14 Managing Container as a Service (Magnum) #
The SUSE OpenStack Cloud Magnum Service provides container orchestration engines such as Docker Swarm, Kubernetes, and Apache Mesos available as first class resources. SUSE OpenStack Cloud Magnum uses heat to orchestrate an OS image which contains Docker and Kubernetes and runs that image in either virtual machines or bare metal in a cluster configuration.
14.1 Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on Fedora Atomic #
14.1.1 Prerequisites #
These steps assume the following have been completed:
The Magnum service has been installed. For more information, see Section 26.2, “Install the Magnum Service”.
Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on Fedora Atomic requires the Fedora Atomic image fedora-atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64.qcow2 prepared specifically for the OpenStack release. You can download the fedora-atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64.qcow2 image from https://fedorapeople.org/groups/magnum/
14.1.2 Creating the Cluster #
The following example is created using Kubernetes Container Orchestration Engine (COE) running on Fedora Atomic guest OS on SUSE OpenStack Cloud VMs.
As stack user, login to the lifecycle manager.
Source openstack admin credentials.
$ source service.osrc
If you haven't already, download Fedora Atomic image, prepared for the Openstack Pike release.
$ wget https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/alt/atomic/stable/Fedora-Atomic-26-20170723.0/CloudImages/x86_64/images/Fedora-Atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64.qcow2
Create a glance image.
$ openstack image create --name fedora-atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64 --visibility public \ --disk-format qcow2 --os-distro fedora-atomic --container-format bare \ --file Fedora-Atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64.qcow2 --progress [=============================>] 100% +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | checksum | 9d233b8e7fbb7ea93f20cc839beb09ab | | container_format | bare | | created_at | 2017-04-10T21:13:48Z | | disk_format | qcow2 | | id | 4277115a-f254-46c0-9fb0-fffc45d2fd38 | | min_disk | 0 | | min_ram | 0 | | name | fedora-atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64 | | os_distro | fedora-atomic | | owner | 2f5b83ab49d54aaea4b39f5082301d09 | | protected | False | | size | 515112960 | | status | active | | tags | [] | | updated_at | 2017-04-10T21:13:56Z | | virtual_size | None | | visibility | public | +------------------+--------------------------------------+
Create a nova keypair.
$ test -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub || ssh-keygen -t rsa -N "" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa $ openstack keypair create --pub-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub testkey
Create a Magnum cluster template.
$ magnum cluster-template-create --name my-template \ --image-id 4277115a-f254-46c0-9fb0-fffc45d2fd38 \ --keypair-id testkey \ --external-network-id ext-net \ --dns-nameserver 8.8.8.8 \ --flavor-id m1.small \ --docker-volume-size 5 \ --network-driver flannel \ --coe kubernetes \ --http-proxy http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080/ \ --https-proxy http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080/
NoteUse the image_id from
openstack image createcommand output in the previous step.Use your organization's DNS server. If the SUSE OpenStack Cloud public endpoint is configured with the hostname, this server should provide resolution for this hostname.
The proxy is only needed if public internet (for example,
https://discovery.etcd.io/orhttps://gcr.io/) is not accessible without proxy.
Create cluster. The command below will create a minimalistic cluster consisting of a single Kubernetes Master (kubemaster) and single Kubernetes Node (worker, kubeminion).
$ magnum cluster-create --name my-cluster --cluster-template my-template --node-count 1 --master-count 1
Immediately after issuing
cluster-createcommand, cluster status should turn to CREATE_IN_PROGRESS and stack_id assigned.$ magnum cluster-show my-cluster +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+ | status | CREATE_IN_PROGRESS | | cluster_template_id | 245c6bf8-c609-4ea5-855a-4e672996cbbc | | uuid | 0b78a205-8543-4589-8344-48b8cfc24709 | | stack_id | 22385a42-9e15-49d9-a382-f28acef36810 | | status_reason | - | | created_at | 2017-04-10T21:25:11+00:00 | | name | my-cluster | | updated_at | - | | discovery_url | https://discovery.etcd.io/193d122f869c497c2638021eae1ab0f7 | | api_address | - | | coe_version | - | | master_addresses | [] | | create_timeout | 60 | | node_addresses | [] | | master_count | 1 | | container_version | - | | node_count | 1 | +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+
You can monitor cluster creation progress by listing the resources of the heat stack. Use the
stack_idvalue from themagnum cluster-statusoutput above in the following command:$ heat resource-list -n2 22385a42-9e15-49d9-a382-f28acef36810 WARNING (shell) "heat resource-list" is deprecated, please use "openstack stack resource list" instead +-------------------------------+--------------------------------------+-----------------------------------+--------------------+----------------------+-------------------------+ | resource_name | physical_resource_id | resource_type | resource_status | updated_time | stack_name | +-------------------------------+--------------------------------------+-----------------------------------+--------------------+----------------------+-------------------------+ | api_address_floating_switch | 06b2cc0d-77f9-4633-8d96-f51e2db1faf3 | Magnum::FloatingIPAddressSwitcher | CREATE_COMPLETE | 2017-04-10T21:25:10Z | my-cluster-z4aquda2mgpv | | api_address_lb_switch | 965124ca-5f62-4545-bbae-8d9cda7aff2e | Magnum::ApiGatewaySwitcher | CREATE_COMPLETE | 2017-04-10T21:25:10Z | my-cluster-z4aquda2mgpv | . . .
