Rancher RBAC
Overview
The SUSE Rancher Prime Observability Extension uses Kubernetes RBAC to grant access to Rancher users in SUSE Observability. If you do not use Rancher, look at How to set up roles in a stand-alone installation.
|
For Rancher RBAC to function,
|
Every authenticated user has the Instance Basic Access role that allows them to use the system. These permissions provide access to the views, settings, metric bindings, and lets a user see system notifications. They do NOT grant access to any SUSE® Observability data. In order to see any data, a user needs to be given an additional role. Two directions for extending the Instance Basic Access role are provided with Rancher Role Templates:
- Instance Roles
-
Enables you to configure or personalize SUSE® Observability.
- Scoped Roles
-
Grants access to SUSE® Observability data from observed clusters.
Instance roles
You can assign the Role Templates for Instance Roles to users or groups in the Project that is running SUSE® Observability. If no instance roles are explicitly assigned to a member of a project, then they will have the permissions of the Instance Basic Access role.
Instance roles with access to SUSE® Observability data
A couple of "global" roles allow access to all SUSE® Observability data - in any of the observed clusters. These roles are intended to be used for setting up the system and for troubleshooting system-level problems. For users with any of these roles, it is not necessary to configure Scoped Roles.
- Instance Admin
-
Grants full access to all views and all permissions.
- Instance Troubleshooter
-
Grants all permissions required to use SUSE Observability for troubleshooting, including the ability to enable/disable monitors, create custom views, and use the CLI.
- Instance Observer
-
Grants access to all data in a SUSE Observability instance.
Instance roles without access to SUSE® Observability data
These roles need to be combined with the Instance Observer role or one of the Scoped Roles (see below). Otherwise, no SUSE® Observability data is accessible and the UI will show a "No components found" message. This applies to all Rancher users, including users, such as Project owners.
- Instance Recommended Access
-
Grants recommended permissions to use SUSE Observability. This role includes permissions that are not strictly necessary, but provide (limited) means of personalization SUSE® Observability.
- Instance Basic Access
-
Grants minimal permissions to use SUSE® Observability. This role does not need to be explicitly assigned and there is no Role Template for it; every logged-in user has it.
You can find the permissions assigned to each predefined SUSE Observability role below. For details of the different permissions and how to manage them using the sts CLI, see Role based access control (RBAC) permissions
-
Basic Access
-
Recommended Access
-
Observer
-
Troubleshooter
-
Admin
Basic access grants minimal permissions for using SUSE Observability. To be combined with an Observer (Instance, Cluster or Project). These permissions are granted to all users.
| Resource | Verbs |
|---|---|
metric-bindings |
get |
settings |
get |
system-notifications |
get |
views |
get |
Recommended access grants permissions that are not strictly necessary, but that make SUSE Observability a lot more useful. It provides a limited degree of personalization. To be combined with an Observer (Instance, Cluster or Project).
| Resource | Verbs |
|---|---|
api-tokens |
get |
favorite-dashboards |
create, delete |
favorite-views |
create, delete |
stackpacks |
get |
visualization-settings |
update |
Observer grants access to all observability data in a SUSE Observability instance. Combine with Recommended Access for a better experience.
| Resource | Verbs |
|---|---|
topology |
get |
metrics |
get |
traces |
get |
The Troubleshooter role has access to all data available in SUSE Observability and the ability to create views and enable/disable monitors.
| Resource | Verbs |
|---|---|
agents |
get |
api-tokens |
get |
component-actions |
execute |
dashboards |
get, create, update, delete |
favorite-dashboards |
create, delete |
favorite-views |
create, delete |
metric-bindings |
get |
metrics |
get |
monitors |
get, create, update, delete, execute |
notifications |
get, create, update, delete |
settings |
get |
stackpack-configurations |
get, create, update, delete |
stackpacks |
get |
system-notifications |
get |
topology |
get |
traces |
get |
views |
get, create, update, delete |
visualization-settings |
get |
The Administrator role has all permissions assigned.
| Resource | Verbs |
|---|---|
agents |
get |
api-tokens |
get |
component-actions |
execute |
dashboards |
get, create, update, delete |
favorite-dashboards |
create, delete |
favorite-views |
create, delete |
ingestion-api-keys |
get, create, update, delete |
metric-bindings |
get |
metrics |
get |
monitors |
get, create, update, delete, execute |
notifications |
get, create, update, delete |
permissions |
get, create, update, delete |
restricted-scripts |
execute |
service-tokens |
get, create, update, delete |
settings |
get, create, update, delete, unlock |
stackpack-configurations |
get, create, update, delete |
stackpacks |
get, create |
sync-data |
get, update, delete |
system-notifications |
get |
topic-messages |
get |
topology |
get |
traces |
get |
views |
get, create, update, delete |
visualization-settings |
update |
Scoped roles
You can assign the following Role Templates to users or groups in an observed cluster. They grant access to SUSE® Observability data coming from (a Project in) the Cluster, giving a user permission to read topology, metrics, logs and trace data.
