Access to the Virtual Machine
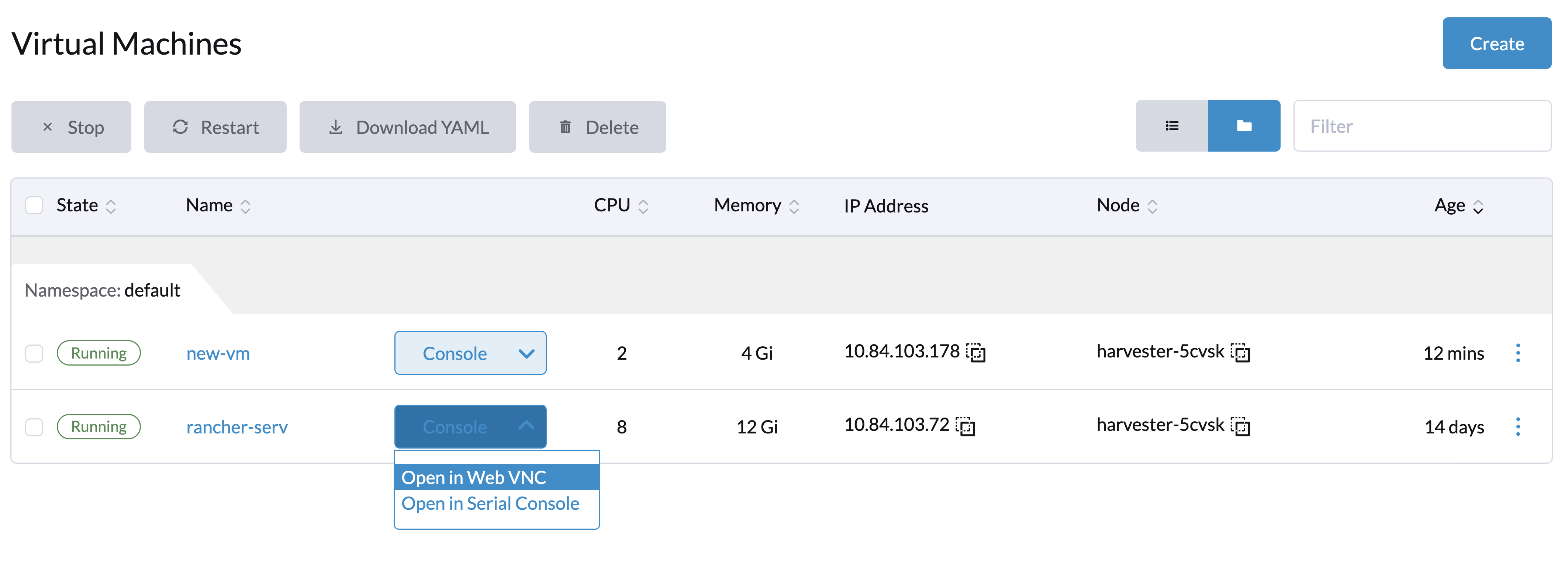
Once the VM is up and running, you can access it using either the Virtual Network Computing (VNC) client or the serial console from the Harvester UI.
Additionally, you can connect directly from your computer’s SSH client.
Access with the Harvester UI
VMs can be accessed from the UI directly using either VNC or the serial console.
If the VGA display is not enabled on the VM, e.g., the Ubuntu-Minimal-Cloud image, the VM can only be accessed with the serial console.
SSH Access
Harvester provides two ways to inject SSH public keys into virtual machines. Generally, these methods fall into two categories. Static key injection, which places keys in the cloud-init script when the virtual machine is first powered on; dynamic injection, which allows keys or basic auth to be updated dynamically at runtime.
Static SSH Key Injection via cloud-init
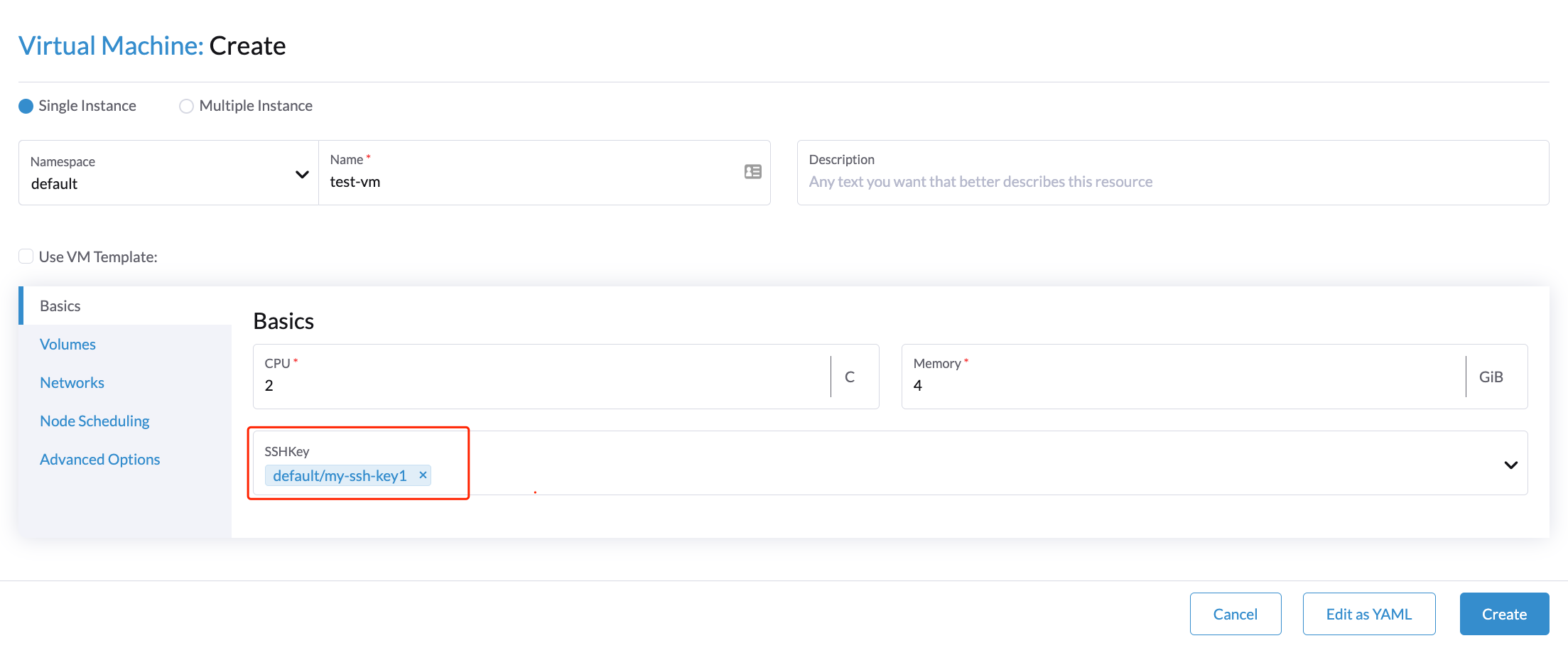