The cluster is complete when all resources show CREATE_COMPLETE.
Install kubectl onto your Cloud Lifecycle Manager.
$ export https_proxy=http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080 $ wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.2.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl $ chmod +x ./kubectl $ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
Generate the cluster configuration using
magnum cluster-config. If the CLI option--tls-disabledwas not specified during cluster template creation, authentication in the cluster will be turned on. In this case,magnum cluster-configcommand will generate client authentication certificate (cert.pem) and key (key.pem). Copy and pastemagnum cluster-configoutput to your command line input to finalize configuration (that is, export KUBECONFIG environment variable).$ mkdir my_cluster $ cd my_cluster /my_cluster $ ls /my_cluster $ magnum cluster-config my-cluster export KUBECONFIG=./config /my_cluster $ ls ca.pem cert.pem config key.pem /my_cluster $ export KUBECONFIG=./config /my_cluster $ kubectl version Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"2", GitVersion:"v1.2.0", GitCommit:"5cb86ee022267586db386f62781338b0483733b3", GitTreeState:"clean"} Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"2", GitVersion:"v1.2.0", GitCommit:"cffae0523cfa80ddf917aba69f08508b91f603d5", GitTreeState:"clean"}Create a simple Nginx replication controller, exposed as a service of type NodePort.
$ cat >nginx.yml <<-EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: ReplicationController metadata: name: nginx-controller spec: replicas: 1 selector: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx ports: - containerPort: 80 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx-service spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 80 nodePort: 30080 selector: app: nginx EOF $ kubectl create -f nginx.ymlCheck pod status until it turns from Pending to Running.
$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-controller-5cmev 1/1 Running 0 2m
Ensure that the Nginx welcome page is displayed at port 30080 using the kubemaster floating IP.
$ http_proxy= curl http://172.31.0.6:30080 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
14.2 Deploying a Kubernetes Cluster on CoreOS #
14.2.1 Prerequisites #
These steps assume the following have been completed:
The Magnum service has been installed. For more information, see Section 26.2, “Install the Magnum Service”.
Creating the Magnum cluster requires the CoreOS image for OpenStack. You can download compressed image file coreos_production_openstack_image.img.bz2 from http://stable.release.core-os.net/amd64-usr/current/.
14.2.2 Creating the Cluster #
The following example is created using Kubernetes Container Orchestration Engine (COE) running on CoreOS guest OS on SUSE OpenStack Cloud VMs.
Login to the Cloud Lifecycle Manager.
Source openstack admin credentials.
$ source service.osrc
If you haven't already, download CoreOS image that is compatible for the OpenStack release.
NoteThe https_proxy is only needed if your environment requires a proxy.
$ export https_proxy=http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080 $ wget https://stable.release.core-os.net/amd64-usr/current/coreos_production_openstack_image.img.bz2 $ bunzip2 coreos_production_openstack_image.img.bz2
Create a glance image.
$ openstack image create --name coreos-magnum --visibility public \ --disk-format raw --os-distro coreos --container-format bare \ --file coreos_production_openstack_image.img --progress [=============================>] 100% +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | checksum | 4110469bb15af72ec0cf78c2da4268fa | | container_format | bare | | created_at | 2017-04-25T18:10:52Z | | disk_format | raw | | id | c25fc719-2171-437f-9542-fcb8a534fbd1 | | min_disk | 0 | | min_ram | 0 | | name | coreos-magnum | | os_distro | coreos | | owner | 2f5b83ab49d54aaea4b39f5082301d09 | | protected | False | | size | 806551552 | | status | active | | tags | [] | | updated_at | 2017-04-25T18:11:07Z | | virtual_size | None | | visibility | public | +------------------+--------------------------------------+
Create a nova keypair.
$ test -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub || ssh-keygen -t rsa -N "" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa $ openstack keypair create --pub-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub testkey
Create a Magnum cluster template.
$ magnum cluster-template-create --name my-coreos-template \ --image-id c25fc719-2171-437f-9542-fcb8a534fbd1 \ --keypair-id testkey \ --external-network-id ext-net \ --dns-nameserver 8.8.8.8 \ --flavor-id m1.small \ --docker-volume-size 5 \ --network-driver flannel \ --coe kubernetes \ --http-proxy http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080/ \ --https-proxy http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080/
NoteUse the image_id from
openstack image createcommand output in the previous step.Use your organization's DNS server. If the SUSE OpenStack Cloud public endpoint is configured with the hostname, this server should provide resolution for this hostname.
The proxy is only needed if public internet (for example,
https://discovery.etcd.io/orhttps://gcr.io/) is not accessible without proxy.
