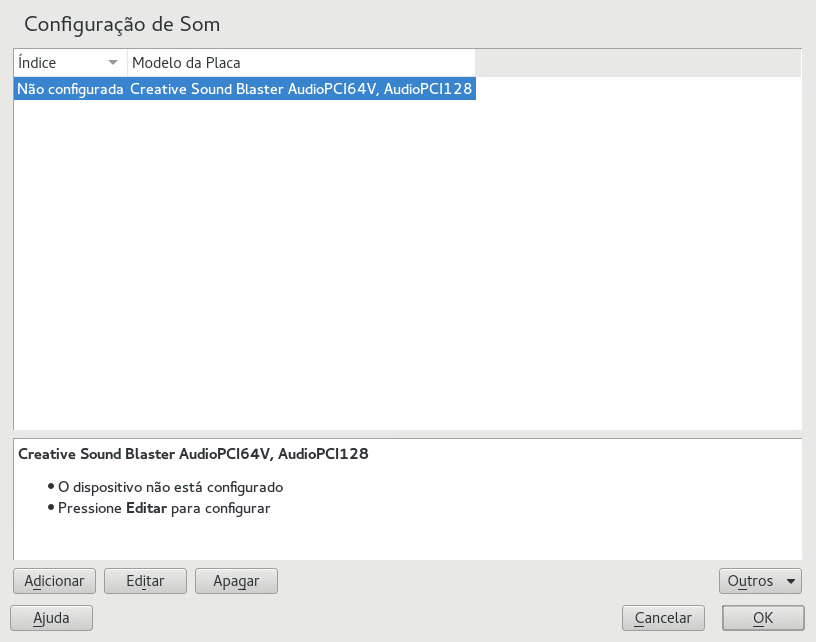
11.2 Setting Up Sound Cards #
YaST detects most sound cards automatically and configures them with the appropriate values. To change the default settings, or to set up a sound card that could not be configured automatically, use the YaST sound module. There, you can also set up additional sound cards or switch their order.
To start the sound module, start YaST and click › .
Alternatively, start the dialog
directly by running yast2 sound & as user root
from a command line.
The dialog shows all sound cards that were detected.
If you have added a new sound card or YaST could not automatically configure an existing sound card, follow the steps below. For configuring a new sound card, you need to know your sound card vendor and model. If in doubt, refer to your sound card documentation for the required information. For a reference list of sound cards supported by ALSA with their corresponding sound modules, see http://www.alsa-project.org/main/index.php/Matrix:Main.
During configuration, you can choose between the following setup options:
You are not required to go through any of the further configuration steps—the sound card is configured automatically. You can set the volume or any options you want to change later.
Allows you to adjust the output volume and play a test sound during the configuration.
For experts only. Allows you to customize all parameters of the sound card.
Importante: Advanced ConfigurationOnly use this option if you know exactly what you are doing. Otherwise leave the parameters untouched and use the normal or the automatic setup options.
Start the YaST sound module.
To configure a detected, but sound card, select the respective entry from the list and click .
To configure a new sound card, click . Select your sound card vendor and model and click .
Choose one of the setup options and click .
If you have chosen , you can now your sound configuration and make adjustments to the volume. You should start at about ten percent volume to avoid damage to your hearing or the speakers.
If all options are set according to your wishes, click .
The dialog shows the newly configured or modified sound card.
To remove a sound card configuration that you no longer need, select the respective entry and click .
Click to save the changes and leave the YaST sound module.
To change the configuration of an individual sound card (for experts only!), select the sound card entry in the dialog and click .
This takes you to the where you can fine-tune several parameters. For more information, click .
To adjust the volume of an already configured sound card or to test the sound card, select the sound card entry in the dialog and click . Select the respective menu item.
Nota: YaST MixerThe YaST mixer settings provide only basic options. They are intended for troubleshooting (for example, if the test sound is not audible). Access the YaST mixer settings from › . For everyday use and fine-tuning of sound options, use the mixer applet provided by your desktop or the
alsasoundcommand line tool.For playback of MIDI files, select › .
When a supported sound card is detected, you can install SoundFonts for playback of MIDI files:
Insert the original driver CD-ROM into your CD or DVD drive.
