VM Import Controller
You can import virtual machines from VMware, OpenStack, and Open Virtual Appliance (OVA) packages into SUSE Virtualization using the vm-import-controller add-on. The add-on must be enabled before you start importing virtual machines.

By default, vm-import-controller leverages ephemeral storage, which is mounted from /var/lib/kubelet.
During the migration, a large VM’s node could run out of space on this mount, resulting in subsequent scheduling failures.
To avoid this, users are advised to enable PVC-backed storage and customize the amount of storage needed. According to the best practice, the PVC size should be twice the size of the largest VM being migrated. This is essential as the PVC is used as scratch space to download the VM, and convert the disks into raw image files.
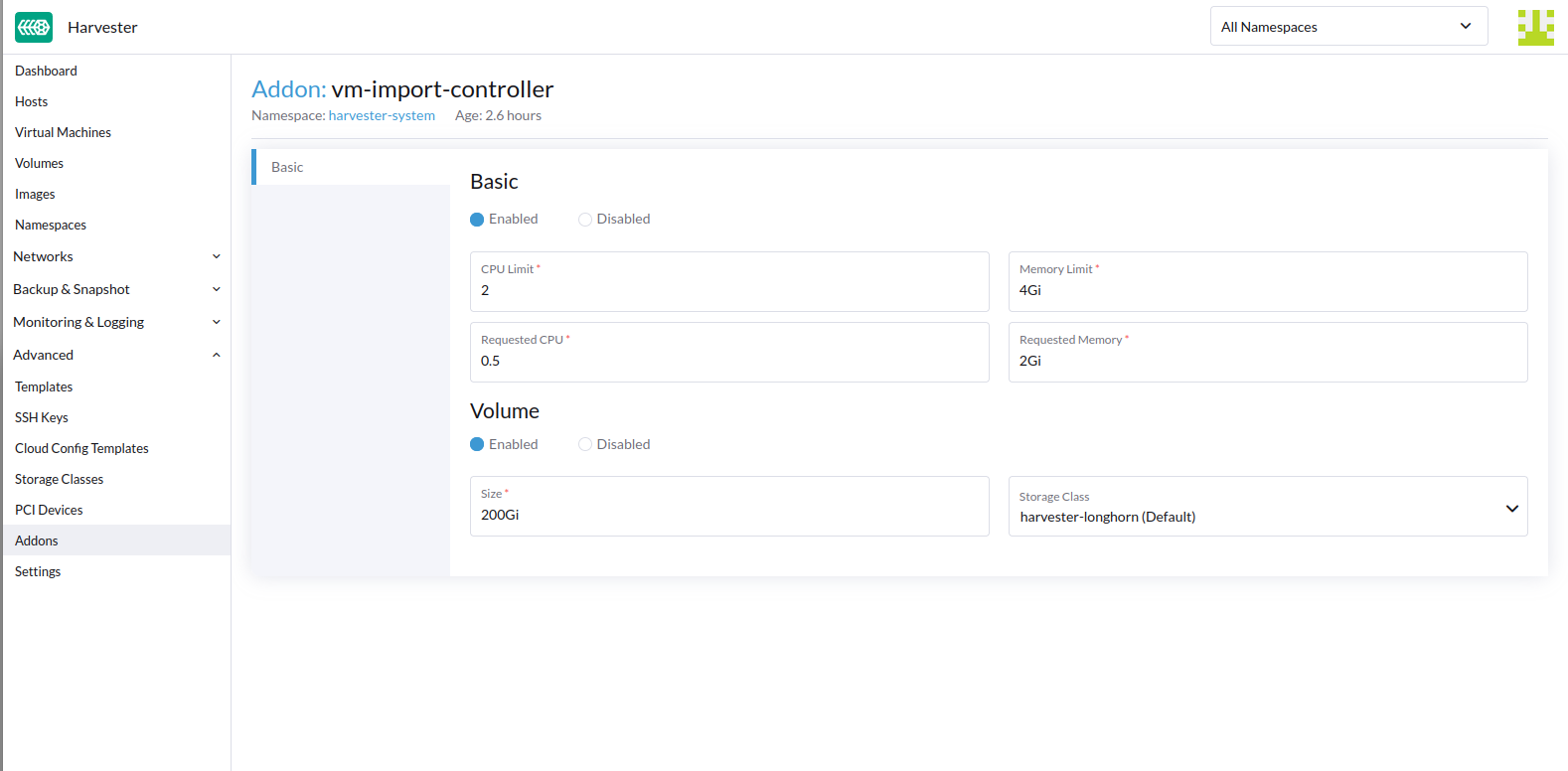
vm-import-controller
Currently, the following source providers are supported:
-
VMware
-
OpenStack
-
Open Virtual Appliance (OVA)
API
The vm-import-controller introduces two CRDs.