Create cluster. The command below will create a minimalistic cluster consisting of a single Kubernetes Master (kubemaster) and single Kubernetes Node (worker, kubeminion).
$ magnum cluster-create --name my-coreos-cluster --cluster-template my-coreos-template --node-count 1 --master-count 1
Almost immediately after issuing
cluster-createcommand, cluster status should turn to CREATE_IN_PROGRESS and stack_id assigned.$ magnum cluster-show my-coreos-cluster +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+ | status | CREATE_IN_PROGRESS | | cluster_template_id | c48fa7c0-8dd9-4da4-b599-9e62dc942ca5 | | uuid | 6b85e013-f7c3-4fd3-81ea-4ea34201fd45 | | stack_id | c93f873a-d563-4721-9bd9-3bae2340750a | | status_reason | - | | created_at | 2017-04-25T22:38:43+00:00 | | name | my-coreos-cluster | | updated_at | - | | discovery_url | https://discovery.etcd.io/6e4c0e5ff5e5b9872173d06880886a0c | | api_address | - | | coe_version | - | | master_addresses | [] | | create_timeout | 60 | | node_addresses | [] | | master_count | 1 | | container_version | - | | node_count | 1 | +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+
You can monitor cluster creation progress by listing the resources of the heat stack. Use the
stack_idvalue from themagnum cluster-statusoutput above in the following command:$ heat resource-list -n2 c93f873a-d563-4721-9bd9-3bae2340750a WARNING (shell) "heat resource-list" is deprecated, please use "openstack stack resource list" instead +--------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------+----------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | resource_name | physical_resource_id | resource_type | resource_status | updated_time | stack_name | +--------------------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------------------------------- ----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------------+----------------------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | api_address_switch | | Magnum::ApiGatewaySwitcher | INIT_COMPLETE | 2017-04-25T22:38:42Z | my-coreos-cluster-mscybll54eoj | . . .The cluster is complete when all resources show CREATE_COMPLETE.
Install kubectl onto your Cloud Lifecycle Manager.
$ export https_proxy=http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080 $ wget https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.2.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl $ chmod +x ./kubectl $ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
Generate the cluster configuration using
magnum cluster-config. If the CLI option--tls-disabledwas not specified during cluster template creation, authentication in the cluster will be turned on. In this case,magnum cluster-configcommand will generate client authentication certificate (cert.pem) and key (key.pem). Copy and pastemagnum cluster-configoutput to your command line input to finalize configuration (that is, export KUBECONFIG environment variable).$ mkdir my_cluster $ cd my_cluster /my_cluster $ ls /my_cluster $ magnum cluster-config my-cluster export KUBECONFIG=./config /my_cluster $ ls ca.pem cert.pem config key.pem /my_cluster $ export KUBECONFIG=./config /my_cluster $ kubectl version Client Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"2", GitVersion:"v1.2.0", GitCommit:"5cb86ee022267586db386f62781338b0483733b3", GitTreeState:"clean"} Server Version: version.Info{Major:"1", Minor:"2", GitVersion:"v1.2.0", GitCommit:"cffae0523cfa80ddf917aba69f08508b91f603d5", GitTreeState:"clean"}Create a simple Nginx replication controller, exposed as a service of type NodePort.
$ cat >nginx.yml <<-EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: ReplicationController metadata: name: nginx-controller spec: replicas: 1 selector: app: nginx template: metadata: labels: app: nginx spec: containers: - name: nginx image: nginx ports: - containerPort: 80 --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: nginx-service spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 80 nodePort: 30080 selector: app: nginx EOF $ kubectl create -f nginx.ymlCheck pod status until it turns from Pending to Running.
$ kubectl get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE nginx-controller-5cmev 1/1 Running 0 2m
Ensure that the Nginx welcome page is displayed at port 30080 using the kubemaster floating IP.
$ http_proxy= curl http://172.31.0.6:30080 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
14.3 Deploying a Docker Swarm Cluster on Fedora Atomic #
14.3.1 Prerequisites #
These steps assume the following have been completed:
The Magnum service has been installed. For more information, see Section 26.2, “Install the Magnum Service”.
Deploying a Docker Swarm Cluster on Fedora Atomic requires the Fedora Atomic image fedora-atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64.qcow2 prepared specifically for the OpenStack Pike release. You can download the fedora-atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64.qcow2 image from https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/alt/atomic/stable/Fedora-Atomic-26-20170723.0/CloudImages/x86_64/
14.3.2 Creating the Cluster #
The following example is created using Kubernetes Container Orchestration Engine (COE) running on Fedora Atomic guest OS on SUSE OpenStack Cloud VMs.
As stack user, login to the lifecycle manager.
Source openstack admin credentials.
$ source service.osrc
If you haven't already, download Fedora Atomic image, prepared for Openstack Pike release.
$ wget https://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/alt/atomic/stable/Fedora-Atomic-26-20170723.0/CloudImages/x86_64/images/Fedora-Atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64.qcow2
Create a glance image.
