8 Fleet #
Fleet is a container management and deployment engine designed to offer users more control on the local cluster and constant monitoring through GitOps. Fleet focuses not only on the ability to scale, but it also gives users a high degree of control and visibility to monitor exactly what is installed on the cluster.
Fleet can manage deployments from Git of raw Kubernetes YAML, Helm charts, Kustomize, or any combination of the three. Regardless of the source, all resources are dynamically turned into Helm charts, and Helm is used as the engine to deploy all resources in the cluster. As a result, users can enjoy a high degree of control, consistency and auditability of their clusters.
For information about how Fleet works, see Fleet Architecture.
8.1 Installing Fleet with Helm #
Fleet comes built-in to Rancher, but it can be also installed as a standalone application on any Kubernetes cluster using Helm.
8.2 Using Fleet with Rancher #
Rancher uses Fleet to deploy applications across managed clusters. Continuous delivery with Fleet introduces GitOps at scale, designed to manage applications running on large numbers of clusters.
Fleet shines as an integrated part of Rancher. Clusters managed with Rancher automatically get the Fleet agent deployed as part of the installation/import process and the cluster is immediately available to be managed by Fleet.
8.3 Accessing Fleet in the Rancher UI #
Fleet comes preinstalled in Rancher and is managed by the Continuous Delivery option in the Rancher UI.
Continuous Delivery section consists of following items:
8.3.1 Dashboard #
An overview page of all GitOps repositories across all workspaces. Only the workspaces with repositories are displayed.
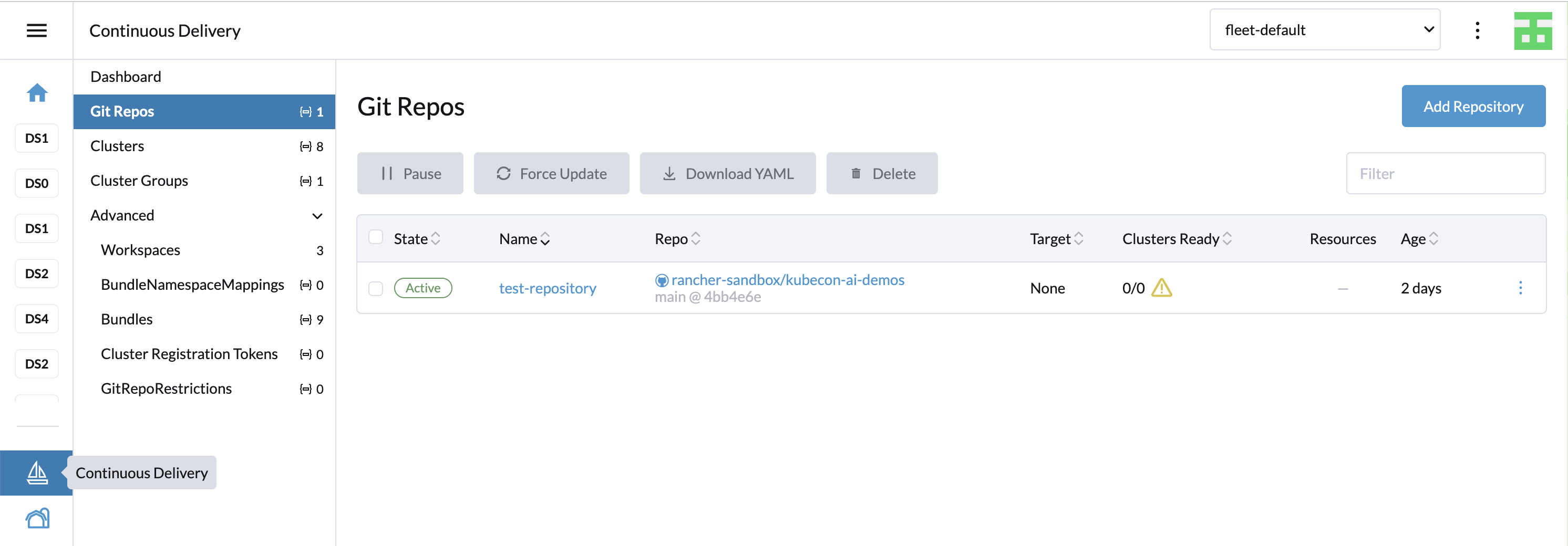
8.3.2 Git repos #
A list of GitOps repositories in the selected workspace. Select the active workspace using the dropdown list at the top of the page.