Sources
Sources allow users to define valid source clusters.
For example:
apiVersion: migration.harvesterhci.io/v1beta1
kind: VmwareSource
metadata:
name: vcsim
namespace: default
spec:
endpoint: "https://vscim/sdk"
dc: "DCO"
credentials:
name: vsphere-credentials
namespace: defaultThe secret contains the credentials for the vCenter endpoint:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: vsphere-credentials
namespace: default
stringData:
"username": "user"
"password": "password"As part of the reconciliation process, the controller will log into vCenter and verify whether the dc specified in the source spec is valid.
Once this check is passed, the source is marked as ready and can be used for VM migrations.
$ kubectl get vmwaresource.migration
NAME STATUS
vcsim clusterReadyFor OpenStack-based source clusters, an example definition is as follows:
apiVersion: migration.harvesterhci.io/v1beta1
kind: OpenstackSource
metadata:
name: devstack
namespace: default
spec:
endpoint: "https://devstack/identity"
region: "RegionOne"
credentials:
name: devstack-credentials
namespace: defaultThe secret contains the credentials for the OpenStack endpoint:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: devstack-credentials
namespace: default
stringData:
"username": "user"
"password": "password"
"project_name": "admin"
"domain_name": "default"
"ca_cert": "pem-encoded-ca-cert"As part of the reconciliation process, the controller attempts to list virtual machines in the project and marks the source as ready.
$ kubectl get openstacksource.migration
NAME STATUS
devstack clusterReadyFor OVA-based sources, an example definition is as follows:
apiVersion: migration.harvesterhci.io/v1beta1
kind: OvaSource
metadata:
name: example
namespace: default
spec:
url: "http://192.168.0.1:8080/example.ova"
httpTimeoutSeconds: 300
credentials:
name: example-ova-credentials
namespace: defaultThe optional httpTimeoutSeconds field allows you to specify the maximum time (in seconds) SUSE Virtualization waits for an HTTP request to be completed. This period covers the entire transaction, including establishing the connection, handling redirects, and reading the response body. When the value is 0, the timeout feature is disabled. The default value is 600 (10 minutes).
When configuring the secret, you can include basic authentication credentials for the URL and a CA certificate if the endpoint uses HTTPS.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example-ova-credentials
namespace: default
stringData:
"username": "user"
"password": "password"
"ca.crt": "pem-encoded-ca-cert"As part of the reconciliation process, the controller issues a HEAD request to the specified URL to confirm its validity before marking the source as ready.
$ kubectl get ovasource.migration
NAME STATUS
example clusterReadyVirtualMachineImport
The VirtualMachineImport CRD provides a way for users to define a source VM and map to the actual source cluster to perform VM export/import.
A sample VirtualMachineImport looks like this:
apiVersion: migration.harvesterhci.io/v1beta1
kind: VirtualMachineImport
metadata:
name: alpine-export-test
namespace: default
spec:
virtualMachineName: "alpine-export-test"
folder: "Discovered VM"
networkMapping:
- sourceNetwork: "dvSwitch 1"
destinationNetwork: "default/vlan1"
- sourceNetwork: "dvSwitch 2"
destinationNetwork: "default/vlan2"
networkInterfaceModel: "e1000"
defaultNetworkInterfaceModel: "virtio"
skipPreflightChecks: false
storageClass: "my-storage-class"
defaultDiskBusType: "scsi"
sourceCluster:
name: vcsim
namespace: default
kind: VmwareSource
apiVersion: migration.harvesterhci.io/v1beta1
forcePowerOff: false
gracefulShutdownTimeoutSeconds: 30This prompts the controller to export the virtual machine named alpine-export-test on the source VMware cluster to be exported, processed, and recreated in the SUSE Virtualization cluster.
The controller checks the configuration before starting the import process, and cancels the import when it detects errors such as unknown StorageClasses or networks. These checks are enabled by default, but can be disabled by setting skipPreflightChecks to true.
The duration of the import process depends on the size of the virtual machine. While the import process may take some time, you should see VirtualMachineImages created for each disk in the defined virtual machine.
If the source virtual machine is placed in a folder, you can specify the folder name in the optional folder field.
The list of items in networkMapping will define how the source network interfaces are mapped to the SUSE Virtualization Networks.
If necessary, you can specify the model of each source network interface individually using the networkInterfaceModel field. The valid values are e1000, e1000e, ne2k_pci, pcnet, rtl8139 and virtio.