You can provide ssh keys to your virtual machines during the creation time on the Basics tab. Additionally, you can place the public ssh keys into your cloud-init script to allow it to take place.
Dynamic SSH Key Injection via Qemu guest agent
Harvester supports dynamically injecting public ssh keys at run time through the use of the qemu guest agent. This is achieved through the qemuGuestAgent propagation method.
|
This method requires the qemu guest agent to be installed within the guest VM. When using |
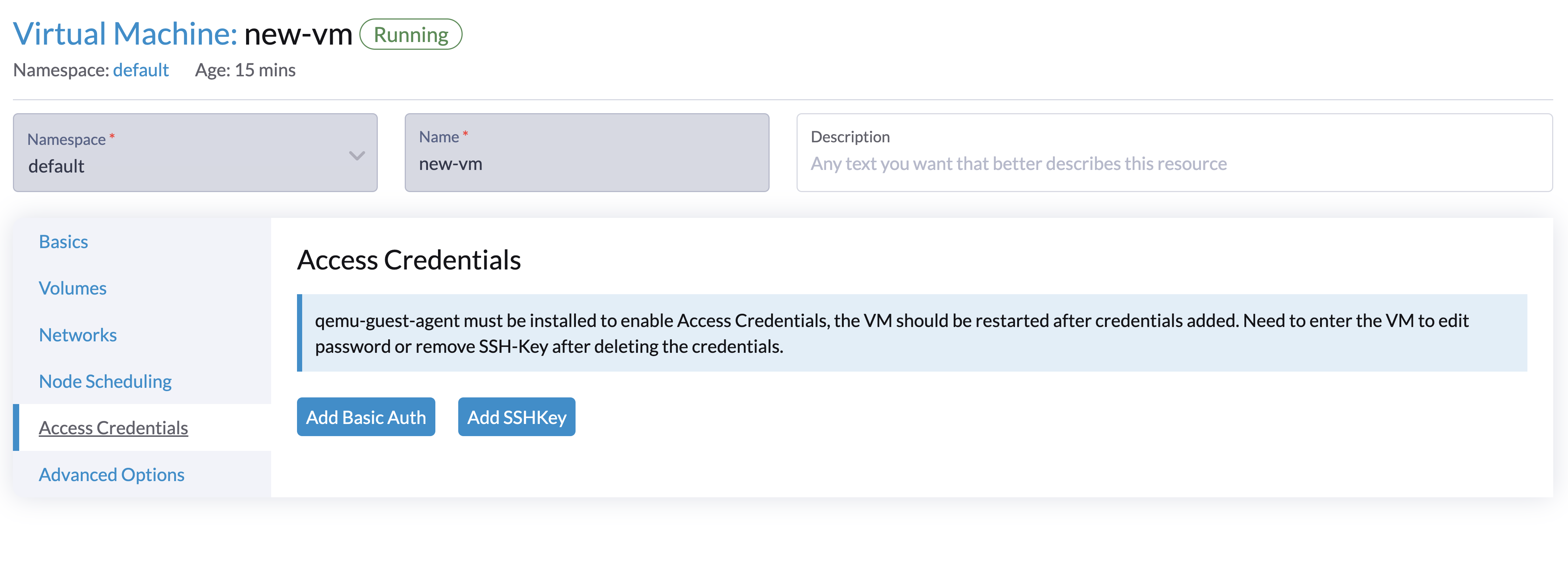
You can inject your access credentials via the Harvester dashboard as below:
-
Select the VM and click
⋮button. -
Click the
Edit Configbutton and go to theAccess Credentialstab. -
Click to add either basic auth credentials or ssh keys, (e.g., add
opensuseas the user and select your ssh keys if your guest OS is OpenSUSE). -
Make sure your qemu guest agent is already installed and the VM should be restarted after the credentials are added.
|
You need to enter the VM to edit password or remove SSH-Key after deleting the credentials from the UI. |