8.3.3 Clusters #
A list of managed clusters. By default, all Rancher-managed clusters are added to the fleet-default workspace. fleet-local workspace includes the local (management) cluster. From here, it is possible to Pause or Force update the clusters or move the cluster into another workspace. Editing the cluster allows to update labels and annotations used for grouping the clusters.
8.3.4 Cluster groups #
This section allows custom grouping of the clusters within the workspace using selectors.
8.3.5 Advanced #
The "Advanced" section allows to manage workspaces and other related Fleet resources.
8.4 Example of installing KubeVirt with Rancher and Fleet using Rancher dashboard #
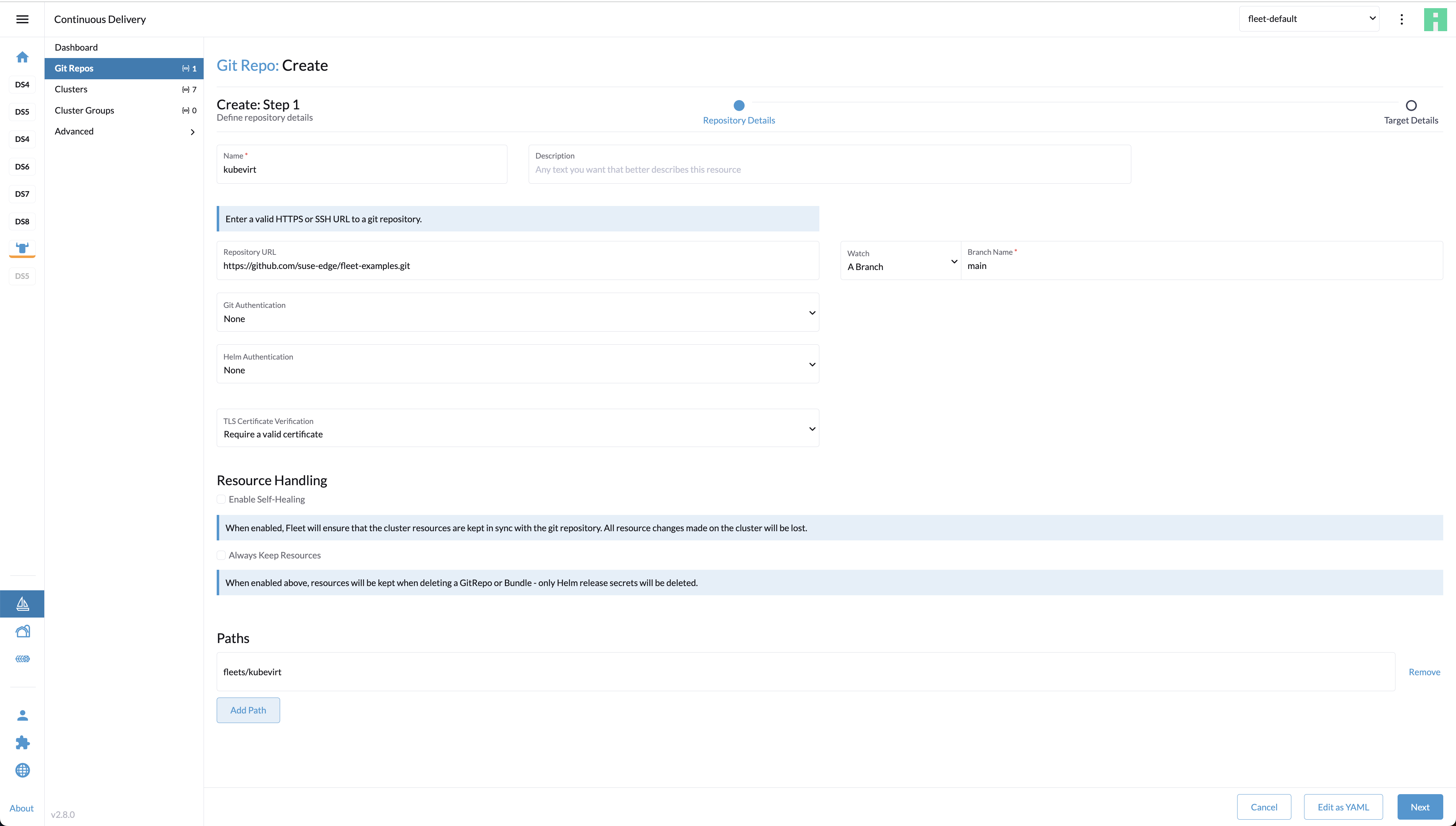
Create a Git repository containing the
fleet.yamlfile:defaultNamespace: kubevirt helm: chart: "oci://registry.suse.com/edge/charts/kubevirt" version: "304.0.1+up0.6.0" # kubevirt namespace is created by kubevirt as well, we need to take ownership of it takeOwnership: trueIn the Rancher dashboard, navigate to ☰ > Continuous Delivery > Git Repos and click
Add Repository.The Repository creation wizard guides through creation of the Git repo. Provide Name, Repository URL (referencing the Git repository created in the previous step) and select the appropriate branch or revision. In the case of a more complex repository, specify Paths to use multiple directories in a single repository.