Select › to copy SF2 SoundFonts™ to your hard disk. The SoundFonts are saved in the directory
/usr/share/sfbank/creative/.
If you have configured more than one sound card in your system you can adjust the order of your sound cards. To set a sound card as primary device, select the sound card in the and click › . The sound device with index
0is the default device and thus used by the system and the applications.By default, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server uses the PulseAudio sound system. It is an abstraction layer that helps to mix multiple audio streams, bypassing any restrictions the hardware may have. To enable or disable the PulseAudio sound system, click › . If enabled, PulseAudio daemon is used to play sounds. Disable to use something else system-wide.
The volume and configuration of all sound cards are saved when you click
and leave the YaST sound module. The mixer settings
are saved to the file /etc/asound.state. The ALSA
configuration data is appended to the end of the file
/etc/modprobe.d/sound and written to
/etc/sysconfig/sound.
11.3 Setting Up a Printer #
YaST can be used to configure a local printer connected to your machine via USB and to set up printing with network printers. It is also possible to share printers over the network. Further information about printing (general information, technical details, and troubleshooting) is available in Chapter 18, Printer Operation.
In YaST, click › to start the printer module. By default it opens in the view, displaying a list of all printers that are available and configured. This is especially useful when having access to a lot of printers via the network. From here you can also and configure printers.
To be able to print from your system, CUPS must run. In case it is not running, you are asked to start it. Answer with , or you cannot configure printing. In case CUPS is not started at boot time, you will also be asked to enable this feature. It is recommended to say , otherwise CUPS would need to be started manually after each reboot.
11.3.1 Configuring Printers #
Usually a USB printer is automatically detected. There are two possible reasons it is not automatically detected:
The USB printer is switched off.
The communication between printer and computer is not possible. Check the cable and the plugs to make sure that the printer is properly connected. If this is the case, the problem may not be printer-related, but rather a USB-related problem.
Configuring a printer is a three-step process: specify the connection type, choose a driver, and name the print queue for this setup.
For many printer models, several drivers are available. When configuring the
printer, YaST defaults to those marked recommended as a
general rule. Normally it is not necessary to change the driver. However, if
you want a color printer to print only in black and white, you can use a driver that does not support color printing. If you experience performance problems with a PostScript printer
when printing graphics, try to switch from a PostScript driver to a
PCL driver (provided your printer understands PCL).
If no driver for your printer is listed, try to select a generic driver with an appropriate standard language from the list. Refer to your printer's documentation to find out which language (the set of commands controlling the printer) your printer understands. If this does not work, refer to Seção 11.3.1.1, “Adding Drivers with YaST” for another possible solution.
A printer is never used directly, but always through a print queue. This ensures that simultaneous jobs can be queued and processed one after the other. Each print queue is assigned to a specific driver, and a printer can have multiple queues. This makes it possible to set up a second queue on a color printer that prints black and white only, for example. Refer to Section 18.1, “The CUPS Workflow” for more information about print queues.
Start the YaST printer module with › .
In the screen click .
If your printer is already listed under
Specify the Connection, proceed with the next step. Otherwise, try to or start the .In the text box under
Find and Assign a Driverenter the vendor name and the model name and click .Choose a driver that matches your printer. It is recommended to choose the driver listed first. If no suitable driver is displayed:
Check your search term
Broaden your search by clicking
Add a driver as described in Seção 11.3.1.1, “Adding Drivers with YaST”
Specify the
Default paper size.In the field, enter a unique name for the print queue.
The printer is now configured with the default settings and ready to use. Click to return to the view. The newly configured printer is now visible in the list of printers.
11.3.1.1 Adding Drivers with YaST #
Not all printer drivers available for SUSE Linux Enterprise Server are installed by default. If no suitable driver is available in the dialog when adding a new printer install a driver package containing drivers for your printers:
Start the YaST printer module with › .
In the screen, click .
In the
Find and Assign a Driversection, click .Choose one or more suitable driver packages from the list. Do not specify the path to a printer description file.
Choose and confirm the package installation.