$ openstack image create --name fedora-atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64 --visibility public \ --disk-format qcow2 --os-distro fedora-atomic --container-format bare \ --file Fedora-Atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64.qcow2 --progress [=============================>] 100% +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | checksum | 9d233b8e7fbb7ea93f20cc839beb09ab | | container_format | bare | | created_at | 2017-04-10T21:13:48Z | | disk_format | qcow2 | | id | 4277115a-f254-46c0-9fb0-fffc45d2fd38 | | min_disk | 0 | | min_ram | 0 | | name | fedora-atomic-26-20170723.0.x86_64 | | os_distro | fedora-atomic | | owner | 2f5b83ab49d54aaea4b39f5082301d09 | | protected | False | | size | 515112960 | | status | active | | tags | [] | | updated_at | 2017-04-10T21:13:56Z | | virtual_size | None | | visibility | public | +------------------+--------------------------------------+
Create a nova keypair.
$ test -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub || ssh-keygen -t rsa -N "" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa $ openstack keypair create --pub-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub testkey
Create a Magnum cluster template.
NoteThe
--tls-disabledflag is not specified in the included template. Authentication via client certificate will be turned on in clusters created from this template.$ magnum cluster-template-create --name my-swarm-template \ --image-id 4277115a-f254-46c0-9fb0-fffc45d2fd38 \ --keypair-id testkey \ --external-network-id ext-net \ --dns-nameserver 8.8.8.8 \ --flavor-id m1.small \ --docker-volume-size 5 \ --network-driver docker \ --coe swarm \ --http-proxy http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080/ \ --https-proxy http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080/
NoteUse the
image_idfromopenstack image createcommand output in the previous step.Use your organization's DNS server. If the SUSE OpenStack Cloud public endpoint is configured with the hostname, this server should provide resolution for this hostname.
The proxy is only needed if public internet (for example,
https://discovery.etcd.io/orhttps://gcr.io/) is not accessible without proxy.
Create cluster. The command below will create a minimalistic cluster consisting of a single Kubernetes Master (kubemaster) and single Kubernetes Node (worker, kubeminion).
$ magnum cluster-create --name my-swarm-cluster --cluster-template my-swarm-template \ --node-count 1 --master-count 1
Immediately after issuing
cluster-createcommand, cluster status should turn to CREATE_IN_PROGRESS andstack_idassigned.$ magnum cluster-show my-swarm-cluster +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+ | status | CREATE_IN_PROGRESS | | cluster_template_id | 17df266e-f8e1-4056-bdee-71cf3b1483e3 | | uuid | c3e13e5b-85c7-44f4-839f-43878fe5f1f8 | | stack_id | 3265d843-3677-4fed-bbb7-e0f56c27905a | | status_reason | - | | created_at | 2017-04-21T17:13:08+00:00 | | name | my-swarm-cluster | | updated_at | - | | discovery_url | https://discovery.etcd.io/54e83ea168313b0c2109d0f66cd0aa6f | | api_address | - | | coe_version | - | | master_addresses | [] | | create_timeout | 60 | | node_addresses | [] | | master_count | 1 | | container_version | - | | node_count | 1 | +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+
You can monitor cluster creation progress by listing the resources of the heat stack. Use the
stack_idvalue from themagnum cluster-statusoutput above in the following command:$ heat resource-list -n2 3265d843-3677-4fed-bbb7-e0f56c27905a WARNING (shell) "heat resource-list" is deprecated, please use "openstack stack resource list" instead +--------------------+--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------+-----------------+----------------------+-------------------------------+ | resource_name | physical_resource_id | resource_type | resource_status | updated_time | stack_name | |--------------------+--------------------------------------+--------------------------------------------+-----------------+----------------------+-------------------------------+ | api_address_switch | 430f82f2-03e3-4085-8c07-b4a6b6d7e261 | Magnum::ApiGatewaySwitcher | CREATE_COMPLETE | 2017-04-21T17:13:07Z | my-swarm-cluster-j7gbjcxaremy | . . .
The cluster is complete when all resources show CREATE_COMPLETE. You can also obtain the floating IP address once the cluster has been created.
$ magnum cluster-show my-swarm-cluster +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+ | status | CREATE_COMPLETE | | cluster_template_id | 17df266e-f8e1-4056-bdee-71cf3b1483e3 | | uuid | c3e13e5b-85c7-44f4-839f-43878fe5f1f8 | | stack_id | 3265d843-3677-4fed-bbb7-e0f56c27905a | | status_reason | Stack CREATE completed successfully | | created_at | 2017-04-21T17:13:08+00:00 | | name | my-swarm-cluster | | updated_at | 2017-04-21T17:18:26+00:00 | | discovery_url | https://discovery.etcd.io/54e83ea168313b0c2109d0f66cd0aa6f | | api_address | tcp://172.31.0.7:2376 | | coe_version | 1.0.0 | | master_addresses | ['172.31.0.7'] | | create_timeout | 60 | | node_addresses | ['172.31.0.5'] | | master_count | 1 | | container_version | 1.9.1 | | node_count | 1 | +---------------------+------------------------------------------------------------+
Generate and sign client certificate using
magnum cluster-configcommand.$ mkdir my_swarm_cluster $ cd my_swarm_cluster/ ~/my_swarm_cluster $ magnum cluster-config my-swarm-cluster {'tls': True, 'cfg_dir': '.', 'docker_host': u'tcp://172.31.0.7:2376'} ~/my_swarm_cluster $ ls ca.pem cert.pem key.pemCopy generated certificates and key to ~/.docker folder on first cluster master node.