- Observer
-
Grants access to data coming from namespaces in a Project. You can use this in the Project Membership section of the cluster configuration.
- Cluster Observer
-
Grants access to all data coming from a Cluster. You can use this template in the Cluster Membership section of the cluster configuration.
The resources in these roles correspond to Scoped Permissions. They are available in the scope.observability.cattle.io API Group (with just verb get as these resources are read only):
-
topology- components (deployments, pods, etcetera) from the cluster or namespace -
traces- spans from the cluster or namespace -
metrics- metric data originating from the cluster or namespace
Note that access to logs is controlled by the topology resource.
Enable personalization for users with these observer roles by granting the Instance Recommended Access role on the Project running SUSE® Observability.
Custom roles
To grant additional permissions beyond Recommended Access, create a custom Project RoleTemplate in Rancher, inheriting from SUSE Observability Instance Recommended Access. Then, for example, to grant the rights to view monitors and metric charts, add rules with:
-
Verb:
get -
Resource:
metricbindingsandmonitors -
ApiGroup:
instance.observability.cattle.io
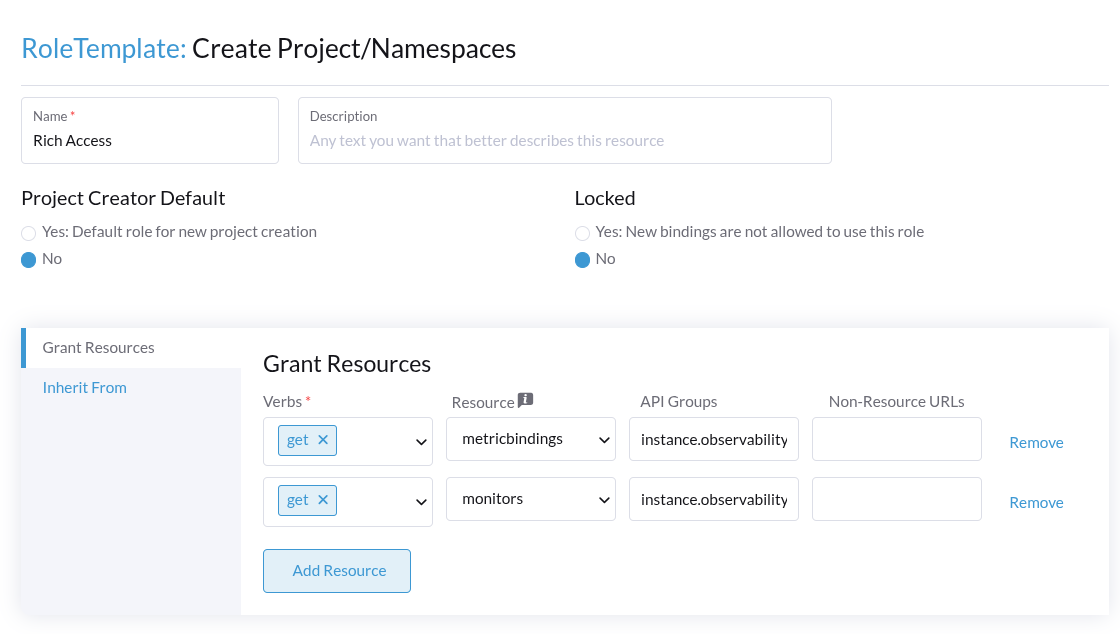
You can specify any resource and verb combination defined in the RBAC Permissions. Note that the dashes (-) are dropped from resource names, so the permission get-metric-bindings becomes the Kubernetes RBAC resource metricbindings with the verb get.
Troubleshooting
-
Verify that the Rbac Agent for the cluster is able to communicate with the platform.
-
Inspect the user subjects (user and roles).
-
Verify any roles configuration on the OIDC provider.
-
-
Inspect the subject permission
-
Verify that the relevant (Cluster)RoleBindings that match the user with a (Cluster)Role are present.
-
Inspect the (Cluster)Role to verify that it grants the correct permissions.
-