Click
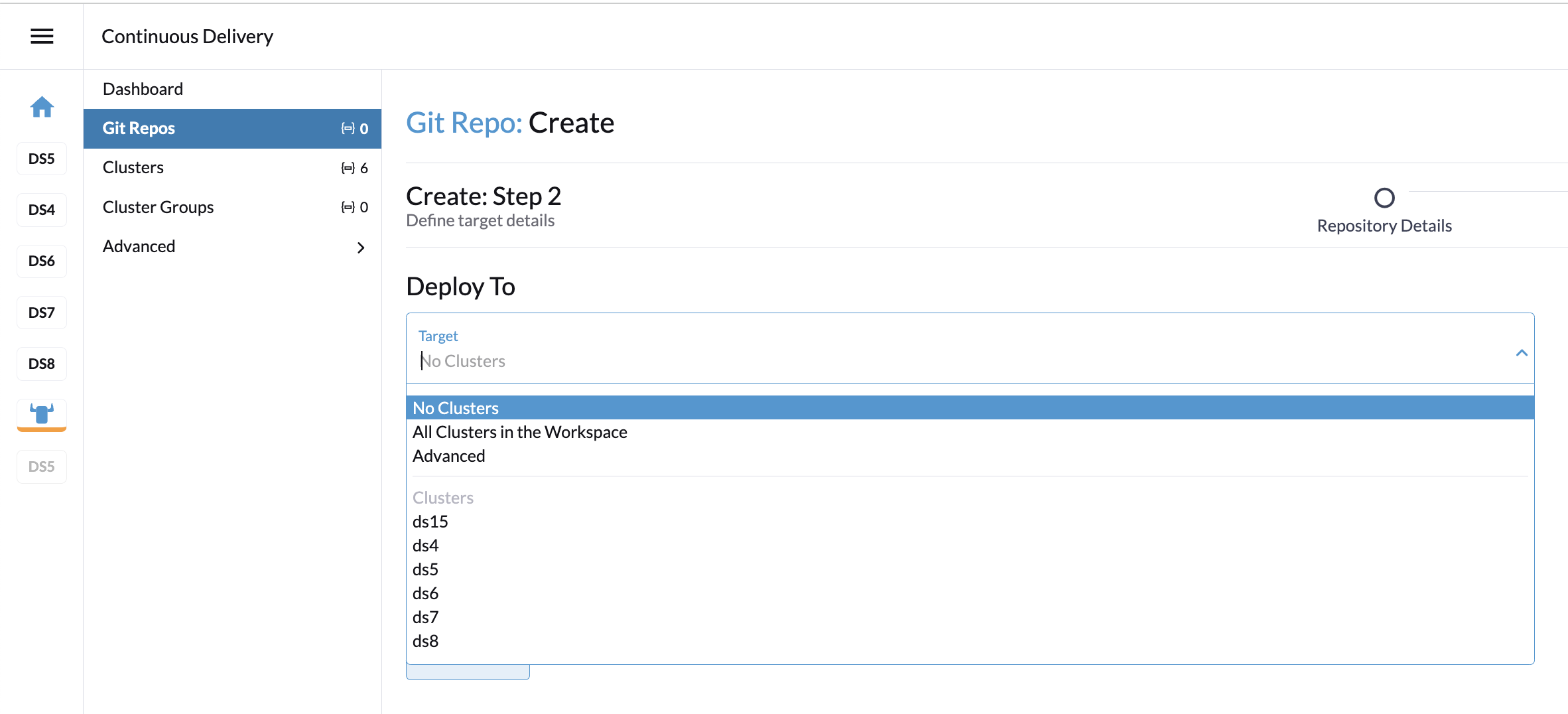
Next.In the next step, you can define where the workloads will get deployed. Cluster selection offers several basic options: you can select no clusters, all clusters, or directly choose a specific managed cluster or cluster group (if defined). The "Advanced" option allows to directly edit the selectors via YAML.