Specifying the default interface model using the defaultNetworkInterfaceModel field is particularly useful in the following situations:
-
You want to override the default model used when the automatic detection does not work for VMware imports or the default model used for all network interfaces for OpenStack imports.
-
No network mapping is provided and the
pod-networknetwork interface is automatically created.
If you do not specify a value, virtio is used by default.
If a match is not found, each unmatched network interface is attached to the default managementNetwork.
The storageClass field specifies the StorageClass to be used for images and provisioning of persistent volumes during the import process. If no value is specified, SUSE Virtualization uses the default StorageClass.
The defaultDiskBusType field allows you to specify the bus type for imported disks. SUSE Virtualization uses this field in the following ways:
-
VMware sources: The value is used only if SUSE Virtualization is unable to automatically detect the bus type.
-
OpenStack sources: The value is used for all imported disks.
-
Open Virtual Appliance (OVA) sources: The value is used only if SUSE Virtualization is unable to automatically detect the bus type.
The valid values are sata, scsi, usb, and virtio. If you do not specify a value, virtio is used by default.
By default, the vm-import-controller attempts to gracefully shut down the guest operating system of the source virtual machine before starting the import process. If the virtual machine is not gracefully shut down within a specific period, a hard power off is forced. You can adjust this time period for the graceful shutdown by changing the value of the gracefulShutdownTimeoutSeconds field, which is set to 60 seconds by default. A hard power off without attempting a graceful shutdown can be forced by setting the forcePowerOff field to true.
If you are importing a VMware-based virtual machine, the vm-import-controller’s behavior depends on whether VMware Tools is installed on the virtual machine.
| VMware Tools Status | vm-import-controller Behavior |
|---|---|
Installed |
Attempts the described graceful shutdown before starting the import process. |
Not installed |
Displays logs similar to |
|
The vm-import-controller only supports the |
Once the virtual machine has been imported successfully, the object will reflect the status:
$ kubectl get virtualmachineimport.migration
NAME STATUS
alpine-export-test virtualMachineRunning
openstack-cirros-test virtualMachineRunningSimilarly, users can define a VirtualMachineImport for an OpenStack source as well:
apiVersion: migration.harvesterhci.io/v1beta1
kind: VirtualMachineImport
metadata:
name: openstack-demo
namespace: default
spec:
virtualMachineName: "openstack-demo" #Name or UUID for instance
networkMapping:
- sourceNetwork: "shared"
destinationNetwork: "default/vlan1"
- sourceNetwork: "public"
destinationNetwork: "default/vlan2"
sourceCluster:
name: devstack
namespace: default
kind: OpenstackSource
apiVersion: migration.harvesterhci.io/v1beta1|
OpenStack allows users to have multiple instances with the same name. In such a scenario, users are advised to use the Instance ID. The reconciliation logic tries to perform a name-to-ID lookup when a name is used. |
Known issues
Source virtual machine name is not RFC1123-compliant
When creating a virtual machine object, the vm-import-controller add-on uses the name of the source virtual machine, which may not meet the Kubernetes object naming criteria. You may need to rename the source virtual machine to allow successful completion of the import.
VMware-based virtual machine without VMware Tools is not migrated
When you attempt to import a VMware-based virtual machine in SUSE Virtualization v1.6.0, the following issues occur if VMware Tools is not installed on the virtual machine:
-
The vm-import-controller does not gracefully shut down the guest operating system.
-
When the graceful shutdown period (
gracefulShutdownTimeoutSeconds) lapses, the vm-import-controller does not force a hard poweroff. -
The virtual machine is not migrated from VMware.
To address the issue, perform one of the following workarounds:
-
Shut down the virtual machine before migrating it to SUSE Virtualization.
-
In the
VirtualMachineImportCRD spec, set theforcePowerOfffield totrue. -
Install VMware Tools or open-vm-tools.
Eviction strategy is not set
The evictionStrategy field is not configured automatically during the virtual machine import process. This prevents live migration of the virtual machine.
To address the issue, run the following command:
kubectl patch VirtualMachine <vm-name> -n <namespace> --type=merge -p '{
"spec": {
"template": {
"spec": {
"evictionStrategy": "LiveMigrateIfPossible"
}
}
}
}'To update all virtual machines with a missing evictionStrategy configuration, run the following command:
for vm in $(kubectl get VirtualMachine -A -o json | jq -r '.items[] | select(.spec.template.spec.evictionStrategy == null) | "\(.metadata.namespace):\(.metadata.name)"'); do \
kubectl patch VirtualMachine ${vm#*:} -n ${vm%:*} --type=merge -p '{"spec":{"template":{"spec":{"evictionStrategy":"LiveMigrateIfPossible"}}}}'; \
doneYou must reboot the virtual machine to apply the changes.