17 Deploying the Non-OpenStack Components #
In addition to OpenStack barclamps, SUSE OpenStack Cloud includes several components that can be configured using the appropriate Crowbar barclamps.
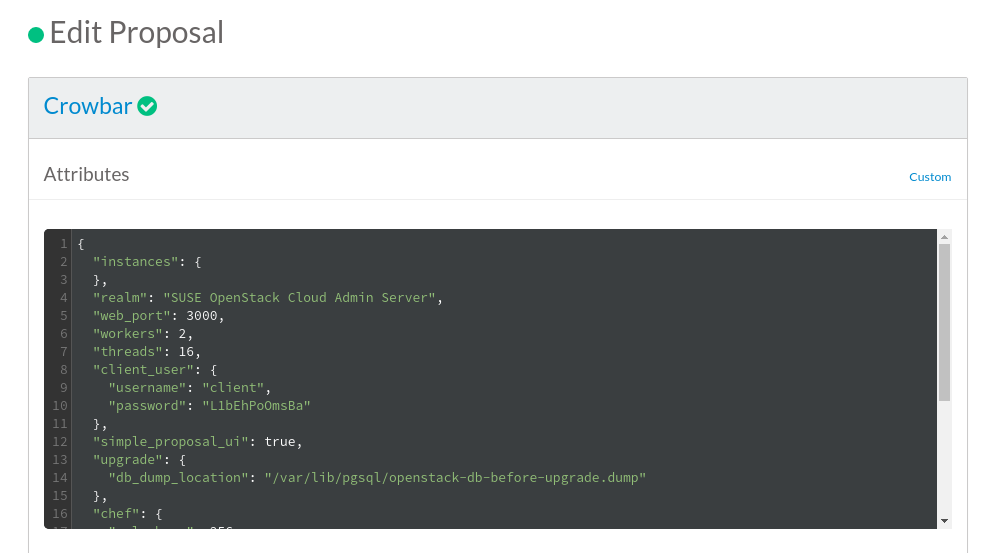
17.1 Tuning the Crowbar Service #
Crowbar is a self-referential barclamp used for enabling other barclamps. By creating a Crowbar proposal, you can modify the default number of threads and workers. This way, you can scale the admin server according to the actual usage or the number of available cores of the admin node.
To change the default settings, create a Crowbar proposal and switch to the
view. Adjust then the
workers and threads
values. The number of threads should be set to the number of available
cores. The default number of workers should be increased to 3 if the
graphical interface becomes slow. Save and apply the changes using the
appropriate buttons.
17.2 Configuring the NTP Service #
The NTP service is responsible for keeping the clocks in your cloud servers in sync. Among other things, synchronized clocks ensure that the chef-client works properly. It also makes it easier to read logs from different nodes by correlating timestamps in them. The NTP component is deployed on the Administration Server automatically using the default settings. The NTP barclamp can be used to specify IP addresses of the external NTP servers and assign specific roles to the desired nodes. The following parameter can be configured using the NTP barclamp:
- External servers
A comma-separated list of IP addresses of external NTP servers.
The NTP service consists of two different roles:
A node that acts as an NTP server for NTP clients in your cloud. There can be more than one node with the ntp-server role in your cloud. In this scenario, the NTP server nodes can communicate with each other and the specified external servers to keep their time in sync.
The
ntp-clientrole can be assigned to any node. Nodes with the ntp-client role assigned to them keep their time in sync using NTP servers in your cloud.
17.3 Installing and using Salt #
Crowbar can setup Salt on the admin node to be able to use
salt-ssh from the admin node.
Salt is not replacing Chef. It can be used in parallel to Chef to automate tasks on the nodes.
Only salt-ssh can currently be used. Installing the
Salt barclamp does not setup a full Salt stack with Salt Master and
Salt Minions.
To be able to apply the Salt proposal, the
https://documentation.suse.com/sles/15-SP1/single-html/SLES-deployment/#sec-yast-install-addons
must be available on the node where the salt-ssh role will be applied
(usually the admin node).
After the Module is available, the barclamp can be applied.
From the node where the salt-ssh role is applied,
Salt can be tested with:
# salt-ssh '*' test.ping
crowbar:
True
storage1:
True
controller:
True
To list the available nodes visible to salt-ssh, do:
# salt-ssh -H
/etc/salt/roster:
----------
controller:
192.168.192.81
crowbar:
192.168.192.10
storage1:
192.168.192.82