Click
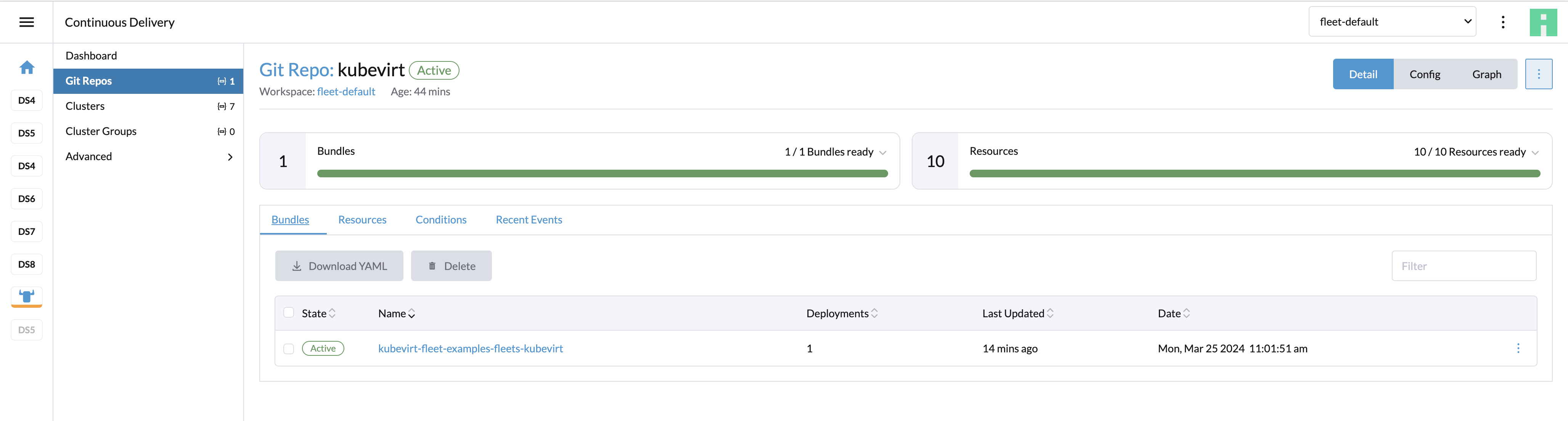
Create. The repository gets created. From now on, the workloads are installed and kept in sync on the clusters matching the repository definition.
8.5 Debugging and troubleshooting #
The "Advanced" navigation section provides overviews of lower-level Fleet resources. A bundle is an internal resource used for the orchestration of resources from Git. When a Git repo is scanned, it produces one or more bundles.
To find bundles relevant to a specific repository, go to the Git repo detail page and click the Bundles tab.
For each cluster, the bundle is applied to a BundleDeployment resource that is created. To view BundleDeployment details, click the Graph button in the upper right of the Git repo detail page.
A graph of Repo > Bundles > BundleDeployments is loaded. Click the BundleDeployment in the graph to see its details and click the Id to view the BundleDeployment YAML.
For additional information on Fleet troubleshooting tips, refer here.
8.6 Fleet examples #
The Edge team maintains a repository with examples of installing Edge projects with Fleet.
The Fleet project includes a fleet-examples repository that covers all use cases for Git repository structure.