$ scp -r ~/my_swarm_cluster fedora@172.31.0.7:.docker ca.pem 100% 1066 1.0KB/s 00:00 key.pem 100% 1679 1.6KB/s 00:00 cert.pem 100% 1005 1.0KB/s 00:00
Login to first master node and set up cluster access environment variables.
$ ssh fedora@172.31.0.7 [fedora@my-6zxz5ukdu-0-bvqbsn2z2uwo-swarm-master-n6wfplu7jcwo ~]$ export DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY=1 [fedora@my-6zxz5ukdu-0-bvqbsn2z2uwo-swarm-master-n6wfplu7jcwo ~]$ export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://172.31.0.7:2376
Verfy that the swarm container is up and running.
[fedora@my-6zxz5ukdu-0-bvqbsn2z2uwo-swarm-master-n6wfplu7jcwo ~]$ docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES fcbfab53148c swarm:1.0.0 "/swarm join --addr 1" 24 minutes ago Up 24 minutes 2375/tcp my-xggjts5zbgr-0-d4qhxhdujh4q-swarm-node-vieanhwdonon.novalocal/swarm-agent
Deploy a sample docker application (nginx) and verify that Nginx is serving requests at port 8080 on worker node(s), on both floating and private IPs:
[fedora@my-6zxz5ukdu-0-bvqbsn2z2uwo-swarm-master-n6wfplu7jcwo ~]$ docker run -itd -p 8080:80 nginx 192030325fef0450b7b917af38da986edd48ac5a6d9ecb1e077b017883d18802 [fedora@my-6zxz5ukdu-0-bvqbsn2z2uwo-swarm-master-n6wfplu7jcwo ~]$ docker port 192030325fef 80/tcp -> 10.0.0.11:8080 [fedora@my-6zxz5ukdu-0-bvqbsn2z2uwo-swarm-master-n6wfplu7jcwo ~]$ curl http://10.0.0.11:8080 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> ... [fedora@my-6zxz5ukdu-0-bvqbsn2z2uwo-swarm-master-n6wfplu7jcwo ~]$ curl http://172.31.0.5:8080 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> ...
14.4 Deploying an Apache Mesos Cluster on Ubuntu #
14.4.1 Prerequisites #
These steps assume the following have been completed:
The Magnum service has been installed. For more information, see Section 26.2, “Install the Magnum Service”.
Deploying an Apache Mesos Cluster requires the Fedora Atomic image that is compatible for the OpenStack release. You can download the ubuntu-mesos-latest.qcow2 image from https://fedorapeople.org/groups/magnum/
14.4.2 Creating the Cluster #
The following example is created using Kubernetes Container Orchestration Engine (COE) running on Fedora Atomic guest OS on SUSE OpenStack Cloud VMs.
As stack user, login to the lifecycle manager.
Source openstack admin credentials.
$ source service.osrc
If you haven't already, download Fedora Atomic image that is compatible for the OpenStack release.
NoteThe
https_proxyis only needed if your environment requires a proxy.$ https_proxy=http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080 wget https://fedorapeople.org/groups/magnum/ubuntu-mesos-latest.qcow2
Create a glance image.
$ openstack image create --name ubuntu-mesos-latest --visibility public --disk-format qcow2 --os-distro ubuntu --container-format bare --file ubuntu-mesos-latest.qcow2 --progress [=============================>] 100% +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +------------------+--------------------------------------+ | checksum | 97cc1fdb9ca80bf80dbd6842aab7dab5 | | container_format | bare | | created_at | 2017-04-21T19:40:20Z | | disk_format | qcow2 | | id | d6a4e6f9-9e34-4816-99fe-227e0131244f | | min_disk | 0 | | min_ram | 0 | | name | ubuntu-mesos-latest | | os_distro | ubuntu | | owner | 2f5b83ab49d54aaea4b39f5082301d09 | | protected | False | | size | 753616384 | | status | active | | tags | [] | | updated_at | 2017-04-21T19:40:32Z | | virtual_size | None | | visibility | public | +------------------+--------------------------------------+
Create a nova keypair.
$ test -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub || ssh-keygen -t rsa -N "" -f ~/.ssh/id_rsa $ openstack keypair create --pub-key ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub testkey
Create a Magnum cluster template.