To directly use these drivers, proceed as described in Procedimento 11.3, “Adding a New Printer”.
PostScript printers do not need printer driver software. PostScript printers need only a PostScript Printer Description (PPD) file which matches the particular model. PPD files are provided by the printer manufacturer.
If no suitable PPD file is available in the dialog when adding a PostScript printer install a PPD file for your printer:
Several sources for PPD files are available. It is recommended to first try additional driver packages that are shipped with SUSE Linux Enterprise Server but not installed by default (see below for installation instructions). If these packages do not contain suitable drivers for your printer, get PPD files directly from your printer vendor or from the driver CD of a PostScript printer. For details, see Section 18.8.2, “No Suitable PPD File Available for a PostScript Printer”. Alternatively, find PPD files at http://www.linuxfoundation.org/collaborate/workgroups/openprinting/database/databaseintro, the “OpenPrinting.org printer database”. When downloading PPD files from OpenPrinting, keep in mind that it always shows the latest Linux support status, which is not necessarily met by SUSE Linux Enterprise Server.
Start the YaST printer module with › .
In the screen, click .
In the
Find and Assign a Driversection, click .Enter the full path to the PPD file into the text box under
Make a Printer Description File Available.Click to return to the
Add New Printer Configurationscreen.To directly use this PPD file, proceed as described in Procedimento 11.3, “Adding a New Printer”.
11.3.1.2 Editing a Local Printer Configuration #
By editing an existing configuration for a printer you can change basic settings such as connection type and driver. It is also possible to adjust the default settings for paper size, resolution, media source, etc. You can change identifiers of the printer by altering the printer description or location.
Start the YaST printer module with › .
In the screen, choose a local printer configuration from the list and click .
Change the connection type or the driver as described in Procedimento 11.3, “Adding a New Printer”. This should only be necessary in case you have problems with the current configuration.
Optionally, make this printer the default by checking .
Adjust the default settings by clicking . To change a setting, expand the list of options by clicking the relative
+sign. Change the default by clicking an option. Apply your changes with .
11.3.2 Configuring Printing via the Network with YaST #
Network printers are not detected automatically. They must be configured manually using the YaST printer module. Depending on your network setup, you can print to a print server (CUPS, LPD, SMB, or IPX) or directly to a network printer (preferably via TCP). Access the configuration view for network printing by choosing from the left pane in the YaST printer module.
11.3.2.1 Using CUPS #
In a Linux environment CUPS is usually used to print via the network. The simplest setup is to only print via a single CUPS server which can directly be accessed by all clients. Printing via more than one CUPS server requires a running local CUPS daemon that communicates with the remote CUPS servers.
CUPS servers announce their print queues over the network either via the
traditional CUPS browsing protocol or via Bonjour/DND-SD. Clients need to
be able to browse these lists, so users can select specific printers to
send their print jobs to. To be able to browse network print queues, the
service cups-browsed provided by
the package
cups-filters-cups-browsed must run on all clients that print via CUPS
servers. cups-browsed is started
automatically when configuring network printing with YaST.
In case browsing does not work after having started
cups-browsed, the CUPS server(s)
probably announce the network print queues via Bonjour/DND-SD. In this
case you need to additionally install the package
avahi and start the associated
service with sudo systemctl start avahi-daemon on all
clients.
Start the YaST printer module with › .
From the left pane, launch the screen.
Check and specify the name or IP address of the server.
Click to make sure you have chosen the correct name or IP address.
Click OK to return to the screen. All printers available via the CUPS server are now listed.
Start the YaST printer module with › .
From the left pane, launch the screen.
Check .
Under
General Settingsspecify which servers to use. You may accept connections from all networks available or from specific hosts. If you choose the latter option, you need to specify the host names or IP addresses.Confirm by clicking and then when asked to start a local CUPS server. After the server has started YaST will return to the screen. Click to see the printers detected by now. Click this button again, in case more printer are to be available.
11.3.2.2 Using Print Servers other than CUPS #
If your network offers print services via print servers other than CUPS, start the YaST printer module with › and launch the screen from the left pane. Start the and choose the appropriate . Ask your network administrator for details on configuring a network printer in your environment.