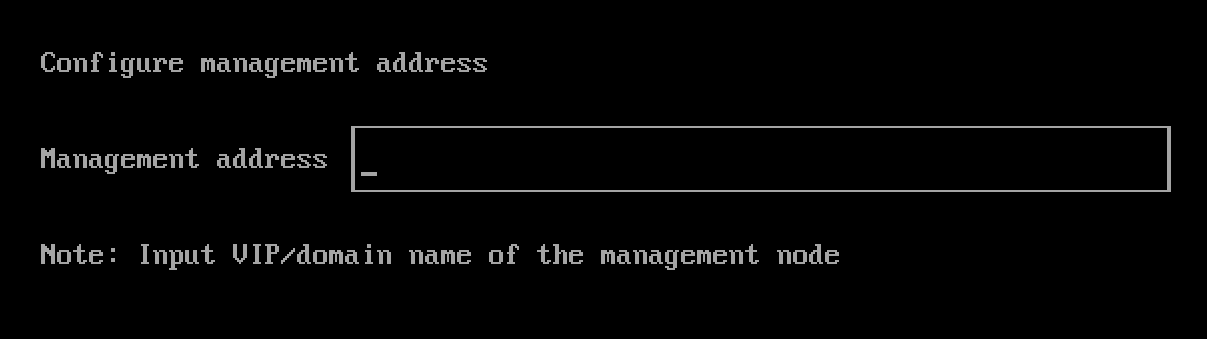
Management Address
SUSE Virtualization provides a fixed virtual IP (VIP) as the management address, VIP must be different from any Node IP. You can find the management address on the console dashboard after the installation.
|
If you selected the IP address to be configured via DHCP, you will need to configure static MAC-to-IP address mapping on your DHCP server in order to have a persistent Virtual IP |
Requirements
-
The VIP and the node management interfaces must belong to the same subnet.
-
All SUSE Virtualization node management interfaces must be on the same layer-2 network segment.
Both are required because the VIP relies on the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which is a layer-2 protocol.
The VIP can be assigned to any SUSE Virtualization node management interface and can change at any time (not only when node failure occurs). When the VIP changes hosts, gratuitous ARPs are sent so that other hosts on the network know where to direct traffic intended for the SUSE Virtualization cluster’s management IP address (the VIP).
|
If you plan to host a SUSE Virtualization cluster in a bare metal data center, the service provider will likely designate a "floating" or "reserved" IP address as the VIP that you can assign to one of your servers. Updating this assignment causes traffic to instantly start flowing to the new node it is assigned to. In these situations, SUSE Virtualization is unable to update the floating/reserved IP assignment in your provider’s systems when the VIP changes hosts. Furthermore, the VIP’s "gratuitous ARPs" may also be ineffective depending on your provider’s networking setup between your SUSE Virtualization nodes (for example, if your SUSE Virtualization hosts are not on the same layer-2 network). You must update the floating/reserved IP assignment manually when the VIP changes hosts to ensure that the cluster functions properly. For more information, see Finding which node the VIP is on. |
How to get the VIP MAC address
To get the VIP MAC address, you can run the following command on the management node:
$ kubectl get svc -n kube-system ingress-expose -ojsonpath='{.metadata.annotations}'Example of output:
{"kube-vip.io/hwaddr":"02:00:00:09:7f:3f","kube-vip.io/requestedIP":"10.84.102.31"}Identifying the Node the VIP Is Assigned To
You can use kubectl (either on your local machine with the SUSE Virtualization kubeconfig file, or when using SSH to connect to any SUSE Virtualization management node as a root user).
kubectl -n kube-system get svc ingress-expose -o jsonpath='{.metadata.annotations.kube-vip\.io/vipHost}'Example output:
harvester-xzj76Alternatively, you can use SSH to connect to each SUSE Virtualization management node and then run the command ip address show mgmt-br.
Example:
harvester-xzj76:~ # ip address show mgmt-br
4: mgmt-br: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 8c:dc:d4:b5:f0:fd brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.19.108.45/21 brd 172.19.111.255 scope global mgmt-br
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 172.19.108.34/32 scope global mgmt-br
valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverWhen the output includes both the VIP and the node address, the VIP is assigned to the node that you are connected to.