$ magnum cluster-template-create --name my-mesos-template \ --image-id d6a4e6f9-9e34-4816-99fe-227e0131244f \ --keypair-id testkey \ --external-network-id ext-net \ --dns-nameserver 8.8.8.8 \ --flavor-id m1.small \ --docker-volume-size 5 \ --network-driver docker \ --coe mesos \ --http-proxy http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080/ \ --https-proxy http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080/
NoteUse the image_id from
openstack image createcommand output in the previous step.Use your organization's DNS server. If the SUSE OpenStack Cloud public endpoint is configured with the hostname, this server should provide resolution for this hostname.
The proxy is only needed if public internet (for example,
https://discovery.etcd.io/orhttps://gcr.io/) is not accessible without proxy.
Create cluster. The command below will create a minimalistic cluster consisting of a single Kubernetes Master (kubemaster) and single Kubernetes Node (worker, kubeminion).
$ magnum cluster-create --name my-mesos-cluster --cluster-template my-mesos-template --node-count 1 --master-count 1
Immediately after issuing
cluster-createcommand, cluster status should turn to CREATE_IN_PROGRESS and stack_id assigned.$ magnum cluster-show my-mesos-cluster +---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | status | CREATE_IN_PROGRESS | | cluster_template_id | be354919-fa6c-4db8-9fd1-69792040f095 | | uuid | b1493402-8571-4683-b81e-ddc129ff8937 | | stack_id | 50aa20a6-bf29-4663-9181-cf7ba3070a25 | | status_reason | - | | created_at | 2017-04-21T19:50:34+00:00 | | name | my-mesos-cluster | | updated_at | - | | discovery_url | - | | api_address | - | | coe_version | - | | master_addresses | [] | | create_timeout | 60 | | node_addresses | [] | | master_count | 1 | | container_version | - | | node_count | 1 | +---------------------+--------------------------------------+
You can monitor cluster creation progress by listing the resources of the heat stack. Use the
stack_idvalue from themagnum cluster-statusoutput above in the following command:$ heat resource-list -n2 50aa20a6-bf29-4663-9181-cf7ba3070a25 WARNING (shell) "heat resource-list" is deprecated, please use "openstack stack resource list" instead +------------------------------+--------------------------------------+-----------------------------------+-----------------+----------------------+-------------------------------+ | resource_name | physical_resource_id | resource_type | resource_status | updated_time | stack_name | +------------------------------+--------------------------------------+-----------------------------------+-----------------+----------------------+-------------------------------+ | add_proxy_master | 10394a74-1503-44b4-969a-44258c9a7be1 | OS::heat::SoftwareConfig | CREATE_COMPLETE | 2017-04-21T19:50:33Z | my-mesos-cluster-w2trq7m46qus | | add_proxy_master_deployment | | OS::heat::SoftwareDeploymentGroup | INIT_COMPLETE | 2017-04-21T19:50:33Z | my-mesos-cluster-w2trq7m46qus | ...
The cluster is complete when all resources show CREATE_COMPLETE.
$ magnum cluster-show my-mesos-cluster +---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | Property | Value | +---------------------+--------------------------------------+ | status | CREATE_COMPLETE | | cluster_template_id | 9e942bfa-2c78-4837-82f5-6bea88ba1bf9 | | uuid | 9d7bb502-8865-4cbd-96fa-3cd75f0f6945 | | stack_id | 339a72b4-a131-47c6-8d10-365e6f6a18cf | | status_reason | Stack CREATE completed successfully | | created_at | 2017-04-24T20:54:31+00:00 | | name | my-mesos-cluster | | updated_at | 2017-04-24T20:59:18+00:00 | | discovery_url | - | | api_address | 172.31.0.10 | | coe_version | - | | master_addresses | ['172.31.0.10'] | | create_timeout | 60 | | node_addresses | ['172.31.0.5'] | | master_count | 1 | | container_version | 1.9.1 | | node_count | 1 | +---------------------+--------------------------------------+
Verify that Marathon web console is available at http://${MASTER_IP}:8080/, and Mesos UI is available at http://${MASTER_IP}:5050/
$ https_proxy=http://proxy.yourcompany.net:8080 curl -LO \ https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.2.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl $ chmod +x ./kubectl $ sudo mv ./kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
Create an example Mesos application.
$ mkdir my_mesos_cluster $ cd my_mesos_cluster/ $ cat > sample.json <<-EOFc { "id": "sample", "cmd": "python3 -m http.server 8080", "cpus": 0.5, "mem": 32.0, "container": { "type": "DOCKER", "docker": { "image": "python:3", "network": "BRIDGE", "portMappings": [ { "containerPort": 8080, "hostPort": 0 } ] } } } EOF$ curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ http://172.31.0.10:8080/v2/apps -d@sample.json | json_pp { "dependencies" : [], "healthChecks" : [], "user" : null, "mem" : 32, "requirePorts" : false, "tasks" : [], "cpus" : 0.5, "upgradeStrategy" : { "minimumHealthCapacity" : 1, "maximumOverCapacity" : 1 }, "maxLaunchDelaySeconds" : 3600, "disk" : 0, "constraints" : [], "executor" : "", "cmd" : "python3 -m http.server 8080", "id" : "/sample", "labels" : {}, "ports" : [ 0 ], "storeUrls" : [], "instances" : 1, "tasksRunning" : 0, "tasksHealthy" : 0, "acceptedResourceRoles" : null, "env" : {}, "tasksStaged" : 0, "tasksUnhealthy" : 0, "backoffFactor" : 1.15, "version" : "2017-04-25T16:37:40.657Z", "uris" : [], "args" : null, "container" : { "volumes" : [], "docker" : { "portMappings" : [ { "containerPort" : 8080, "hostPort" : 0, "servicePort" : 0, "protocol" : "tcp" } ], "parameters" : [], "image" : "python:3", "forcePullImage" : false, "network" : "BRIDGE", "privileged" : false }, "type" : "DOCKER" }, "deployments" : [ { "id" : "6fbe48f0-6a3c-44b7-922e-b172bcae1be8" } ], "backoffSeconds" : 1 }Wait for sample application to start. Use REST API or Marathon web console to monitor status:
$ curl -s http://172.31.0.10:8080/v2/apps/sample | json_pp { "app" : { "deployments" : [], "instances" : 1, "tasks" : [ { "id" : "sample.7fdd1ee4-29d5-11e7-9ee0-02427da4ced1", "stagedAt" : "2017-04-25T16:37:40.807Z", "version" : "2017-04-25T16:37:40.657Z", "ports" : [ 31827 ], "appId" : "/sample", "slaveId" : "21444bc5-3eb8-49cd-b020-77041e0c88d0-S0", "host" : "10.0.0.9", "startedAt" : "2017-04-25T16:37:42.003Z" } ], "upgradeStrategy" : { "maximumOverCapacity" : 1, "minimumHealthCapacity" : 1 }, "storeUrls" : [], "requirePorts" : false, "user" : null, "id" : "/sample", "acceptedResourceRoles" : null, "tasksRunning" : 1, "cpus" : 0.5, "executor" : "", "dependencies" : [], "args" : null, "backoffFactor" : 1.15, "ports" : [ 10000 ], "version" : "2017-04-25T16:37:40.657Z", "container" : { "volumes" : [], "docker" : { "portMappings" : [ { "servicePort" : 10000, "protocol" : "tcp", "hostPort" : 0, "containerPort" : 8080 } ], "forcePullImage" : false, "parameters" : [], "image" : "python:3", "privileged" : false, "network" : "BRIDGE" }, "type" : "DOCKER" }, "constraints" : [], "tasksStaged" : 0, "env" : {}, "mem" : 32, "disk" : 0, "labels" : {}, "tasksHealthy" : 0, "healthChecks" : [], "cmd" : "python3 -m http.server 8080", "backoffSeconds" : 1, "maxLaunchDelaySeconds" : 3600, "versionInfo" : { "lastConfigChangeAt" : "2017-04-25T16:37:40.657Z", "lastScalingAt" : "2017-04-25T16:37:40.657Z" }, "uris" : [], "tasksUnhealthy" : 0 } }Verify that deployed application is responding on automatically assigned port on floating IP address of worker node.
$ curl http://172.31.0.5:31827 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8"> <title>Directory listing for /</title> ...
14.5 Creating a Magnum Cluster with the Dashboard #
You can alternatively create a cluster template and cluster with the Magnum
UI in horizon. The example instructions below demonstrate how to deploy a
Kubernetes Cluster using the Fedora Atomic image. Other deployments such as
Kubernetes on CoreOS, Docker Swarm on Fedora, and Mesos on Ubuntu all follow
the same set of instructions mentioned below with slight variations to their
parameters. You can determine those parameters by looking at the previous
set of CLI instructions in the
magnum cluster-template-create and
magnum cluster-create commands.
14.5.1 Prerequisites #
Magnum must be installed before proceeding. For more information, see Section 26.2, “Install the Magnum Service”.
ImportantPay particular attention to
external-name:indata/network_groups.yml. This cannot be set to the defaultmyardana.testand must be a valid DNS-resolvable FQDN. If you do not have a DNS-resolvable FQDN, remove or comment out theexternal-nameentry and the public endpoint will use an IP address instead of a name.The image for which you want to base your cluster on must already have been uploaded into glance. See the previous CLI instructions regarding deploying a cluster on how this is done.
14.5.2 Creating the Cluster Template #
You will need access to the Dashboard to create the cluster template.
Open a web browser that has both JavaScript and cookies enabled. In the address bar, enter the host name or IP address for the dashboard.
On the page, enter your user name and password and then click .
Make sure you are in the appropriate domain and project in the left pane. Below is an example image of the drop-down box:
A key pair is required for cluster template creation. It is applied to VMs created during the cluster creation process. This allows SSH access to your cluster's VMs. If you would like to create a new key pair, do so by going to › › › .
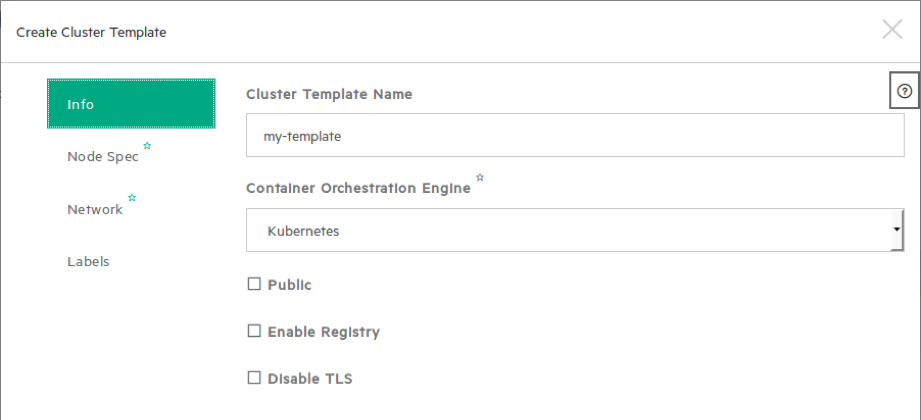
Go to › › . Insert CLUSTER_NAME and click on with the following options:
- makes the template available for others to use.
- creates and uses a private docker registry backed by OpenStack swift in addition to using the public docker registry.
- turns off TLS encryption. For Kubernetes clusters which use client certificate authentication, disabling TLS also involves disabling authentication.
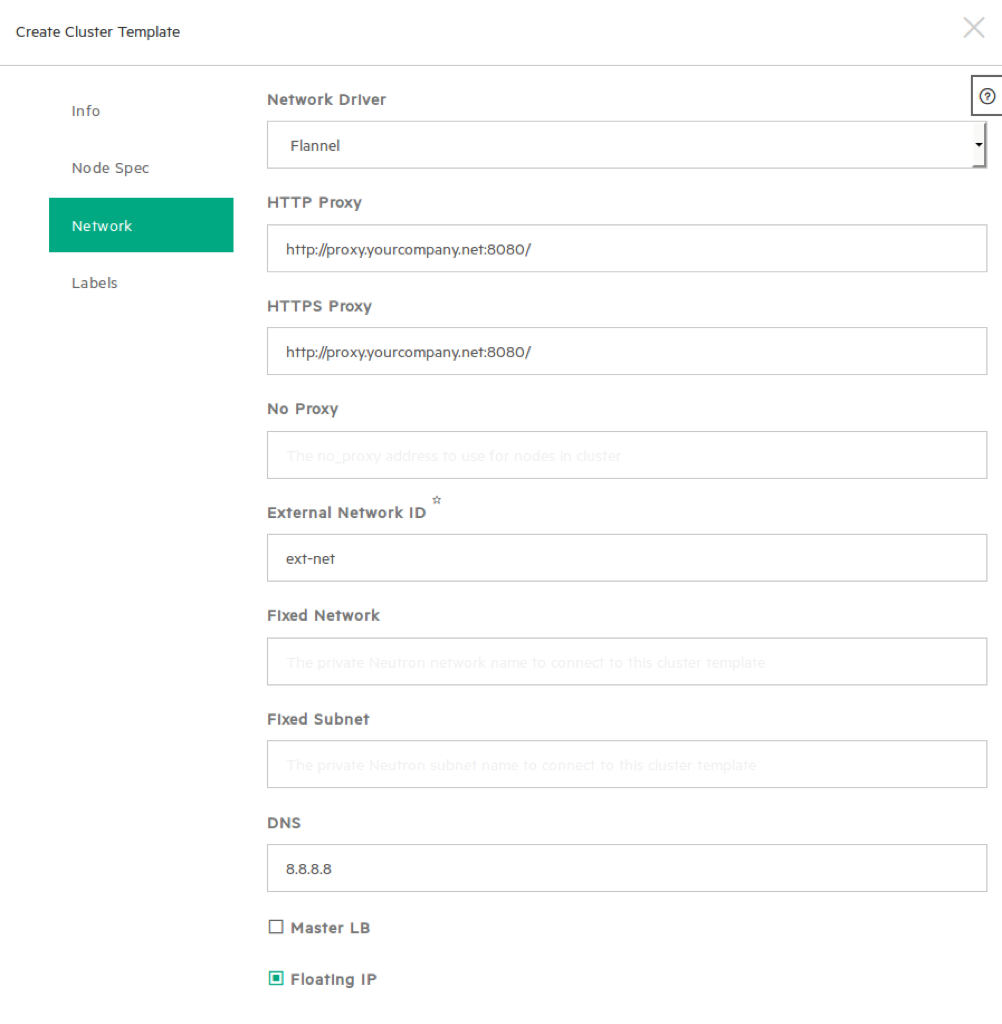
Proxies are only needed if the created VMs require a proxy to connect externally.
– This should be turned off; LbaaS v2 (Octavia) is not available in SUSE OpenStack Cloud.
– This assigns floating IPs to the cluster nodes when the cluster is being created. This should be selected if you wish to ssh into the cluster nodes, perform diagnostics and additional tuning to Kubernetes.
Click the button to create the cluster template and you should see my-template in the list of templates.